Portal maintenance status: (September 2018)
|
The Painting Portal

Painting is a visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and airbrushes, can be used.
In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate multiple other materials, including sand, clay, paper, plaster, gold leaf, and even whole objects.
Painting is an important form of visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture, narration, and abstraction. Paintings can be naturalistic and representational (as in still life and landscape painting), photographic, abstract, narrative, symbolistic (as in Symbolist art), emotive (as in Expressionism) or political in nature (as in Artivism).
A portion of the history of painting in both Eastern and Western art is dominated by religious art. Examples of this kind of painting range from artwork depicting mythological figures on pottery, to Biblical scenes on the Sistine Chapel ceiling, to scenes from the life of Buddha (or other images of Eastern religious origin). (Full article...)
Selected general articles
![Image 1An artist working on a watercolor using a round brushWatercolor (American English) or watercolour (British English; see spelling differences), also aquarelle (French: [akwaʁɛl]; from Italian diminutive of Latin aqua "water"), is a painting method in which the paints are made of pigments suspended in a water-based solution. Watercolor refers to both the medium and the resulting artwork. Aquarelles painted with water-soluble colored ink instead of modern water colors are called aquarellum atramento (Latin for "aquarelle made with ink") by experts. However, this term has now tended to pass out of use.The conventional and most common support — material to which the paint is applied—for watercolor paintings is watercolor paper. Other supports or substrates include stone, ivory, silk, reed, papyrus, bark papers, plastics, vellum, leather, fabric, wood, and watercolor canvas (coated with a gesso that is specially formulated for use with watercolors). Watercolor paper is often made entirely or partially with cotton. This gives the surface the appropriate texture and minimizes distortion when wet. Watercolor papers are usually cold-pressed papers that provide better texture and appearance with a weight at least 300 gsm. Under 300 gsm is commonly not recommended for anything but sketching. Transparency is the main characteristic of watercolors. Watercolors can also be made opaque by adding Chinese white. This is not a method to be used in "true watercolor" (traditional). (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 1
Image 1 An artist working on a watercolor using a round brush
An artist working on a watercolor using a round brush
Watercolor (American English) or watercolour (British English; see spelling differences), also aquarelle (French: [akwaʁɛl]; from Italian diminutive of Latin aqua "water"), is a painting method in which the paints are made of pigments suspended in a water-based solution. Watercolor refers to both the medium and the resulting artwork. Aquarelles painted with water-soluble colored ink instead of modern water colors are called aquarellum atramento (Latin for "aquarelle made with ink") by experts. However, this term has now tended to pass out of use.
The conventional and most common support — material to which the paint is applied—for watercolor paintings is watercolor paper. Other supports or substrates include stone, ivory, silk, reed, papyrus, bark papers, plastics, vellum, leather, fabric, wood, and watercolor canvas (coated with a gesso that is specially formulated for use with watercolors). Watercolor paper is often made entirely or partially with cotton. This gives the surface the appropriate texture and minimizes distortion when wet. Watercolor papers are usually cold-pressed papers that provide better texture and appearance with a weight at least 300 gsm. Under 300 gsm is commonly not recommended for anything but sketching. Transparency is the main characteristic of watercolors. Watercolors can also be made opaque by adding Chinese white. This is not a method to be used in "true watercolor" (traditional). (Full article...) Image 2
Image 2 Signwriters painting a KB Lager advertisement on the side of a building in Australia
Signwriters painting a KB Lager advertisement on the side of a building in Australia
Signwriters design, manufacture and install signs, including advertising signs for shops, businesses and public facilities as well as signs for transport systems. (Full article...) Image 3The idea of founding a theory of painting after the model of music theory was suggested by Goethe in 1807 and gained much regard among the avant-garde artists of the 1920s, the Weimar culture period, like Paul Klee. (Full article...)
Image 3The idea of founding a theory of painting after the model of music theory was suggested by Goethe in 1807 and gained much regard among the avant-garde artists of the 1920s, the Weimar culture period, like Paul Klee. (Full article...) Image 4
Image 4
In the visual arts, style is a "... distinctive manner which permits the grouping of works into related categories" or "... any distinctive, and therefore recognizable, way in which an act is performed or an artifact made or ought to be performed and made". Style refers to the visual appearance of a work of art that relates to other works with similar aesthetic roots, by the same artist, or from the same period, training, location, "school", art movement or archaeological culture: "The notion of style has long been historian's principal mode of classifying works of art".
Style can be divided into the general style of a period, country or cultural group, group of artists or art movement, and the individual style of the artist within that group style. Divisions within both types of styles are often made, such as between "early", "middle" or "late". In some artists, such as Picasso for example, these divisions may be marked and easy to see; in others, they are more subtle. Style is seen as usually dynamic, in most periods always changing by a gradual process, though the speed of this varies greatly, from the very slow development in style typical of prehistoric art or Ancient Egyptian art to the rapid changes in Modern art styles. Style often develops in a series of jumps, with relatively sudden changes followed by periods of slower development. (Full article...) Image 5
Image 5 David (1504)
David (1504)
"What spirit is so empty and blind, that it cannot recognize the fact that the foot is more noble than the shoe, and skin more beautiful than the garment with which it is clothed?"
— Michelangelo
The nude, as a form of visual art that focuses on the unclothed human figure, is an enduring tradition in Western art. It was a preoccupation of Ancient Greek art, and after a semi-dormant period in the Middle Ages returned to a central position with the Renaissance. Unclothed figures often also play a part in other types of art, such as history painting, including allegorical and religious art, portraiture, or the decorative arts. From prehistory to the earliest civilizations, nude female figures were generally understood to be symbols of fertility or well-being.
In India, the Khajuraho Group of Monuments built between 950 and 1050 CE are known for their nude sculptures, which comprise about 10% of the temple decorations, a minority of them being erotic. Japanese prints are one of the few non-western traditions that can be called nudes, but the activity of communal bathing in Japan is portrayed as just another social activity, without the significance placed upon the lack of clothing that exists in the West. Through each era, the nude has reflected changes in cultural attitudes regarding sexuality, gender roles, and social structure. (Full article...) Image 6
Image 6 Image 7
Image 7 The Idle Servant; housemaid troubles were the subject of several of Nicolaes Maes' works.
The Idle Servant; housemaid troubles were the subject of several of Nicolaes Maes' works.
Genre art is the pictorial representation in any of various media of scenes or events from everyday life, such as markets, domestic settings, interiors, parties, inn scenes, work, and street scenes. Such representations (also called genre works, genre scenes, or genre views) may be realistic, imagined, or romanticized by the artist. Some variations of the term genre art specify the medium or type of visual work, as in genre painting, genre prints, genre photographs, and so on.
The following concentrates on painting, but genre motifs were also extremely popular in many forms of the decorative arts, especially from the Rococo of the early 18th century onwards. Single figures or small groups decorated a huge variety of objects such as porcelain, furniture, wallpaper, and textiles. (Full article...) Image 8
Image 8 Ghost sign advertising Bile Beans in York, England
Ghost sign advertising Bile Beans in York, England
A ghost sign is an old hand-painted advertising sign that has been preserved on a building for an extended period of time. The sign may be kept for its nostalgic appeal, or simply indifference by the owner. (Full article...) Image 9Boston Expressionism is an arts movement marked by emotional directness, dark humor, social and spiritual themes, and a tendency toward figuration strong enough that Boston Figurative Expressionism is sometimes used as an alternate term to distinguish it from abstract expressionism, with which it overlapped.
Image 9Boston Expressionism is an arts movement marked by emotional directness, dark humor, social and spiritual themes, and a tendency toward figuration strong enough that Boston Figurative Expressionism is sometimes used as an alternate term to distinguish it from abstract expressionism, with which it overlapped.
Strongly influenced by German Expressionism and by the immigrant, and often Jewish, experience, the movement originated in Boston, Massachusetts, in the 1930s, continues in a third-wave form today, and flourished most markedly in the 1950s–70s. (Full article...) Image 10
Image 10_2.jpg.webp)
A cabinet painting (or "cabinet picture") is a small painting, typically no larger than two feet (0.6 meters) in either dimension, but often much smaller. The term is especially used for paintings that show full-length figures or landscapes at a small scale, rather than a head or other object painted nearly life-size. Such paintings are done very precisely, with a great degree of "finish". From the fifteenth century onward, wealthy collectors of art would keep these paintings in a cabinet, which was a relatively small and private room (often very small even in large houses) to which only those with whom they were on especially intimate terms would be admitted. A cabinet, also known as a closet, study (from the Italian studiolo), office, or by other names, might be used as an office or just a sitting room. Heating the main rooms in large palaces or mansions in the winter was difficult, so small rooms such as cabinets were more comfortable. They offered more privacy from servants or other household members and visitors. Typically, a cabinet would be for the use of a single individual; a large house might have at least two (his and hers) and often more.
