| Solar eclipse of January 3, 1908 | |
|---|---|
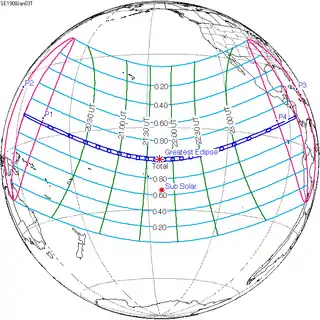 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.1934 |
| Magnitude | 1.0437 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 254 sec (4 m 14 s) |
| Coordinates | 11°48′S 145°06′W / 11.8°S 145.1°W |
| Max. width of band | 149 km (93 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 21:45:22 |
| References | |
| Saros | 130 (46 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9299 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on January 3, 1908.[1][2][3][4] A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Ebon Atoll in German New Guinea (now in Marshall Islands), British Western Pacific Territories (the part now belonging to Kiribati), Line Islands (now in Kiribati), Phoenix Islands (now in Kiribati) on January 4 (Saturday), and Costa Rica on January 3 (Friday). The green line means eclipse begins or ends at sunrise or sunset. The magenta line means mid eclipse at sunrise or sunset, or northern or southern penumbra limits. The green point means eclipse obscuration of 50%. The blue line means umbral northern and southern limits.
Observations
The eclipse was observed by astronomer William Wallace Campbell of Lick Observatory, viewed from Flint Island, Kiribati:[5]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1906–1909
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[6]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1906–1909 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| 115 | July 21, 1906 Partial |
120 | January 14, 1907 Total | |
| 125 | July 10, 1907 Annular |
130 | January 3, 1908 Total | |
| 135 | June 28, 1908 Annular |
140 | December 23, 1908 Hybrid | |
| 145 | June 17, 1909 Hybrid |
150 | December 12, 1909 Partial | |
Saros 130
This eclipse is a part of Saros cycle 130, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 73 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on August 20, 1096. It contains total eclipses from April 5, 1475 through July 18, 2232. There are no annular eclipses in the series. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on October 25, 2394. The longest duration of totality was 6 minutes, 41 seconds on July 11, 1619. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s descending node.[7]
| Series members 43–56 between 1853 and 2300 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 43 | 44 | 45 |
 November 30, 1853 |
 December 12, 1871 |
 December 22, 1889 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
 January 3, 1908 |
 January 14, 1926 |
 January 25, 1944 |
| 49 | 50 | 51 |
 February 5, 1962 |
 February 16, 1980 |
 February 26, 1998 |
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
 March 9, 2016 |
 March 20, 2034 |
 March 30, 2052 |
| 55 | 56 | 57 |
 April 11, 2070 |
 April 21, 2088 |
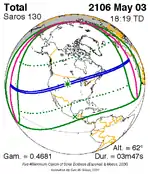 May 3, 2106 |
| 58 | 59 | 60 |
 May 14, 2124 |
 May 25, 2142 |
 June 4, 2160 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 |
 June 16, 2178 |
 June 26, 2196 |
 July 8, 2214 |
| 64 | 65 | 66 |
 July 18, 2232 |
 July 30, 2250 |
 August 9, 2268 |
| 67 | ||
 August 20, 2286 | ||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 January 3, 1908 (Saros 130) |
 December 13, 1936 (Saros 131) |
 November 23, 1965 (Saros 132) |
 November 3, 1994 (Saros 133) |
 October 14, 2023 (Saros 134) |
 September 22, 2052 (Saros 135) |
 September 3, 2081 (Saros 136) |
||
Notes
- ↑ "Obscured by the clouds". The Journal and Tribune. Knoxville, Tennessee. 1908-01-04. p. 8. Retrieved 2023-11-01 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ "Clouds hide eclipse; many are disappointmented". St. Louis Globe-Democrat. St. Louis, Missouri. 1908-01-04. p. 1. Retrieved 2023-11-01 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ "FLINT ISLAND PARTY VIEWS SUN ECLIPSE". The San Francisco Examiner. San Francisco, California. 1908-01-04. p. 6. Retrieved 2023-11-01 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ "The sun's obscuration". The Daily Telegraph. Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. 1908-01-04. p. 10. Retrieved 2023-11-01 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ Powerhouse Museum. "Solar Eclipse, Flint Island, Kiribati, 1908". Powerhouse Museum, Australia. Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ "Saros Series catalog of solar eclipses". NASA.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Photo of Solar Corona January 3, 1908

.jpg.webp)

