Raversbeuren | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Raversbeuren within Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis district 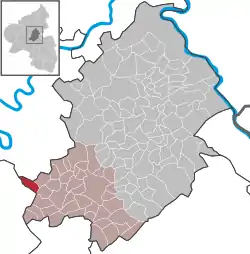 | |
 Raversbeuren 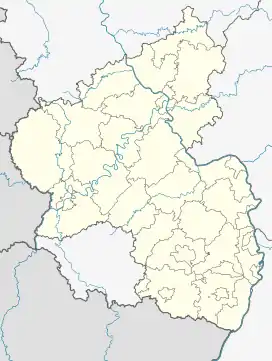 Raversbeuren | |
| Coordinates: 49°57′31″N 7°13′40″E / 49.95861°N 7.22778°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis |
| Municipal assoc. | Kirchberg |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–24) | Horst Möhringer[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5.14 km2 (1.98 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 420 m (1,380 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 130 |
| • Density | 25/km2 (66/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 56850 |
| Dialling codes | 06543 |
| Vehicle registration | SIM |
| Website | www.kirchberg-hunsrueck.de |
Raversbeuren is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Kirchberg, whose seat is in the like-named town.
Geography
Location
The municipality lies on a high plateau in the northern Hunsrück between the Hunsrückhöhenstraße (“Hunsrück Heights Road”, a scenic road across the Hunsrück built originally as a military road on Hermann Göring’s orders) and the Moselle. Raversbeuren borders directly on Frankfurt-Hahn Airport, and is a residential community with an agricultural character. The municipal area measures 5.14 km², of which 1.93 km² is wooded.
History
The oldest evidence of human presence is a stone axe that was found within Raversbeuren’s municipal limits. Near the village, not far from the “Briedeler Heck” estate buildings, two further such axes were unearthed. A few hundred metres from that find, a great many flint chips were also found.
Notable are the great many graves from late Hallstatt times (roughly 600 to 500 BC). Almost every hilltop harbours such graves. It has been established that some burial grounds were used over a number of centuries. Tribes and customs changed over time.
It is quite clear that there was a building from Roman times within municipal limits. Coins from Maximian’s time, just after Diocletian’s time in power (AD 204 to 305), have been found. Three further settlements existed not far from the municipal limit, among which was the great manor on what is now the estate lands. Smaller finds come to light almost every time that a major excavation is undertaken.
In 908, Raversbeuren had its first documentary mention when Carolingian King Louis the Child donated the royal estate that he held at Raversbeuren to the Archbishopric of Trier, then headed by Archbishop Ratbod.
In the Frankish Empire’s early days, Raversbeuren belonged to the Nahegau. The Gau counts were the Emichones. Later, sometime before 1125, it passed, likely with Enkirch, as it was a branch of that parish, into the hereditary ownership of the Count of Sponheim. Administration of the royal estate was transferred to the Ravengiersburg Monastery.
It was in the 13th century that the Raversbeuren churchtower was built for what was then only a chapel. From about the same time comes the “small” bell bearing the Latin inscription in uppercase Gothic letters: MAGISTER CONRADUS DE WORMATIA FECIT * MARIA VOCOR* (“Master Conrad from Worms made me; I am called Maria”). According to the Glockenatlas (“Bell Atlas”), “Maria” is said to be Germany's oldest bell that actually bears the bellfounder's name.
In 1374, reports of Flagellants in Raversbeuren crop up. in 1422, the local lordships furnished horsemen for the struggle against the Hussites.
In 1511, the Ravengiersburg Monastery, whose prior at this time was Kaspar von Grünberg, had its considerable monastic holding at Raversbeuren, measuring 120 Morgen, leased. The hereditary leaseholder exercised lower jurisdiction (that is, not blood court) in the village. The leaseholder's house was thus known as Anwalt’s (Anwalt being German for “lawyer”); even today, a local rural cadastral area still bears the name “Anwaltsland”. The later hereditary leaseholding family remained the only Catholics in Raversbeuren through the introduction of the Reformation in 1545 and 1557, even centuries later.
In 1515, the village counted nine dwellers with townsman's rights. Any feudal underlings that they may have had are not mentioned.