Later, cabinet paintings might be housed in a display case, also known as a cabinet, but the term cabinet arose from the name (originally in Italian) of the room, not the piece of furniture. Other small and precious objects, including miniature paintings, "curiosities" of all sorts (see cabinet of curiosities), old master prints, books, or small sculptures might also be displayed in the room. (Full article...) Image 11
Image 11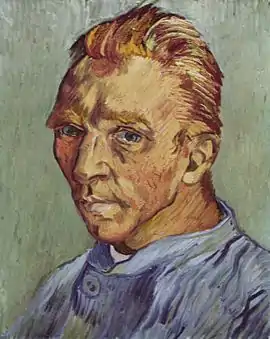 Vincent van Gogh, Self-portrait without beard, end September 1889, (F 525), Oil on canvas, 40 × 31 cm., Private collection. This may have been Van Gogh's last self-portrait. Given as a birthday gift to his mother.
Vincent van Gogh, Self-portrait without beard, end September 1889, (F 525), Oil on canvas, 40 × 31 cm., Private collection. This may have been Van Gogh's last self-portrait. Given as a birthday gift to his mother.
A self-portrait is a portrait of an artist made by themselves. Although self-portraits have been made since the earliest times, it is not until the Early Renaissance in the mid-15th century that artists can be frequently identified depicting themselves as either the main subject, or as important characters in their work. With better and cheaper mirrors, and the advent of the panel portrait, many painters, sculptors and printmakers tried some form of self-portraiture. Portrait of a Man in a Turban by Jan van Eyck of 1433 may well be the earliest known panel self-portrait. He painted a separate portrait of his wife, and he belonged to the social group that had begun to commission portraits, already more common among wealthy Netherlanders than south of the Alps. The genre is venerable, but not until the Renaissance, with increased wealth and interest in the individual as a subject, did it become truly popular.
By the Baroque period, most artists with an established reputation at least left drawings of themselves. Printed portraits of artists had a market, and many were self-portraits. They were also sometimes given as gifts to family and friends. If nothing else, they avoided the need to arrange for a model, and for the many professional portrait-painters, a self-portrait kept in the studio acted as a demonstration of the artist's skill for potential new clients. The unprecedented number of self-portraits by Rembrandt, both as paintings and prints, made clear the potential of the form, and must have further encouraged the trend. (Full article...) Image 12
Image 12%252C_RP-P-OB-10.336.jpg.webp)
Figura serpentinata (lit. 'serpentine figure') is a style in painting and sculpture, intended to make the figure seem more dynamic, that is typical of Mannerism. It is similar, but not identical, to contrapposto, and features figures often in a spiral pose. Early examples can be seen in the work of Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael and Michelangelo.
Emil Maurer writes of the painter and theorist Gian Paolo Lomazzo (1538–1600): "The recommended ideal form unites, after Lomazzo, three qualities: the pyramid, the serpentinata movement and a certain numerical proportion, all three united to form one whole. At the same time, precedence is given to the "moto", that is, to the meandering movement, which should make the pyramid, in exact proportion, into the geometrical form of a cone." (Full article...) Image 13
Image 13 Paintings conservation laboratory, Heritage Conservation Centre, Singapore
Paintings conservation laboratory, Heritage Conservation Centre, Singapore
The conservation and restoration of paintings is carried out by professional painting conservators. Paintings cover a wide range of various mediums, materials, and their supports (i.e. the painted surface made from fabric, paper, wood panel, fabricated board, or other). Painting types include fine art to decorative and functional objects spanning from acrylics, frescoes, and oil paint on various surfaces, egg tempera on panels and canvas, lacquer painting, water color and more. Knowing the materials of any given painting and its support allows for the proper restoration and conservation practices. All components of a painting will react to its environment differently, and impact the artwork as a whole. These material components along with collections care (also known as preventive conservation) will determine the longevity of a painting. The first steps to conservation and restoration is preventive conservation followed by active restoration with the artist's intent in mind. (Full article...) Image 14
Image 14 Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave, in Kalimantan, Indonesia, contains one of the oldest known figurative paintings, a 40,000-year-old depiction of a bull.
Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave, in Kalimantan, Indonesia, contains one of the oldest known figurative paintings, a 40,000-year-old depiction of a bull.
The history of painting reaches back in time to artifacts and artwork created by pre-historic artists, and spans all cultures. It represents a continuous, though periodically disrupted, tradition from Antiquity. Across cultures, continents, and millennia, the history of painting consists of an ongoing river of creativity that continues into the 21st century. Until the early 20th century it relied primarily on representational, religious and classical motifs, after which time more purely abstract and conceptual approaches gained favor.
Developments in Eastern painting historically parallel those in Western painting, in general, a few centuries earlier. African art, Jewish art, Islamic art, Indonesian art, Indian art, Chinese art, and Japanese art each had significant influence on Western art, and vice versa. (Full article...) Image 15Inscape, in visual art, is a term especially associated with certain works of Chilean artist Roberto Matta, but it is also used in other senses within the visual arts. Though the term inscape has been applied to stylistically diverse artworks, it usually conveys some notion of representing the artist's psyche as a kind of interior landscape. The word inscape can therefore be read as a kind of portmanteau, combining interior (or inward) with landscape. (Full article...)
Image 15Inscape, in visual art, is a term especially associated with certain works of Chilean artist Roberto Matta, but it is also used in other senses within the visual arts. Though the term inscape has been applied to stylistically diverse artworks, it usually conveys some notion of representing the artist's psyche as a kind of interior landscape. The word inscape can therefore be read as a kind of portmanteau, combining interior (or inward) with landscape. (Full article...) Image 16Paint Dancing is an American art and dance craze which involves both painting and dancing. Paint Dancers, using paint, brushes and paper, attend organized events dressed in ready-to-paint and dance clothing. The concept of combining movement and painting originated during the later part of the American and European Modern art period; however, Evangeline Welch of Shreveport, Louisiana has been credited with being the "brainchild" of Paint Dancing in the United States of America. This departure from traditional painting styles was often referred to as Action painting. Over the years, several variations of the art form have evolved, including an adaptation introduced by the Hippies during the Summer of Love, that integrated the art of body painting with dancing. One of the more recent introductions of Paint Dancing to American culture is being popularized by a grassroots movement created in 2006 by Seattle artist and activist Matt Jones. The phrases "paint dancing" and "paint dancer" and other variations were originally coined in 1996 by Gloria M. Buono, author, illustrator and publisher of The Painting Ballerina. (Full article...)
Image 16Paint Dancing is an American art and dance craze which involves both painting and dancing. Paint Dancers, using paint, brushes and paper, attend organized events dressed in ready-to-paint and dance clothing. The concept of combining movement and painting originated during the later part of the American and European Modern art period; however, Evangeline Welch of Shreveport, Louisiana has been credited with being the "brainchild" of Paint Dancing in the United States of America. This departure from traditional painting styles was often referred to as Action painting. Over the years, several variations of the art form have evolved, including an adaptation introduced by the Hippies during the Summer of Love, that integrated the art of body painting with dancing. One of the more recent introductions of Paint Dancing to American culture is being popularized by a grassroots movement created in 2006 by Seattle artist and activist Matt Jones. The phrases "paint dancing" and "paint dancer" and other variations were originally coined in 1996 by Gloria M. Buono, author, illustrator and publisher of The Painting Ballerina. (Full article...) Image 17
Image 17
A tondo (pl.: tondi or tondos) is a Renaissance term for a circular work of art, either a painting or a sculpture. The word derives from the Italian rotondo, "round". The term is usually not used in English for small round paintings, but only those over about 60 cm (two feet) in diameter, thus excluding many round portrait miniatures – for sculpture the threshold is rather lower.
A circular or oval relief sculpture is also called a roundel. The infrequently-encountered synonym rondo usually refers to the musical form. (Full article...) Image 18
Image 18 Mona Lisa was created by Leonardo da Vinci using oil paints during the Renaissance period in the 15th century.
Mona Lisa was created by Leonardo da Vinci using oil paints during the Renaissance period in the 15th century.
Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments with a medium of drying oil as the binder. It has been the most common technique for artistic painting on canvas, wood panel or copper for several centuries, spreading from Europe to the rest of the world. The advantages of oil for painting images include "greater flexibility, richer and denser colour, the use of layers, and a wider range from light to dark". But the process is slower, especially when one layer of paint needs to be allowed to dry before another is applied.
