| St. Marys Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Neogene | |
| Type | Formation |
| Unit of | Chesapeake Group |
| Underlies | Eastover Formation |
| Overlies | Choptank Formation |
| Location | |
| Region | |
| Country | |
The St. Marys Formation is a geologic formation in Maryland and Virginia, United States. It preserves fossils dating back to the Miocene Epoch of the Neogene period. It is the youngest Miocene formation present in the Calvert Cliffs and is part of the Chesapeake Group.
Vertebrate paleofauna
A diverse vertebrate paleofauna is known from the St. Marys Formation:
| Genus | Species | Notes | Tooth example | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Notorynchus | N. primigenius | This species is possibly synonymous with the broadnose sevengill shark. |  Notorhynchus primigenius from the Calvert Formation |
[1] |
| Hexanchus | H. gigas | A species of cow shark. This species is extremely rare in this formation. |  Hexanchus gigas teeth (not from St. Marys Formation) |
[1] |
| Squalus | Commonly known as the spurdog. | [1] | ||
| Squatina | Commonly known as the angel shark. | [1] | ||
| Rhincodon | R. typus | Commonly known as the whale shark. This species is extremely rare in this formation. |  Modern Rhincodon typus teeth |
[1] |
| Carcharodon | C. hastalis | Putative ancestor to the extant great white shark |  Carcharodon hastalis from the Calvert Formation |
[1] |
| Carcharomodus | C. escheri | Commonly known as Escher's mako. It is also known as Carcharodon subserratus and is sometimes placed in Isurus. It is extremely rare in this formation. |  Carcharomodus escheri teeth from Germany |
[1] |
| Otodus | O. megalodon | This is the largest shark known to have existed. |  C. megalodon from Chile |
[1] |
| Alopias | A. latidens | This species may be synonymous with the extant common thresher shark. |  Alopias latidens from the Old Church Formation |
[1] |
| Mustelus | Commonly known as smooth-hounds | [1] | ||
| Hemipristis | H. serra | Commonly known as the snaggletooth shark. It is related to the extant snaggletooth shark. |  Hemipristis serra teeth (Bone Valley) |
[1] |
| Carcharhinus | C. falciformus | Commonly known as the silky shark. |  Carcharhinus falciformis upper teeth (modern) |
[1] |
| C. leucas | Commonly known as the bull shark |  Carcharhinus leucas teeth (modern) |
[1] | |
| C. perezii | Commonly known as the Caribbean reef shark |  Carcharhinus perezii upper teeth (modern) |
[1] | |
| C. priscus | An extinct requiem shark | [1] | ||
| C. plumbeus | Commonly known as the sandbar shark |  Carcharhinus plumbeus upper teeth (modern) |
[1] | |
| Negaprion | N. brevrostris | Commonly known as the lemon shark |  Negaprion brevirostris upper teeth |
[1] |
| Rhizoprionodon | Commonly known as the sharpnose shark | [1] | ||
| Pteromylaeus | Commonly known as the bull ray | [1] | ||
| Aetobatus | Commonly known as the eagle ray | [1] |
| Genus | Notes | Image | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acipenseridae gen. indet. | .jpg.webp) Extant Japanese sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) |
[1] | |
| Lepisosteus |  Extant spotted gar (Lepisosteus oculatus) |
[1] | |
| Amia | cf. A. calva | .jpg.webp) Extant Amia calva |
[1] |
| Alosa |  Extant Alosa maeotica |
[1] | |
| Ictalurus |  Drawing of extant Ictalurus punctatus |
[1] | |
| Merluccius |  Drawing of extant Merluccius merluccius |
[1] | |
| Belone | B. countermani |  Extant Belona belona |
[1][2] |
| Prionotus | .jpg.webp) Extant bandtail searobin (Prionotus ophryas) |
[1] | |
| Agonidae gen. indet. |  Extant Agonus cataphractus |
[1] | |
| "Paralbula" | "P." dorisiae | [1] | |
| Lagodon | _(12598284094).jpg.webp) Extant Lagodon rhomboides |
[1] | |
| Stenotomus | _(12592129064).jpg.webp) Extant Stenotomus chrysops |
[1] | |
| Pogonias |  Extant black drum |
[1] | |
| Sciaenops | _(12527956414).jpg.webp) Extant Sciaenops ocellatus |
[1] | |
| Tautoga | _(15611353592).jpg.webp) Extant Tautoga onitis |
[1] | |