For a few decades there were boundary disputes and protracted court proceedings (1549 to 1553) with the municipality of Briedel, which apparently went all the way to the Reichskammergericht before being resolved. There also followed differences in opinion as to the alignment of boundaries with other neighbouring municipalities.
The Plague beset Raversbeuren more than once. It came to the area in 1567, and again in 1621. This second outbreak came during the Thirty Years' War, which brought its own hardship and misery. Early in the war, in 1619, the Spaniards plundered Raversbeuren. On 6 November 1620, they came ransacking once more. They molested the village a third time, on 16 June 1622. On 17 December 1631, three companies of Swedish troops defeated ten companies of Spaniards in battle, but the Swedes treated Raversbeuren no better, and indeed so badly “that not one head of livestock was left”. Even Croats were mentioned along with the Swedes. On 21 June 1633, the Swedes showed up in the village once again, robbing it of, among other things, eight horses. In September 1634, the French sacked Raversbeuren. Two months later, the Swedes came yet again.
A record from 14 January 1630 shows that Abbot Mathias of Himmerod Abbey in the Eifel had meadows in Rabersbeuren leased for a term of 24 years for 6 Moselgulden a year. According to old taxation registers, the Counts Kratz of Scharffenstein also had minor holdings – meadows – in Raversbeuren.
In a later document, the village is named as Ravenssteyer; it was then in the Schultheißerei of Unzenberg. After the Counts of Sponheim had died out in 1437, and after their heritable holdings had been shared out, the eastern stretch of Raversbeuren's municipal area became a three-state common point, shared by Baden, the Electorate of Trier and the Electorate of the Palatinate.
A village record from 11 July 1727 gives a thorough report about how the Rhinegraves’ and Waldgraves’ subjects were transferred to the Elector Palatine (Heidelberg). Of 29 townsmen, 26 were named all together, 9 of them Palatine subjects, 13 of them Obersteinisch (that is, belonging to the Rhinegraves and Waldgraves at Castle Dhaun) and 6 Sponheimisch (likely the Veldenz-Zweibrücken line). In 1767, there were 24 townsmen.
As to what year Raversbeuren's church was built, nothing is known. In 1707, the whole church but for the tower was torn down, and a new building arose. It contains a gallery with balustrade-field paintings from the 18th century and a Stumm organ.
The first clergyman in Raversbeuren mentioned after the Reformation was Johann Rühling. He worked as a minister in both Raversbeuren and Lötzbeuren. From 1664 to 1715, this office was held by Barthel Wagner. The local minister was put in charge of all Lutheran communities within the Oberamt of Simmern. Mentioned in 1723 as the local teacher was Johann Heinrich Barthelmes.
Under Napoleon, after an end had been put to the tangle of small lordships in the wake of the French Revolution, all monastic lands were auctioned off and became farmland. Under the French flag, quite a few men from Raversbeuren took part in Napoleon's campaign against Russia, while on the way back, many also fought under the Prussian flag against the French in the War of the Sixth Coalition.
During the war years from 1806 to 1815, there was great hardship. Municipalities found themselves burdened with war debts. Charcoal from felled forests brought very little money in. The municipality auctioned off great swathes of land. The main burden was borne, as it so often is, by individual citizens. As was so everywhere in Germany, many people from Raversbeuren emigrated to the New World. The main destination was Brazil, and more particularly Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Sul and Porto Alegre. Despite the general state of neediness, it was in this time that the old watermain, a channel first mentioned about 1670, was renovated with masonry pipes. In 1895, the watermain was renovated yet again, this time with cast-iron pipes; these are still in use today.
Beginning in 1794, Raversbeuren lay under French rule. In 1815 it was assigned to the Kingdom of Prussia at the Congress of Vienna.
In 1857 and 1858, a new municipal bakehouse was built with a hall upstairs. The next year a great fire burnt many barns and houses to ashes. A later fire in 1893 was confined to two barns, although one of these housed the big threshing machine, which was also destroyed. It had been bought in 1871, after the formation of a village corporation, along with a traction engine from Heinrich Lanz AG of Mannheim. It was the third machine delivered by this well-known company. Even today, there is still a communally run threshing set in Raversbeuren. Also about 1871, a village livestock insurance plan was established.
In the 1880s, Flurbereinigung was already being discussed in Raversbeuren, sometimes heatedly. Nevertheless, actual preparations for rationalizing the confusion of property lines in the municipality did not begin until 1912. Work carried on through the First World War, ending only in 1924.