The oldest known oil paintings were created by Buddhist artists in Afghanistan and date back to the 7th century AD. Oil paint was used by Europeans for painting statues and woodwork from at least the 12th century, but its common use for painted images began with Early Netherlandish painting in Northern Europe, and by the height of the Renaissance, oil painting techniques had almost completely replaced the use of egg tempera paints for panel paintings in most of Europe, though not for Orthodox icons or wall paintings, where tempera and fresco, respectively, remained the usual choice. (Full article...) Image 19A problem picture is a genre of art popular in late Victorian painting, characterised by the deliberately ambiguous depiction of a key moment in a narrative that can be interpreted in several different ways, or which portrays an unresolved dilemma. It has some relation to the problem play. The viewer of the picture is invited to speculate about several different possible explanations of the scene. The genre has much in common with that of book illustration, then at its most popular, but with the text belonging to the illustration omitted.
Image 19A problem picture is a genre of art popular in late Victorian painting, characterised by the deliberately ambiguous depiction of a key moment in a narrative that can be interpreted in several different ways, or which portrays an unresolved dilemma. It has some relation to the problem play. The viewer of the picture is invited to speculate about several different possible explanations of the scene. The genre has much in common with that of book illustration, then at its most popular, but with the text belonging to the illustration omitted. Defendant and Counsel (1895), by William Frederick Yeames, an example of the problem picture, which invites the viewer to speculate on the woman's alleged crime and on whether or not she may be guilty.
Defendant and Counsel (1895), by William Frederick Yeames, an example of the problem picture, which invites the viewer to speculate on the woman's alleged crime and on whether or not she may be guilty.
The genre began to emerge in the second half of the nineteenth century, along with the development of book illustrations that depicted "pregnant" moments in a narrative. One of the earliest problem pictures is John Everett Millais' Trust Me, which depicts an older man demanding that a young woman hand him a letter she has received. Either character might be uttering the words. The significance and content of the letter is left to the imagination. Their relationship is also unclear; in view of their ages, they might be a married couple, or a father and daughter. (Full article...) Image 20The conservation-restoration of panel paintings involves preventive and treatment measures taken by paintings conservators to slow deterioration, preserve, and repair damage. Panel paintings consist of a wood support, a ground (linen or parchment sized with glues, resin, and gesso), and an image layer (encaustic, tempera, oil). They are typically constructed of two or more panels joined together by crossbeam braces which can separate due to age and material instability caused by fluctuations in relative humidity and temperature. These factors compromise structural integrity and can lead to warping and paint flaking. Because wood is particularly susceptible to pest damage, an IPM plan and regulation of the conditions in storage and display are essential. Past treatments that have fallen out of favor because they can cause permanent damage include transfer of the painting onto a new support, planing, and heavy cradling. Today's conservators often have to remediate damage from previous restoration efforts. Modern conservation-restoration techniques favor minimal intervention that accommodates wood's natural tendency to react to environmental changes. Treatments may include applying flexible battens to minimize deformation or simply leaving distortions alone, instead focusing on preventive care to preserve the artwork in its original state. (Full article...)
Image 20The conservation-restoration of panel paintings involves preventive and treatment measures taken by paintings conservators to slow deterioration, preserve, and repair damage. Panel paintings consist of a wood support, a ground (linen or parchment sized with glues, resin, and gesso), and an image layer (encaustic, tempera, oil). They are typically constructed of two or more panels joined together by crossbeam braces which can separate due to age and material instability caused by fluctuations in relative humidity and temperature. These factors compromise structural integrity and can lead to warping and paint flaking. Because wood is particularly susceptible to pest damage, an IPM plan and regulation of the conditions in storage and display are essential. Past treatments that have fallen out of favor because they can cause permanent damage include transfer of the painting onto a new support, planing, and heavy cradling. Today's conservators often have to remediate damage from previous restoration efforts. Modern conservation-restoration techniques favor minimal intervention that accommodates wood's natural tendency to react to environmental changes. Treatments may include applying flexible battens to minimize deformation or simply leaving distortions alone, instead focusing on preventive care to preserve the artwork in its original state. (Full article...) Image 21
Image 21 An artist drawing on a graphics tablet in 2014
An artist drawing on a graphics tablet in 2014
Digital painting is an art medium created with computer technologies. It employs pixels (picture elements) which are assigned a color to create imagery. It is also known as raster graphics. It is called digital painting because it initially distinguished itself from vector graphics in its ability to render gradiated or blended colors in imagery which mimicked traditional drawing and painting media. (Full article...) Image 22Historic paint analysis, or architectural paint research, is the scientific analysis of a broad range of architectural finishes, and is primarily used to determine the color and behavior of surface finishes at any given point in time. This helps us to understand the building's structural history and how its appearance has changed over time.
Image 22Historic paint analysis, or architectural paint research, is the scientific analysis of a broad range of architectural finishes, and is primarily used to determine the color and behavior of surface finishes at any given point in time. This helps us to understand the building's structural history and how its appearance has changed over time.
Historic paint analysis shares a common methodology with the conservation and restoration of paintings used to conserve and restore two- and three dimensional works of art. This involves the identification of components such as organic or inorganic pigments and dyes contained in the pigments. Historic paint analysis also identifies the pigments' media of suspension such as (water, oil, or latex and the paints' associated substrate. A variety of techniques are used to identify and analyze the pigment layers and finish exposure, including Finish Exposure, optical microscopy, fluorescent light microscopy, polarized light microscopy, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. (Full article...)![Image 23The Peintres de la Réalité [pɛ͂tʀ də la ʀealite] (French for "Painters of Reality") were founded after the Second World War by Henri Cadiou to connect artists who were specialized on still life and genre motifs. It later evolved to the Mouvement trompe l'oeil / Réalité. The painting of the group is no reappearance of antiquity or of the 17th century, but the logical consequence of the place in the 20th century development of a realism that has taken over the sequence of surrealism to the modern trompe-l'œil to lead.1973, the group exhibited at the Cultural Center of New York and the Corcoran Gallery in Washington. In 1989, after the death of Henri Cadiou, Pierre Gilou continued his father's work within the group. In 1993, the group had a sensational success as part of the Grand Palais in Paris, the exhibition "le triomphe du trompe-l'oeil" had more than 65,000 visitors in two weeks. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 23The Peintres de la Réalité [pɛ͂tʀ də la ʀealite] (French for "Painters of Reality") were founded after the Second World War by Henri Cadiou to connect artists who were specialized on still life and genre motifs. It later evolved to the Mouvement trompe l'oeil / Réalité. The painting of the group is no reappearance of antiquity or of the 17th century, but the logical consequence of the place in the 20th century development of a realism that has taken over the sequence of surrealism to the modern trompe-l'œil to lead.
Image 23The Peintres de la Réalité [pɛ͂tʀ də la ʀealite] (French for "Painters of Reality") were founded after the Second World War by Henri Cadiou to connect artists who were specialized on still life and genre motifs. It later evolved to the Mouvement trompe l'oeil / Réalité. The painting of the group is no reappearance of antiquity or of the 17th century, but the logical consequence of the place in the 20th century development of a realism that has taken over the sequence of surrealism to the modern trompe-l'œil to lead.
1973, the group exhibited at the Cultural Center of New York and the Corcoran Gallery in Washington. In 1989, after the death of Henri Cadiou, Pierre Gilou continued his father's work within the group. In 1993, the group had a sensational success as part of the Grand Palais in Paris, the exhibition "le triomphe du trompe-l'oeil" had more than 65,000 visitors in two weeks. (Full article...) Image 24
Image 24.JPG.webp) Annibale Carracci, An Allegory of Truth and Time (1584–85), an allegorical history painting relying very little upon realism.
Annibale Carracci, An Allegory of Truth and Time (1584–85), an allegorical history painting relying very little upon realism.
A hierarchy of genres is any formalization which ranks different genres in an art form in terms of their prestige and cultural value.
In literature, the epic was considered the highest form, for the reason expressed by Samuel Johnson in his Life of John Milton: "By the general consent of criticks, the first praise of genius is due to the writer of an epick poem, as it requires an assemblage of all the powers which are singly sufficient for other compositions." Below that came lyric poetry, and comic poetry, with a similar ranking for drama. The novel took a long time to establish a firm place in the hierarchy, doing so only as belief in any systematic hierarchy of forms expired in the 19th century. (Full article...) Image 25A range-finder painting, sometimes called range-finding painting, is a large landscape painting produced as a training device to help gunners improve their accuracy. Historically, the best-documented use of such paintings was in the United States during World War I. (Full article...)
Image 25A range-finder painting, sometimes called range-finding painting, is a large landscape painting produced as a training device to help gunners improve their accuracy. Historically, the best-documented use of such paintings was in the United States during World War I. (Full article...)
Selected painting techniques
 Image 1Speed painting is an artistic technique where the artist has a limited time to finish the work. The time can vary, usually a duration is set from several minutes to a few hours. Unlike sketches, speed paintings may be considered "finished" after the time limit is up.
