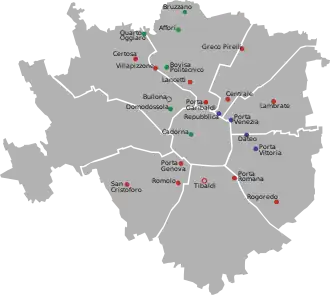
Milan has 23 railway stations in use today. Of these, 18 are managed by RFI, while the remaining 6 are operated by Ferrovienord. Three more stations are currently under construction or in the planning stage for the city area: Canottieri, Dergano and Zama.
History of rail transport in Milan
In the huge explosion of rail transport in the 19th century, Milan was one of the places that invested in the development of this type of transport.
In the late 1830s, Emperor Ferdinand I of Austria granted "the privilege to build a road on iron rails from Milan to Monza" to the Holzhammer company of Bolzano. The privilege authorized the construction of a railway project developed by the Milanese engineer Giulio Sarti.[1]
The Milan–Monza railway, opened in 1840, was the first railway line in Lombardy, and the second in Italy after the Naples–Portici railway. Milan's first railway station, Porta Nuova,[2] formed part of the new railway. It was placed outside the circle of ramparts, near the Porta Nuova city gate, from which it took its name.
In February 1846 came the second Milanese railway station, Porta Tosa-Vittoria, near the city gate of the same name, and outside the circle of ramparts.[3] For eleven years, this station served as the terminus of the Milan–Treviglio railway, which is the Lombard section of the Milan-Venice railway. Since 1857, with the opening of the Treviglio–Bergamo–Coccaglio railway, Porta Tosa station became the western terminus of the railway linking Milan with Venice, the other capital city of the then Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia.
With the decision to extend the Monza railway further north to Como, it was necessary to widen the Porta Nuova railway station by adding extra space, along the banks of the Naviglio Martesana. The new larger station, with a sizeable three bay train hall covering the tracks and trains, entered service in 1850.[1] Today, the station building of this now former station, which was closed in 1931, can still be recognized inside the barracks of the Guardia di Finanza, in via Melchiorre Gioia.
Chronological list of stations
| Name | Inauguration | Current state | Type | Manager |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porta Nuova (I) | 1840 | Sold | Terminal station, surface | N/A |
| Porta Tosa | 1846 | Demolished | Terminal station, surface | N/A |
| Porta Nuova (II) | 1850 | Sold | Terminal station, surface | N/A |
| Certosa | 1858 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Centrale (old) | 1864 | Demolished | Through station, surface | N/A |
| Porta Genova | 1870 | In use | Terminal station,[4] surface | RFI |
| S.M. Garibaldi | 1873 | Sold | Goods yard | N/A |
| Cadorna | 1879 | In use | Terminal station, surface | FERROVIENORD |
| Bruzzano | 1879 | In use | Through station, surface | FERROVIENORD |
| Affori | 1879 | In use | Through station, surface | FERROVIENORD |
| Bovisa | 1879[5] | In use | Through station, surface | FERROVIENORD |
| S.M. Sempione | 1883 | Sold | Goods yard | N/A |
| Rogoredo | 1891 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI/Centostazioni |
| Porta Romana (freight) | 1891 | In use | Goods yard, through station, surface | RFI |
| Lambrate (old) | 1896 | Sold | Through station, surface | N/A |
| Porta Vittoria | 1911[6] | In use | Through station, underground | RFI |
| Greco Pirelli | 1914 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| San Cristoforo | 1915[7] | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Porta Romana (passenger) | 1918 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Bullona | 1929 | Sold | Through station, surface | FERROVIENORD |
| Bovisa FS | 19?? | Sold | Through station, surface | N/A |
| Centrale | 1931 | In use | Terminal station, surface | RFI/Grandi Stazioni |
| Lambrate | 1931 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Porta Nuova (III)[8] | 1931[9] | Sold | Terminal station, surface | FS |
| Quarto Oggiaro | 195? | In use | Through station, surface | FERROVIENORD |
| Porta Garibaldi | 1963 | In use | Terminal and through station, surface and underground | RFI/Centostazioni |
| Repubblica | 1997 | In use | Through station, underground | RFI |
| Porta Venezia | 1997 | In use | Through station, underground | RFI |
| Lancetti | 1997 | In use | Through station, underground | RFI |
| Dateo | 2002 | In use | Through station, underground | RFI |
| Villapizzone | 2002 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Domodossola | 2003 | In use | Through station, underground | FERROVIENORD |
| Romolo | 2006 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Forlanini | 2015 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
| Tibaldi | 2022 | In use | Through station, surface | RFI |
See also
References
- 1 2 "::: Storia di Milano ::: Binari e stazioni a Milano". Storiadimilano.it. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- ↑ The main two storey building still exists, and is currently occupied by the Office of Testing and Materials Service of the Ferrovie dello Stato.
- ↑ Where today via Corridoni intersects with via Archimedes and viale Premuda. Via Archimede and via Pasquale Sottocorno border the station yard of the original station.
- ↑ Loop until the mid-1930s
- ↑ Opening of the Bovisa-Paderno Dugnano railway.
- ↑ Rebuilt in 2004.
- ↑ Opening of the Milan (Bivio Naviglio Grande)-Milano (S. Cristoforo) railway.
- ↑ Known unofficially as the Varesine.
- ↑ Opened in 1911 as a section of the old Centrale railway station.