Seven men from Raversbeuren fell in the First World War. Eighteen made the ultimate sacrifice in the Second World War. Before the Americans marched in on 17 March 1945, the village had suffered considerable damage in a three-day (14–16 March 1945) artillery barrage. One barn had burnt right down. Worse yet, 16 people – both military and civilian – had been killed; there were also quite a few wounded.
In 1937 a new shed was built for the communal threshing machine. Even during the war, infrastructure improvements continued: the waterworks were expanded by a newly bored spring. In 1947 and 1948, a new communal barn with livestock stable was built, and the following year, and electrically driven communal mill at the upper entrance to Raversbeuren replaced the four watermills.
Although the municipality's economic circumstances were rather circumscribed by the French occupation's seizure of almost all the spruce trees that were fit for felling, enough trees could be obtained from the last few suitable ones that the French had left, and through the purchase from the French of more from the stock that they had harvested to build a new schoolhouse in 1951. Promised assistance from the then newly founded state of Rhineland-Palatinate, to which Raversbeuren had belonged since 1946, never materialized.
The community centre was expanded and rebuilt in 1956 to accommodate the village's growing needs.[3]
Politics
Municipal council
The council is made up of 6 council members, who were elected by majority vote at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.[4]
Mayor
Raversbeuren's mayor is Horst Möhringer, and his deputy is Frank Spier.[5]
Coat of arms
The German blazon reads: In Blau, 2:1 gestellt, eine goldene Glocke, zwei goldene Ähren, ein silbernes Brunnenhaus mit Schwengelbrunnen.
The municipality's arms might in English heraldic language be described thus: Azure in chief a bell on a yoke and two ears of rye conjoined on a stem leafed of two Or, and in base a wellhouse with a well boom with pail argent.
The bell is Maria, mentioned above, held to be Germany's oldest bell that has its maker's name on it. The ears of rye symbolize the municipality's former agricultural character. The well, believed to have come into being in the late 18th century and still preserved now, was once an important source of water for the villagers.[6]
Culture and sightseeing


Buildings
The following are listed buildings or sites in Rhineland-Palatinate’s Directory of Cultural Monuments:[7]
- Backesweg 5 – Evangelical church; Baroque aisleless church, 1707, Late Gothic portal, west tower, late 13th century
- Dorfstraße – well; wellhouse, slate quarrystone
- Dorfstraße 37 – L-shaped estate; timber-frame house, partly solid, earlier half of the 19th century, barn
Roman villa
Northwest of Raversbeuren, within Briedel’s municipal limits, near Margaretenhof, a Roman villa rustica was discovered and in 1875 investigated and partly unearthed by the Rheinisches Landesmuseum Bonn. The estate complex, not counting outlying buildings, covered an area of 41 × 26 m. More than 30 rooms were laid bare. The occupants had running water, brought in through leaden pipes. The estate existed into late Roman times.
Natural monuments
- Wackensteine (quartz canals) on the road to Briedeler Heck
Regular events
The Lott-Festival is held in Raversbeuren’s municipal area. It has existed since 1977 and, given its broad range of musical genres, has been called the “Woodstock on the Hunsrück”. The name “Lott” comes from the name of the rural cadastral area in Enkirch, a municipality on the Moselle, where the festival was held until 1985. It moved to its current location after complaints from tenant hunters (Jagdpächter).
Famous people
The Hunsrück writer Albert Bauer lived in Raversbeuren. The writer Elly Kramb is buried here.
References
- ↑ Direktwahlen 2019, Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 4 August 2021.
- ↑ "Bevölkerungsstand 2021, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden" (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz. 2022.
- ↑ Hammen, Dirk. "Geschichte". Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ↑ Rheinland-Pfalz, Statistisches Landesamt. "LWL RLP - Kommunalwahlen: Ergebnisse der Ratswahlen: Wahlergebnisse 2009: Stadt- und Gemeinderatswahlen:". Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ↑ Hammen, Dirk. "Gemeinderat". Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ↑ Description and explanation of Raversbeuren’s arms
- ↑ Directory of Cultural Monuments in Rhein-Hunsrück district
External links
- Raversbeuren in the collective municipality's webpages (in German)
- Municipality’s official webpage (in German)