Image 1Speed painting is an artistic technique where the artist has a limited time to finish the work. The time can vary, usually a duration is set from several minutes to a few hours. Unlike sketches, speed paintings may be considered "finished" after the time limit is up.
Speed painting is particularly common among digital media artists, because digital painting mediums allow for a work to circumvent drying times of traditional media. Digital media artists primarily use speed painting to practice working quickly and efficiently. Speed painting techniques are also frequently used in concept art, particularly in the early stages of a production when the polish of an individual image matters less than a clear basic presentation of many candidate concepts for consideration. (Full article...) Image 2
Image 2 Frans Hals, Jasper Schade van Westrum (1645); painted mostly wet-on-wet. The forehead has portions of wet (white) over dry (brown/black).
Frans Hals, Jasper Schade van Westrum (1645); painted mostly wet-on-wet. The forehead has portions of wet (white) over dry (brown/black).
Wet-on-wet, or alla prima (Italian, meaning at first attempt), direct painting or au premier coup, is a painting technique in which layers of wet paint are applied to previously administered layers of wet paint. Used mostly in oil painting, the technique requires a fast way of working, because the work has to be finished before the first layers have dried. (Full article...)![Image 3In two-dimensional works of art, such as painting, printmaking, photography or bas-relief, repoussoir (French: [ʁəpuswaʁ], pushing back) is an object along the right or left foreground that directs the viewer's eye into the composition by bracketing (framing) the edge. It became popular with Mannerist and Baroque artists, and is found frequently in Dutch seventeenth-century landscape paintings. Jacob van Ruisdael, for example, often included a tree along one side to enclose the scene (see illustration). Figures are also commonly employed as repoussoir devices by artists such as Paolo Veronese, Peter Paul Rubens and Impressionists such as Gustave Caillebotte. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 3In two-dimensional works of art, such as painting, printmaking, photography or bas-relief, repoussoir (French: [ʁəpuswaʁ], pushing back) is an object along the right or left foreground that directs the viewer's eye into the composition by bracketing (framing) the edge. It became popular with Mannerist and Baroque artists, and is found frequently in Dutch seventeenth-century landscape paintings. Jacob van Ruisdael, for example, often included a tree along one side to enclose the scene (see illustration). Figures are also commonly employed as repoussoir devices by artists such as Paolo Veronese, Peter Paul Rubens and Impressionists such as Gustave Caillebotte. (Full article...)
Image 3In two-dimensional works of art, such as painting, printmaking, photography or bas-relief, repoussoir (French: [ʁəpuswaʁ], pushing back) is an object along the right or left foreground that directs the viewer's eye into the composition by bracketing (framing) the edge. It became popular with Mannerist and Baroque artists, and is found frequently in Dutch seventeenth-century landscape paintings. Jacob van Ruisdael, for example, often included a tree along one side to enclose the scene (see illustration). Figures are also commonly employed as repoussoir devices by artists such as Paolo Veronese, Peter Paul Rubens and Impressionists such as Gustave Caillebotte. (Full article...) Image 4A rotary atomizer is an automatic electrostatic paint applicator used in high volume, automatic production painting environments. Also called a 'paint bell', "rotary bell atomizer" or 'bell applicator', it is preferred for high volume paint application for its superior transfer efficiency, spray pattern consistency, and low compressed air consumption, when compared to a paint spray gun. It can be mounted in a fixed position, reciprocating arm, or an industrial robot. (Full article...)
Image 4A rotary atomizer is an automatic electrostatic paint applicator used in high volume, automatic production painting environments. Also called a 'paint bell', "rotary bell atomizer" or 'bell applicator', it is preferred for high volume paint application for its superior transfer efficiency, spray pattern consistency, and low compressed air consumption, when compared to a paint spray gun. It can be mounted in a fixed position, reciprocating arm, or an industrial robot. (Full article...) Image 5
Image 5 The mural Westward the Course of Empire Takes Its Way was made using stereochromy
The mural Westward the Course of Empire Takes Its Way was made using stereochromy
Mineral painting or Keim's process, also known as stereochromy, is a mural or fresco painting technique that uses a water glass-based paint to maximize the lifetime of the finished work.
The name "stereochromy" was first used in about 1825 by Johann Nepomuk von Fuchs and Schlotthaurer. In the original technique, pigments were applied to plaster or stone and sealed with water glass to preserve and enhance the colors. The method was then improved in the 1880s by Adolf Wilhelm Keim and renamed mineral painting or Keim's process. (Full article...) Image 6
Image 6 U.S. President George W. Bush examines a Yirrkala bark painting during a tour of the Australian National Maritime Museum in Sydney on 6 September 2007.
U.S. President George W. Bush examines a Yirrkala bark painting during a tour of the Australian National Maritime Museum in Sydney on 6 September 2007.
Bark painting is an Australian Aboriginal art form, involving painting on the interior of a strip of tree bark. This is a continuing form of artistic expression in Arnhem Land (especially among the Yolngu peoples) and other regions in the Top End of Australia, including parts of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Traditionally, bark paintings were produced for instructional and ceremonial purposes and were transient objects. Today, they are keenly sought after by collectors and public arts institutions. (Full article...) Image 7
Image 7 The mural Westward the Course of Empire Takes Its Way was made using stereochromy
The mural Westward the Course of Empire Takes Its Way was made using stereochromy
Mineral painting or Keim's process, also known as stereochromy, is a mural or fresco painting technique that uses a water glass-based paint to maximize the lifetime of the finished work.
The name "stereochromy" was first used in about 1825 by Johann Nepomuk von Fuchs and Schlotthaurer. In the original technique, pigments were applied to plaster or stone and sealed with water glass to preserve and enhance the colors. The method was then improved in the 1880s by Adolf Wilhelm Keim and renamed mineral painting or Keim's process. (Full article...)![Image 8Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, 1565, 24 cm × 34 cm (9.4 in × 13.4 in)Grisaille (/ɡrɪˈzaɪ/ or /ɡrɪˈzeɪl/; French: grisaille, lit. 'greyed' French pronunciation: [ɡʁizaj], from gris 'grey') is a painting executed entirely in shades of grey or of another neutral greyish colour. It is particularly used in large decorative schemes in imitation of sculpture. Many grisailles include a slightly wider colour range.A grisaille may be executed for its own sake, as an underpainting for an oil painting (in preparation for glazing layers of colour over it) or as a model from which an engraver may work (as was done by Rubens and his school). Full colouring of a subject makes many demands of an artist, and working in grisaille was often chosen as it may be quicker and cheaper than traditional painting, although the effect was sometimes deliberately chosen for aesthetic reasons. Grisaille paintings resemble the drawings, normally in monochrome, that artists from the Renaissance on were trained to produce; as with drawings, grisaille can betray the hand of a less-talented assistant more easily than would a fully coloured painting. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 8
Image 8 Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, 1565, 24 cm × 34 cm (9.4 in × 13.4 in)
Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, 1565, 24 cm × 34 cm (9.4 in × 13.4 in)
Grisaille (/ɡrɪˈzaɪ/ or /ɡrɪˈzeɪl/; French: grisaille, lit. 'greyed' French pronunciation: [ɡʁizaj], from gris 'grey') is a painting executed entirely in shades of grey or of another neutral greyish colour. It is particularly used in large decorative schemes in imitation of sculpture. Many grisailles include a slightly wider colour range.
A grisaille may be executed for its own sake, as an underpainting for an oil painting (in preparation for glazing layers of colour over it) or as a model from which an engraver may work (as was done by Rubens and his school). Full colouring of a subject makes many demands of an artist, and working in grisaille was often chosen as it may be quicker and cheaper than traditional painting, although the effect was sometimes deliberately chosen for aesthetic reasons. Grisaille paintings resemble the drawings, normally in monochrome, that artists from the Renaissance on were trained to produce; as with drawings, grisaille can betray the hand of a less-talented assistant more easily than would a fully coloured painting. (Full article...) Image 9
Image 9 Ombré: black to blue
Ombré: black to blue
Ombré /ˈɒmbreɪ/ (literally "shaded" in French) is the blending of one color hue to another, usually moving tints and shades from light to dark. It has become a popular feature for hair coloring, nail art, and even baking, in addition to its uses in home decorating and graphic design.
In contrast to ombré, sombré is a much softer and gradual shading of one color to another. (Full article...) Image 10
Image 10 Grand Prix de France 1913
Grand Prix de France 1913
Ernest Montaut
Speed line is the art technique which uses streaks to convey the impression of speed. The French artist Ernest Montaut is usually credited with its invention. He used the technique freely in his posters which were produced at a time when auto racing, speedboat racing and aircraft races were in their infancy. The effect is similar to the blur caused by panning in still photography.