| Astroscopus | A. countermani |  Artists rendition of Astroscopus countermani |
[3][1] |
| Sphyraena |  Extant school of Sphyraena barracuda |
[1] | |
| Istiophoridae gen. indet. |  Extant Atlantic blue marlin |
[1] |
| Genus | Species | Notes | Image | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thecachampsa | T. antiquus | A Tomistominae |  Thecachampsa sp. Vertebra possibly derived from this formation |
[1] |
| Type | Genus | Species | Notes | Image | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sirenians (sea cows) | Metaxytherium | M. floridanum |  Metaxytherium floridanum skeleton |
[1] | |
| Cetaceans (whales, dolphins and porpoises) | Aulophyseter | A. mediatlanticus | A sperm whale |  Artists depiction of Aulophyseter |
[4] |
| Lophocetus | L. calvertensis | [5] | |||
| Messapicetus | 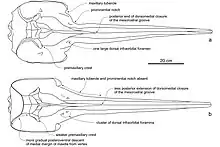 Messapicetus gregarius and M. longirostris skull diagrams |
[6] | |||
| Stenasodelphis | S. russellae | [7] |
| Name | Notes | Images | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procamelus | cf. P. minor |  Fossilized Procamelus mummy from Oklahoma |
[8] |
| Desmathyus | [8] | ||
| Tapirus | .JPG.webp) Extant South American tapir (Tapirus terrestris) |
[8] | |
| Neohipparion lenticulare | _(17322549474).jpg.webp) Skeleton and artists rendition of Neohipparion |
[8] | |
| Equidae indet. | Larger than Parahippus | [8] | |
| Rhinoceratidae | [8] | ||
| Cormohipparion |  Cranium of Cormohipparion occidentale |
[8] |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Godfrey, Stephen J., ed. (2018-09-25). "The Geology and Vertebrate Paleontology of Calvert Cliffs, Maryland, USA". Smithsonian Contributions to Paleobiology (100): 2–274. doi:10.5479/si.1943-6688.100. ISSN 1943-6688.
- ↑ de Sant'Anna, V. B., Collette, B. B., & Godfrey, S. J. (2013). † Belone countermani, a new Miocene needlefish (Belonidae) from the St. Marys Formation of Calvert Cliffs, Maryland. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 126 (2), 137-150.
- ↑ Carnevale, Giorgio; Godfrey, Stephen J.; Pietsch, Theodore W. (2011-11-01). "Stargazer (Teleostei, Uranoscopidae) cranial remains from the Miocene Calvert Cliffs, Maryland, U.S.A. (St. Marys Formation, Chesapeake Group)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 31 (6): 1200–1209. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.606856. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 196608143.
- ↑ Aulophyseter at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ Fuller, Anna J.; Godfrey, Stephen J. (2007-06-12). "A late Miocene ziphiid (Messapicetus sp.: Odontoceti: Cetacea) from the St. Marys Formation of Calvert Cliffs, Maryland". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (2): 535–540. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[535:ALMZMS]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 85606021.
- ↑ Fuller, Anna J.; Godfrey, Stephen J. (2007-06-12). "A late Miocene ziphiid (Messapicetus sp.: Odontoceti: Cetacea) from the St. Marys Formation of Calvert cliffs, Maryland". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (2): 535–540. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[535:almzms]2.0.co;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 85606021.
- ↑ Godfrey, Stephen J.; Barnes, Lawrence G. (2008-06-12). "A new genus and species of late Miocene pontoporiid dolphin (Cetacea: Odontoceti) from the St. Marys Formation in Maryland". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 28 (2): 520–528. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2008)28[520:ANGASO]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 86216551.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Eshelman, R. Terrestrial Mammal Remains from the Miocene Chesapeake Group of Calvert Cliffs, Maryland, and Comparisons With Miocene.
External links
- Various Contributors to the Paleobiology Database. "Fossilworks: Gateway to the Paleobiology Database". Retrieved 17 December 2021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.