Speed lines are frequently used in Japanese manga and anime, of which Speed Racer is a classic example. (Full article...) Image 11Ink wash painting (simplified Chinese: 水墨画; traditional Chinese: 水墨畫; pinyin: shuǐmòhuà); is a type of Chinese ink brush painting which uses washes of black ink, such as that used in East Asian calligraphy, in different concentrations. It emerged during the Tang dynasty of China (618–907), and overturned earlier, more realistic techniques. It is typically monochrome, using only shades of black, with a great emphasis on virtuoso brushwork and conveying the perceived "spirit" or "essence" of a subject over direct imitation. Ink wash painting flourished from the Song dynasty in China (960–1279) onwards, as well as in Japan after it was introduced by Zen Buddhist monks in the 14th century. Some Western scholars divide Chinese painting (including ink wash painting) into three periods: times of representation, times of expression, and historical Oriental art. Chinese scholars have their own views which may be different; they believe that contemporary Chinese ink wash paintings are the pluralistic continuation of multiple historical traditions.
Image 11Ink wash painting (simplified Chinese: 水墨画; traditional Chinese: 水墨畫; pinyin: shuǐmòhuà); is a type of Chinese ink brush painting which uses washes of black ink, such as that used in East Asian calligraphy, in different concentrations. It emerged during the Tang dynasty of China (618–907), and overturned earlier, more realistic techniques. It is typically monochrome, using only shades of black, with a great emphasis on virtuoso brushwork and conveying the perceived "spirit" or "essence" of a subject over direct imitation. Ink wash painting flourished from the Song dynasty in China (960–1279) onwards, as well as in Japan after it was introduced by Zen Buddhist monks in the 14th century. Some Western scholars divide Chinese painting (including ink wash painting) into three periods: times of representation, times of expression, and historical Oriental art. Chinese scholars have their own views which may be different; they believe that contemporary Chinese ink wash paintings are the pluralistic continuation of multiple historical traditions.
In China, Japan and, to a lesser extent, Korea, ink wash painting formed a distinct stylistic tradition with a different set of artists working in it than from those in other types of painting. In China especially it was a gentlemanly occupation associated with poetry and calligraphy. It was often produced by the scholar-official or literati class, ideally illustrating their own poetry and producing the paintings as gifts for friends or patrons, rather than painting for payment. (Full article...)![Image 12Raphael's La belle jardinière, showing the use of unioneAccording to the theory of the art historian Marcia B. Hall, which has gained considerable acceptance, unione (Italian: [uˈnjoːne]) is one of the canonical painting modes of the Renaissance; that is, one of four modes of painting colours available to Italian High Renaissance painters, along with sfumato, chiaroscuro and cangiante. Unione was developed by Raphael, who exemplified it in the Stanza della Segnatura.Unione is similar to sfumato, but is more useful for the edges of chiaroscuro, where vibrant colors are involved. As with chiaroscuro, unione conveys the contrasts, and as sfumato it strives for harmony and unity, but also for coloristic richness. Unione is softer than chiaroscuro in the search for the right tonal key. There should be the harmony between light and dark, without the excesses and accentuation of a chiaroscuro mode. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 12
Image 12 Raphael's La belle jardinière, showing the use of unione
Raphael's La belle jardinière, showing the use of unione
According to the theory of the art historian Marcia B. Hall, which has gained considerable acceptance, unione (Italian: [uˈnjoːne]) is one of the canonical painting modes of the Renaissance; that is, one of four modes of painting colours available to Italian High Renaissance painters, along with sfumato, chiaroscuro and cangiante. Unione was developed by Raphael, who exemplified it in the Stanza della Segnatura.
Unione is similar to sfumato, but is more useful for the edges of chiaroscuro, where vibrant colors are involved. As with chiaroscuro, unione conveys the contrasts, and as sfumato it strives for harmony and unity, but also for coloristic richness. Unione is softer than chiaroscuro in the search for the right tonal key. There should be the harmony between light and dark, without the excesses and accentuation of a chiaroscuro mode. (Full article...) Image 13Graining is the practice of imitating wood grain on a non-wood surface, or on relatively undesirable wood surface, in order to give it the appearance of a rare or higher quality wood, thereby increase that surface's aesthetic appeal. Graining was common in the 19th century, as people were keen on imitating hard, expensive woods by applying a superficial layer of paint onto soft, inexpensive woods or other hard surfaces. Graining can be accomplished using either rudimentary tools or highly specialized tools. A specialized thick brush used for graining is often called a mottler. Fan brushes, floggers, softening brushes, texture combs and even fingers are used to create various effects. The painting is carried out in layers, with the first layer being a base. Today that is usually done with latex paint in a gold or orange or tan tone, depending on the type of wood the artist is aiming to imitat. A second layer of tempera or thinned paint is applied over the dry base, by means of a sponge or large inexpensive brush. During the 19th century, however, brushes were more commonly used. It can also be applied on bricks and brass, as is more common today.
Image 13Graining is the practice of imitating wood grain on a non-wood surface, or on relatively undesirable wood surface, in order to give it the appearance of a rare or higher quality wood, thereby increase that surface's aesthetic appeal. Graining was common in the 19th century, as people were keen on imitating hard, expensive woods by applying a superficial layer of paint onto soft, inexpensive woods or other hard surfaces. Graining can be accomplished using either rudimentary tools or highly specialized tools. A specialized thick brush used for graining is often called a mottler. Fan brushes, floggers, softening brushes, texture combs and even fingers are used to create various effects. The painting is carried out in layers, with the first layer being a base. Today that is usually done with latex paint in a gold or orange or tan tone, depending on the type of wood the artist is aiming to imitat. A second layer of tempera or thinned paint is applied over the dry base, by means of a sponge or large inexpensive brush. During the 19th century, however, brushes were more commonly used. It can also be applied on bricks and brass, as is more common today.
Graining can also mean the production of any artificial texture on any surface. For example, in printing, making the smooth metal sheets used in modern printing processes coarse. A stoneworking equivalent of graining is marbling. (Full article...) Image 14
Image 14 The Ghent Altarpiece by Jan van Eyck and his brothers, 1432. A large altarpiece on panel. The outer wings are hinged, and painted on both sides.
The Ghent Altarpiece by Jan van Eyck and his brothers, 1432. A large altarpiece on panel. The outer wings are hinged, and painted on both sides.
A panel painting is a painting made on a flat panel of wood, either a single piece or a number of pieces joined together. Until canvas became the more popular support medium in the 16th century, panel painting was the normal method, when not painting directly onto a wall (fresco) or on vellum (used for miniatures in illuminated manuscripts). Wood panels were also used for mounting vellum paintings. (Full article...) Image 15
Image 15 Example of a theorem painting (c.1850) from the Metropolitan Museum of Art
Example of a theorem painting (c.1850) from the Metropolitan Museum of Art
Theorem stencil, sometimes also called theorem painting or velvet painting, is the art of making stencils and using them to make drawings or paintings on fabric or paper.
A vogue for theorem stencil painting began in England at the turn of the 18th century and through the mid-1800s. The art was first taught to women in academies and boarding schools throughout colonial New England. It continued to be taught into the mid-1800s in many other areas. (Full article...) Image 16Overspray refers to the application of any form of paint, varnish, stain or other non-water-soluble airborne particulate material onto an unintended location. This concept is most commonly encountered in graffiti, auto detailing, and when commercial paint jobs drift onto unintended objects. (Full article...)
Image 16Overspray refers to the application of any form of paint, varnish, stain or other non-water-soluble airborne particulate material onto an unintended location. This concept is most commonly encountered in graffiti, auto detailing, and when commercial paint jobs drift onto unintended objects. (Full article...) Image 17
Image 17_-False_Dome.jpg.webp) The illusionistic perspective of Andrea Pozzo's trompe-l'œil dome at Sant'Ignazio (1685) creates an illusion of an actual architectural space on what is, in actuality, a slightly concave painted surface.
The illusionistic perspective of Andrea Pozzo's trompe-l'œil dome at Sant'Ignazio (1685) creates an illusion of an actual architectural space on what is, in actuality, a slightly concave painted surface.
Illusionistic ceiling painting, which includes the techniques of perspective di sotto in sù and quadratura, is the tradition in Renaissance, Baroque and Rococo art in which trompe-l'œil, perspective tools such as foreshortening, and other spatial effects are used to create the illusion of three-dimensional space on an otherwise two-dimensional or mostly flat ceiling surface above the viewer. It is frequently used to create the illusion of an open sky, such as with the oculus in Andrea Mantegna's Camera degli Sposi, or the illusion of an architectural space such as the cupola, one of Andrea Pozzo's frescoes in Sant'Ignazio, Rome. Illusionistic ceiling painting belongs to the general class of illusionism in art, designed to create accurate representations of reality. (Full article...) Image 18
Image 18 A 6th-century encaustic icon from Saint Catherine's Monastery, Egypt.
A 6th-century encaustic icon from Saint Catherine's Monastery, Egypt.
Encaustic painting, also known as hot wax painting, is a form of painting that involves a heated wax medium to which colored pigments have been added. The molten mix is applied to a surface—usually prepared wood, though canvas and other materials are sometimes used. The simplest encaustic medium could be made by adding pigments to wax, though recipes most commonly consist of beeswax and damar resin, potentially with other ingredients. For pigmentation, dried powdered pigments can be used, though some artists use pigmented wax, inks, oil paints or other forms of pigmentation.
Metal tools and special brushes can be used to shape the medium as it cools. Also, heated metal tools, including spatulas, knives and scrapers, can be used to manipulate the medium after it has cooled onto the surface. Additionally, heat lamps, torches, heat guns, and other methods of applying heat are used by encaustic artists to fuse and bind the medium. Because encaustic medium is thermally malleable, the medium can be also sculpted. And/or, materials can be encased, collaged or layered into the medium. (Full article...) Image 19
Image 19 Captain Joseph – Chinese reverse glass painting from c. 1785 – 1789.
Captain Joseph – Chinese reverse glass painting from c. 1785 – 1789.
Reverse painting on glass is an art form consisting of applying paint to a piece of glass and then viewing the image by turning the glass over and looking through the glass at the image. Another term used to refer to the art of cold painting and gilding on the back of glass is verre églomisé, named after the French decorator Jean-Baptiste Glomy (1711–86), who framed prints using glass that had been reverse-painted. In German it is known as Hinterglasmalerei.
This art form has been around for many years. It was widely used for sacral paintings since the Middle Ages. The most famous was the art of icons in the Byzantine Empire. Later the painting on glass spread to Italy, where in Venice it influenced its Renaissance art. Since the middle of the 18th century, painting on glass became favored by the Church and the nobility throughout Central Europe. A number of clock faces were created using this technique in the early-to-mid-19th century. Throughout the 19th century painting on glass was widely popular as folk art in Austria, Bavaria, Moravia, Bohemia and Slovakia. Unfortunately, during the inter-war period (1914–1945) this traditional "naive" technique fell nearly to a complete oblivion and its methods of paint composition and structural layout had to be re-invented by combining acrylic and oil paints. A new method of reverse painting emerged using polymer glazing methods that permitted the artworks to be painted direct to an acrylic UV coating on the glass. The unique under glass effect retains a curious depth even though the layered painting on the glass was bonded to a final linen support and now stretcher bar mounted after being carefully removed from the original 'glass easel'. Current glass painting may disappear with the advent of using aerospace mylar as a preliminary support. (Full article...) Image 20
Image 20 Example of spray fireproofing, using a gypsum based plaster in a low-rise industrial building in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Example of spray fireproofing, using a gypsum based plaster in a low-rise industrial building in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Intonaco is an Italian term for the final, very thin layer of plaster on which a fresco is painted. The plaster is painted while still wet, in order to allow the pigment to penetrate into the intonaco itself. An earlier layer, called arriccio, is laid slightly coarsely to provide a key for the intonaco, and must be allowed to dry, usually for some days, before the final very thin layer is applied and painted on. In Italian the term intonaco is also used much more generally for normal plaster or mortar wall-coatings in buildings.
Intonaco is traditionally a mixture of sand (with granular dimensions less than two millimeters) and a binding substance. (Full article...) Image 21
Image 21 Rose painting with floral paintings in a traditional design
Rose painting with floral paintings in a traditional design
Rose-painting, rosemaling, rosemåling or rosmålning is a Scandinavian decorative folk painting that flourished from the 1700s to the mid-1800s, particularly in Norway. In Sweden, rose-painting began to be called dalmålning, c. 1901, for the region where it had been most popular and kurbitsmålning (kurbits), in the 1920s, for a characteristic trait, but in Norway the old name still predominates beside terms for local variants. Rose-painting was used to decorate church walls and ceilings. It then spread to wooden items commonly used in daily life, such as ale bowls, stools, chairs, cupboards, boxes, and trunks. Using stylized ornamentation made up of fantasy flowers, scrollwork, fine line work, flowing patterns and sometimes geometric elements give rose-painting its unique feel. Some paintings may include landscapes and architectural elements. Rose-painting also utilizes other decorative painting techniques such as glazing, spattering, marbleizing, manipulating the paint with the fingers or other objects. Regional styles of rose-painting developed, and some varied only slightly from others, while others may be noticeably distinct. (Full article...) Image 22
Image 22 A Fresco-secco wall painting in St Just in Penwith Parish Church, Cornwall, UK. The painting was created in the 15th century and depicts Saint George fighting the dragon.
A Fresco-secco wall painting in St Just in Penwith Parish Church, Cornwall, UK. The painting was created in the 15th century and depicts Saint George fighting the dragon.
Fresco-secco (or a secco or fresco finto) is a wall painting technique where pigments mixed with an organic binder and/or lime are applied onto dry plaster. The paints used can e.g. be casein paint, tempera, oil paint, silicate mineral paint. If the pigments are mixed with lime water or lime milk and applied to a dry plaster the technique is called lime secco painting.
The secco technique contrasts with the fresco technique, where the painting is executed on a layer of wet plaster.
Because the pigments do not become part of the wall, as in buon fresco, fresco-secco paintings are less durable. The colors may flake off the painting as time goes by, but this technique has the advantages of a longer working time and retouchability. In Italy, the fresco technique was reintroduced around 1300 and led to an increase in the general quality of mural painting. This technological change coincided with the realistic turn in Western art and the changing liturgical use of murals. (Full article...) Image 23
Image 23 Installation view of Irrational Geometrics 2008 by Pascal Dombis
Installation view of Irrational Geometrics 2008 by Pascal Dombis
Generative art refers to art that in whole or in part has been created with the use of an autonomous system. An autonomous system in this context is generally one that is non-human and can independently determine features of an artwork that would otherwise require decisions made directly by the artist. In some cases the human creator may claim that the generative system represents their own artistic idea, and in others that the system takes on the role of the creator.
"Generative art" often refers to algorithmic art (algorithmically determined computer generated artwork) and synthetic media (general term for any algorithmically generated media), but artists can also make it using systems of chemistry, biology, mechanics and robotics, smart materials, manual randomization, mathematics, data mapping, symmetry, tiling, and more. (Full article...)![Image 24Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, 1565, 24 cm × 34 cm (9.4 in × 13.4 in)Grisaille (/ɡrɪˈzaɪ/ or /ɡrɪˈzeɪl/; French: grisaille, lit. 'greyed' French pronunciation: [ɡʁizaj], from gris 'grey') is a painting executed entirely in shades of grey or of another neutral greyish colour. It is particularly used in large decorative schemes in imitation of sculpture. Many grisailles include a slightly wider colour range.A grisaille may be executed for its own sake, as an underpainting for an oil painting (in preparation for glazing layers of colour over it) or as a model from which an engraver may work (as was done by Rubens and his school). Full colouring of a subject makes many demands of an artist, and working in grisaille was often chosen as it may be quicker and cheaper than traditional painting, although the effect was sometimes deliberately chosen for aesthetic reasons. Grisaille paintings resemble the drawings, normally in monochrome, that artists from the Renaissance on were trained to produce; as with drawings, grisaille can betray the hand of a less-talented assistant more easily than would a fully coloured painting. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 24
Image 24 Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, 1565, 24 cm × 34 cm (9.4 in × 13.4 in)
Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, 1565, 24 cm × 34 cm (9.4 in × 13.4 in)
Grisaille (/ɡrɪˈzaɪ/ or /ɡrɪˈzeɪl/; French: grisaille, lit. 'greyed' French pronunciation: [ɡʁizaj], from gris 'grey') is a painting executed entirely in shades of grey or of another neutral greyish colour. It is particularly used in large decorative schemes in imitation of sculpture. Many grisailles include a slightly wider colour range.
A grisaille may be executed for its own sake, as an underpainting for an oil painting (in preparation for glazing layers of colour over it) or as a model from which an engraver may work (as was done by Rubens and his school). Full colouring of a subject makes many demands of an artist, and working in grisaille was often chosen as it may be quicker and cheaper than traditional painting, although the effect was sometimes deliberately chosen for aesthetic reasons. Grisaille paintings resemble the drawings, normally in monochrome, that artists from the Renaissance on were trained to produce; as with drawings, grisaille can betray the hand of a less-talented assistant more easily than would a fully coloured painting. (Full article...) Image 25A glaze is a thin transparent or semi-transparent layer on a painting which modifies the appearance of the underlying paint layer. Glazes can change the chroma, value, hue and texture of a surface. Glazes consist of a great amount of binding medium in relation to a very small amount of pigment. Drying time will depend on the amount and type of paint medium used in the glaze. The medium, base, or vehicle is the mixture to which the dry pigment is added. Different media can increase or decrease the rate at which oil paints dry.
Image 25A glaze is a thin transparent or semi-transparent layer on a painting which modifies the appearance of the underlying paint layer. Glazes can change the chroma, value, hue and texture of a surface. Glazes consist of a great amount of binding medium in relation to a very small amount of pigment. Drying time will depend on the amount and type of paint medium used in the glaze. The medium, base, or vehicle is the mixture to which the dry pigment is added. Different media can increase or decrease the rate at which oil paints dry.
Often, because a paint is too opaque, painters will add a medium like linseed oil or alkyd to the paint to make them more transparent and pliable for the purposes of glazing. While these media are usually liquids, there are solid and semi-solid media used in the making of paints as well. For example, many classical oil painters have also been known to use ground glass and semi-solid resins to increase the translucency of their paint. (Full article...)
Need help?
Do you have a question about Painting that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Painting-related articles, see WikiProject Painting.
General images
.jpg.webp)
 Image 2Honoré Daumier, The Painter (1808–1879), oil on panel with visible brushstrokes (from Painting)
Image 2Honoré Daumier, The Painter (1808–1879), oil on panel with visible brushstrokes (from Painting) Image 3Francis Picabia, (Left) Le saint des saints c'est de moi qu'il s'agit dans ce portrait, 1 July 1915; (center) Portrait d'une jeune fille americaine dans l'état de nudité, 5 July 1915: (right) J'ai vu et c'est de toi qu'il s'agit, De Zayas! De Zayas! Je suis venu sur les rivages du Pont-Euxin, New York, 1915 (from History of painting)
Image 3Francis Picabia, (Left) Le saint des saints c'est de moi qu'il s'agit dans ce portrait, 1 July 1915; (center) Portrait d'une jeune fille americaine dans l'état de nudité, 5 July 1915: (right) J'ai vu et c'est de toi qu'il s'agit, De Zayas! De Zayas! Je suis venu sur les rivages du Pont-Euxin, New York, 1915 (from History of painting) Image 4Diego Rivera, Recreation of Man at the Crossroads (renamed Man, Controller of the Universe), originally created in 1934, Mexican muralism movement (from History of painting)
Image 4Diego Rivera, Recreation of Man at the Crossroads (renamed Man, Controller of the Universe), originally created in 1934, Mexican muralism movement (from History of painting)
 Image 6Bharat Mata by Abanindranath Tagore (1871–1951), a nephew of the poet Rabindranath Tagore, and a pioneer of the movement (from History of painting)
Image 6Bharat Mata by Abanindranath Tagore (1871–1951), a nephew of the poet Rabindranath Tagore, and a pioneer of the movement (from History of painting)
 Image 8Hand stencils in the "Tree of Life" cave painting in Gua Tewet, Kalimantan, Indonesia (from History of painting)
Image 8Hand stencils in the "Tree of Life" cave painting in Gua Tewet, Kalimantan, Indonesia (from History of painting) Image 9Krishna and Radha, might be the work of Nihâl Chand, master of Kishangarh school of Rajput Painting (from Painting)
Image 9Krishna and Radha, might be the work of Nihâl Chand, master of Kishangarh school of Rajput Painting (from Painting) Image 10Two Scribes Seated with Books and a Writing Table Fragment of a decorative margin Northern India (Mughal school), ca. 1640–1650 (from History of painting)
Image 10Two Scribes Seated with Books and a Writing Table Fragment of a decorative margin Northern India (Mughal school), ca. 1640–1650 (from History of painting) Image 11The Eternal Father Painting the Virgin of Guadalupe. Attributed to Joaquín Villegas (1713 – active in 1753) (Mexican) (painter, Museo Nacional de Arte. (from History of painting)
Image 11The Eternal Father Painting the Virgin of Guadalupe. Attributed to Joaquín Villegas (1713 – active in 1753) (Mexican) (painter, Museo Nacional de Arte. (from History of painting)

 Image 14Rudolf Reschreiter, Blick von der Höllentalangerhütte zum Höllentalgletscher und den Riffelwandspitzen, Gouache (1921) (from Painting)
Image 14Rudolf Reschreiter, Blick von der Höllentalangerhütte zum Höllentalgletscher und den Riffelwandspitzen, Gouache (1921) (from Painting).jpg.webp)
 Image 16Piet Mondrian, Composition en rouge, jaune, bleu et noir (1921), Gemeentemuseum Den Haag (from Painting)
Image 16Piet Mondrian, Composition en rouge, jaune, bleu et noir (1921), Gemeentemuseum Den Haag (from Painting) Image 17Pettakere Cave are more than 44,000 years old, Maros, South Sulawesi, Indonesia (from History of painting)
Image 17Pettakere Cave are more than 44,000 years old, Maros, South Sulawesi, Indonesia (from History of painting)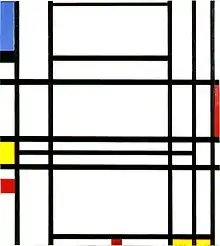
 Image 19Marcel Duchamp, Nude Descending a Staircase, No. 2, 1912, Philadelphia Museum of Art (from History of painting)
Image 19Marcel Duchamp, Nude Descending a Staircase, No. 2, 1912, Philadelphia Museum of Art (from History of painting)
 Image 21A fresco showing Hades and Persephone riding in a chariot, from the tomb of Queen Eurydice I of Macedon at Vergina, Greece, 4th century BC (from History of painting)
Image 21A fresco showing Hades and Persephone riding in a chariot, from the tomb of Queen Eurydice I of Macedon at Vergina, Greece, 4th century BC (from History of painting)

 Image 24Hellenistic Greek terracotta funerary wall painting, 3rd century BC (from History of painting)
Image 24Hellenistic Greek terracotta funerary wall painting, 3rd century BC (from History of painting) Image 25Muromachi period, Shingei (1431–1485), Viewing a Waterfall, Nezu Museum, Tokyo. (from History of painting)
Image 25Muromachi period, Shingei (1431–1485), Viewing a Waterfall, Nezu Museum, Tokyo. (from History of painting)
 Image 27Pictographs from the Great Gallery, Canyonlands National Park, Horseshoe Canyon, Utah, c. 1500 BCE (from History of painting)
Image 27Pictographs from the Great Gallery, Canyonlands National Park, Horseshoe Canyon, Utah, c. 1500 BCE (from History of painting) Image 28An artistic depiction of a group of rhinos was painted in the Chauvet Cave 30,000 to 32,000 years ago. (from Painting)
Image 28An artistic depiction of a group of rhinos was painted in the Chauvet Cave 30,000 to 32,000 years ago. (from Painting) Image 29Mother Goddess A miniature painting of the Pahari style, dating to the eighteenth century. Pahari and Rajput miniatures share many common features. (from History of painting)
Image 29Mother Goddess A miniature painting of the Pahari style, dating to the eighteenth century. Pahari and Rajput miniatures share many common features. (from History of painting)_cropped.jpg.webp) Image 30Khan Bahadur Khan with Men of his Clan, c. 1815, from the Fraser Album, Company Style (from Painting)
Image 30Khan Bahadur Khan with Men of his Clan, c. 1815, from the Fraser Album, Company Style (from Painting)
%252C_oil_on_canvas%252C_133_x_154_cm%252C_Kunstsammlung_Nordrhein-Westfalen%252C_D%C3%BCsseldorf.jpg.webp) Image 32Max Beckmann, The Night (Die Nacht), 1918–1919, Kunstsammlung Nordrhein-Westfalen, Düsseldorf (from History of painting)
Image 32Max Beckmann, The Night (Die Nacht), 1918–1919, Kunstsammlung Nordrhein-Westfalen, Düsseldorf (from History of painting)
%252C_oil_on_canvas%252C_73_x_54_cm_DSC05359...jpg.webp) Image 34Jean Metzinger, La danse (Bacchante) (c. 1906), oil on canvas, 73 x 54 cm, Kröller-Müller Museum (from Painting)
Image 34Jean Metzinger, La danse (Bacchante) (c. 1906), oil on canvas, 73 x 54 cm, Kröller-Müller Museum (from Painting)


 Image 38Andreas Achenbach, Clearing Up, Coast of Sicily (1847), The Walters Art Museum (from Painting)
Image 38Andreas Achenbach, Clearing Up, Coast of Sicily (1847), The Walters Art Museum (from Painting) Image 39Joan Miró, Horse, Pipe and Red Flower, 1920, abstract Surrealism, Philadelphia Museum of Art (from History of painting)
Image 39Joan Miró, Horse, Pipe and Red Flower, 1920, abstract Surrealism, Philadelphia Museum of Art (from History of painting)
 Image 41Spring Morning in the Han Palace, by Ming-era artist Qiu Ying (1494–1552 AD) (from History of painting)
Image 41Spring Morning in the Han Palace, by Ming-era artist Qiu Ying (1494–1552 AD) (from History of painting) Image 42An Ethiopian illuminated Evangelist portrait of Mark the Evangelist, from the Ethiopian Garima Gospels, 6th century AD, Kingdom of Aksum (from History of painting)
Image 42An Ethiopian illuminated Evangelist portrait of Mark the Evangelist, from the Ethiopian Garima Gospels, 6th century AD, Kingdom of Aksum (from History of painting)



 Image 47Jean de Court (attributed), painted Limoges enamel dish in detail (mid-16th century), Waddesdon Bequest, British Museum (from Painting)
Image 47Jean de Court (attributed), painted Limoges enamel dish in detail (mid-16th century), Waddesdon Bequest, British Museum (from Painting)
'_by_Barnett_Newman%252C_1968.jpg.webp) Image 49Barnett Newman, Untitled Etching 1 (First Version), 1968, Minimalism (from History of painting)
Image 49Barnett Newman, Untitled Etching 1 (First Version), 1968, Minimalism (from History of painting)
 Image 51The oldest known figurative painting is a depiction of a bull that was discovered in the Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave in Indonesia. It was painted 40,000–52,000 years ago or earlier. (from Painting)
Image 51The oldest known figurative painting is a depiction of a bull that was discovered in the Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave in Indonesia. It was painted 40,000–52,000 years ago or earlier. (from Painting)




 Image 57Nino Pisano, Apelles or the Art of painting in detail (1334–1336); relief of the Giotto's Bell Tower in Florence, Italy
Image 57Nino Pisano, Apelles or the Art of painting in detail (1334–1336); relief of the Giotto's Bell Tower in Florence, Italy
.jpg.webp) Image 59Francisco de Zurbarán, Still Life with Pottery Jars (Spanish: Bodegón de recipientes) (1636), oil on canvas, 46 x 84 cm, Museo del Prado, Madrid (from Painting)
Image 59Francisco de Zurbarán, Still Life with Pottery Jars (Spanish: Bodegón de recipientes) (1636), oil on canvas, 46 x 84 cm, Museo del Prado, Madrid (from Painting).jpg.webp)
 Image 61Loquats and Mountain Bird, anonymous artist of the Southern Song dynasty; paintings in leaf album style such as this were popular in the Southern Song (1127–1279). (from History of painting)
Image 61Loquats and Mountain Bird, anonymous artist of the Southern Song dynasty; paintings in leaf album style such as this were popular in the Southern Song (1127–1279). (from History of painting)
 Image 63Sesshū Tōyō, Landscapes of the Four Seasons (1486), ink and light color on paper (from Painting)
Image 63Sesshū Tōyō, Landscapes of the Four Seasons (1486), ink and light color on paper (from Painting) Image 64Prehistoric cave painting of aurochs (French: Bos primigenius primigenius), Lascaux, France (from Painting)
Image 64Prehistoric cave painting of aurochs (French: Bos primigenius primigenius), Lascaux, France (from Painting)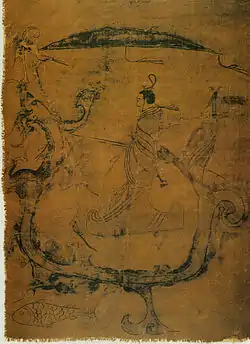 Image 65Silk painting depicting a man riding a dragon, painting on silk, dated to 5th–3rd century BC, Warring States period, from Zidanku Tomb no. 1 in Changsha, Hunan Province (from History of painting)
Image 65Silk painting depicting a man riding a dragon, painting on silk, dated to 5th–3rd century BC, Warring States period, from Zidanku Tomb no. 1 in Changsha, Hunan Province (from History of painting)


 Image 69Mona Lisa (1503–1517) by Leonardo da Vinci is one of the world's most recognizable paintings. (from Painting)
Image 69Mona Lisa (1503–1517) by Leonardo da Vinci is one of the world's most recognizable paintings. (from Painting)




.JPG.webp)


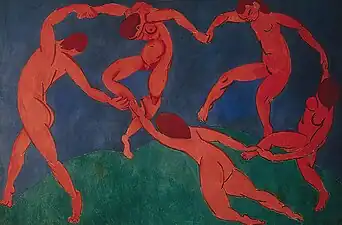
 Image 79Gwion Gwion rock paintings found in the north-west Kimberley region of Western Australia c. 15,000 BC (from History of painting)
Image 79Gwion Gwion rock paintings found in the north-west Kimberley region of Western Australia c. 15,000 BC (from History of painting) Image 80The Sakyamuni Buddha, by Zhang Shengwen, 1173–1176 AD, Song dynasty period. (from History of painting)
Image 80The Sakyamuni Buddha, by Zhang Shengwen, 1173–1176 AD, Song dynasty period. (from History of painting) Image 81Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for Cave of the Hands) in the Santa Cruz province in Argentina, c. 7300 BC (from History of painting)
Image 81Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for Cave of the Hands) in the Santa Cruz province in Argentina, c. 7300 BC (from History of painting)
.jpg.webp)

Categories
- Select [►] to view subcategories
Topics
General painting topics
- 20th-century Western painting
- Abstract art
- Accidentalism
- Animal-made art
- Architectural painting
- Binder
- Boston Expressionism
- Boston School
- Cabinet painting
- Coloring book
- Combine painting
- Conservation and restoration of paintings
- Conservation and restoration of panel paintings
- Digital painting
- En plein air
- Figura serpentinata
- Figure painting
- Flatness
- French standard sizes for oil paintings
- Genre art
- Genre painting
- Ghost sign
- Grand manner
- Hierarchy of genres
- Historic paint analysis
- House painter and decorator
- Incised painting
- Inscape
- ISCC–NBS system
- Jerwood Painting Prize
- Letras y figuras
- Live painting
- Local color
- Mixed media
- Mural
- Night in paintings (Eastern art)
- Night in paintings (Western art)
- Nocturne
- Nude
- Oil painting
- Oil painting reproduction
- Orange peel
- Overdoor
- Paint and sip industry
- Paint Dancing
- Paint robot
- Painterliness
- History of painting
- Panoramic painting
- Peintres de la Réalité
- Pendant painting
- Pentimento
- Picture frame
- Pinxit
- Pliage
- Portrait painting
- Prime version
- Problem picture
- Raking light
- Range-finder painting
- Scottish genre art
- Self-portrait
- Sign painting
- Signwriter
- Staffage
- Style
- Tenebrism
- Theory of painting
- Tondo
- Volume solid
- Wash
- Watercolor painting
- Western painting
Painting techniques
- Acrylic painting techniques
- Action painting
- Airbrush
- Al-Qatt Al-Asiri
- Atelier
- Bark painting
- Brain painting
- Brunaille
- Buon fresco
- Cangiante
- Carnation
- Ceramic glaze
- China painting
- Cobweb art
- Cobweb painting
- Craquelure
- Distemper
- Double-sided painting
- Drip painting
- Drybrush
- Electrostatic coating
- Encaustic painting
- Fat over lean
- Figure painting
- Fingerpaint
- Fore-edge painting
- Freehand brush work
- Fresco
- Fresco-secco
- Gambier Parry process
- Generative art
- Giornata
- Glaze
- Glue-size
- Gongbi
- Graffiti
- Graining
- Grisaille
- Haboku
- Illusionism
- Illusionistic ceiling painting
- Impasto
- Imprimatura
- Industrial painting
- Ink wash painting
- Intonaco
- Keim's process
- Lacquer painting
- Leaf painting
- Licked finish
- Lining of paintings
- Maki-e
- Marouflage
- Masking
- Matte painting
- Microbial art
- Mineral painting
- Mischtechnik
- Mold painting
- Mouth and foot painting
- Nocturne
- Notan
- Oil sketch
- Ombré
- Overpainting
- Overspray
- Paint by number
- Painting
- Panel painting
- Papier collé
- Pastiglia
- Pen painting
- Pinstriping
- Pointillism
- Polychrome
- Powder painting
- Prestezza
- Protoquadro
- Quadratura
- Quadro riportato
- Repoussoir
- Reverse glass painting
- Rosemåling
- Rotational bell painting
- Sandpainting
- Sfumato
- Shaped canvas
- Shigajiku
- Silk painting
- Speed line
- Speed painting
- Spray painting
- Tempera
- Texture
- Theorem stencil
- Trompe-l'œil
- Underdrawing
- Underpainting
- Unione
- Velvet painting
- Verdaccio
- Verdaille
- Vitreography
- Wash
- Watercolor painting
- Wet-on-wet
- Working in layers
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals