| Piano Quartet | |
|---|---|
| by Robert Schumann | |
 Title page of the first edition (1845), autographed by the composer | |
| Key | E♭ major |
| Opus | 47 |
| Composed | 1842 |
| Dedication | Mathieu Wielhorsky |
| Published | 1845 |
| Duration | c. 27 minutes |
| Movements | four |
| Scoring |
|
| Premiere | |
| Date | 8 December 1844 |
| Location | Leipzig |
| Performers |
|
The Piano Quartet in E♭ major, Op. 47, was composed by Robert Schumann in 1842 for piano, violin, viola and cello. Written during a productive period in which he produced several large-scale chamber music works, it has been described as the "creative double" of his Piano Quintet, finished weeks earlier. Though dedicated to the Russian cellist Mathieu Wielhorsky, it was written with Schumann's wife Clara in mind, who would be the pianist at the premiere on 8 December 1844 in Leipzig.
The work consists of four movements. The first movement is in sonata form and begins with a hymn-like introduction that leads to a more figural section. The second movement, a scherzo, features a quick staccato figure that moves around a G minor scale, with two contrasting trio sections. The third movement (Andante cantabile) has been called the highlight of the work, with one of the most beautiful cello themes of the Romantic period. The finale includes contrapunctal writing and makes many references to the preceding movements.
At the premiere, the Piano Quartet was well received. Today, it is recognized as the culmination of virtually all previous exploration of the piano quartet as a genre up to that time, forming the foundations for later composers to build on.
Background

The Piano Quartet in E♭ major is preceded by a Piano Quartet in C minor, WoO E1, that Schumann composed in 1829, near the end of his first year of study in Leipzig. Possibly inspired by Mozart's Piano Quartet in G minor[1] and clearly influenced by Schubert's Piano Trio No. 2,[2] it was Schumann's most notable accomplishment to that date,[3] and a "remarkably polished work for someone who was as yet without formal training in composition".[2] Nonetheless, the Piano Quartet in C minor remained unpublished until 1979.[4]
Schumann would not compose any major chamber music until 1842, in which he produced several large-scale works for varying instrumentation. The first were his three String Quartets, Op. 41, which were completed by July, followed by the Piano Quintet, Op. 44 that was written from September to October. The Piano Quartet was sketched from 24 to 30 October, and written out in a fair copy between 7 and 26 November; the inscription "Leipzig, 26 November 1842" appears at the end of the manuscript.[5] After the quartet, he wrote the Fantasiestücke for piano trio, Op. 88 in December, and the Andante and Variations for two pianos, French horn and two cellos, Op. 46 between January and February 1843.[6]
.jpg.webp)
Like the Piano Quintet, the Piano Quartet was written with his wife Clara in mind, though it was dedicated to Count Mathieu Wielhorsky, a Russian cellist and impresario.[7] A private performance of the work took place on 5 April 1843 at the Schumanns' home in Leipzig, with Clara at the piano, who described the quartet in her diary as a "beautiful work, so youthful and fresh, as if it were his first".[7] After making several revisions, on 24 August 1843 Schumann offered the work to the publisher Friedrich Whistling and received a fee of 100 thaler. After several delays due to the Schumanns' tour of Russia in 1844, where the work was performed at a private recital, it was published in May 1845.[8] The manuscript is today held at the Berlin State Library, while the initial sketches have been lost.[9]
The premiere took place on 8 December 1844 at the Gewandhaus in Leipzig with Clara Schumann (piano), Ferdinand David (violin), Niels Gade (viola), and Franz Karl Wittmann (cello),[10] as part of a farewell concert for the Schumanns, who were leaving Leipzig for Dresden.[11][8]
Relationship to the Piano Quintet
According to Schumann scholar John Daverio, the Piano Quartet can be interpreted as the "creative double" to the Piano Quintet, also in E♭ major, and bringing together the piano with a complement of strings.[12] Though both displaying the "extroverted, exuberant side of the composer's creative genius", he did not consider them twins, as the absence of one violin in the Piano Quartet makes for a more intimate and individual sound, with a neo-classic tone not felt in the Quintet.[13]
Compared to the far more common piano trio, the addition of a viola in the piano quartet adds density to the texture of the ensemble's middle range, that may result in sharp contrasts between the piano and the strings.[14] This effect is even more pronounced when another violin is added: in the Piano Quintet, the piano and strings confront each other as distinct musical forces, the strings often presenting a concerto-like accompaniment to the piano. In contrast, the Piano Quartet emphasizes a chamber texture, in which the instruments permeate to form an unified ensemble. This is particularly evident in the slow movement.[5]
Form
| External audio | |
|---|---|
| Performed by Menahem Pressler and the Emerson String Quartet | |
The piece is in four movements, with the usual order of the internal movements reversed:
- Sostenuto assai – Allegro ma non troppo
- Scherzo: Molto vivace – Trio I – Trio II
- Andante cantabile
- Finale: Vivace
A performance takes around 27 minutes.
Sostenuto assai – Allegro ma non troppo
The brief introduction of the first movement (Sostenuto assai) resembles a hymn with four- and five-part harmony, all strings using double stoppings to achieve a chordal texture.[15] It leads to a more figural and abstract Allegro ma non troppo (mm. 13f.) that bears resemblance in its tone to Beethoven's "Harp" Quartet and Archduke Trio.[13] Three striking chords lead to a held dominant seventh, the right hand of the piano then presenting the first subject:[16]
The second subject group begins abruptly in the dominant G minor, following a full close in the tonic, producing a "startling, though, temporary disruption of the harmonic rhythm":[16]
A transient return to the Sostenuto (mm. 125f.) leads to another Allegro section (mm. 136f.) in which the themes are developed. The coda, marked Più agitato (mm. 320f.) concludes the movement.[17]
Scherzo: Molto vivace – Trio I – Trio II
Although the scherzo is marked Molto vivace, it is not exuberant in a manner similar to Mendelssohn; a "slightly sinister undercurrent" is said to emerge throughout the movement.[18] According to musicologist Basil Smallman, it hints at the "aura of fantasy" found in various parts of Schumann's Kreisleriana, and in his setting of Heinrich Heine's "Es leuchtet meine Liebe".[16]
The scherzo features a quick staccato figure moving up and down a G minor scale:[19]
There are two contrasting trios in related keys.[18] The first trio arises out of the same impulse as the scherzo's subject:[20]
The second trio has been described as "thoroughly Schumannesque", featuring a series of sustained, syncopated chords:[20]
Andante cantabile
The Andante cantabile is a lyric song-like movement full of romanticism.[19] According to musicologist Karl Böhmer, it is the highlight of the work, featuring one of the most beautiful cello themes of the Romantic period.[21] Music writer James Keller has called it one of Schumann's most "sublime" melodies, "perfect in its balance, soulfulness, and apparent simplicity", remarking that it constitutes "one of the magical Schumann moments in which the entire universe seems to hold its breath".[18] The main theme unfolds in a "rhapsodic" manner through five variations, interjected with a chorale episode in G♭ major, and concluding with a coda.[22]
| Section | Excerpt | Audio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Theme | Cello | Score 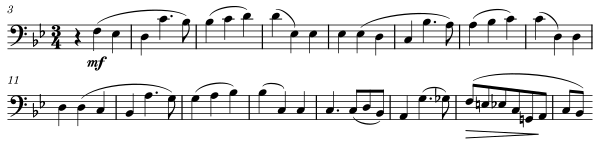 |
|
| Var. I | Quasi-canon: violin & cello | Score  |
||
| Var. II | Duo: piano & viola | Score  |
||
| B | Chorale episode | Score  |
||
| A' | Var. III | Duo: viola & violin | Score  |
|
| Var. IV | Quasi-canon: violin & viola | Score  |
||
| Var. V | Cello | |||
| Coda | Finale prefigured | Score  |
||
In the coda, a three-note figure is introduced, and subjected to a spiraling series of melodic and harmonic transpositions. Daverio counted these final 14 measures among the "most evocative passages in all of Schumann's chamber music", conjuring up a "psychological state in which time and space seem to have been abrogated".[23] In an unusual application of a scordatura, the cello tunes the bottom C down to a B♭ so that it can act as a pedal note.[13] Smallman called this an "ingenious piece of scoring, but not likely to win much favour with the participating performer".[24]
This movement inspired Brahms in his Piano Quartet in C minor, where the slow movement is also opened with a cello solo of similar style.[13]
Finale: Vivace
The finale, constructed partly on fugal and partly on sonata lines, opens with the three-note figure from the coda of the preceding movement:[13][24]
Exposition and development are followed by a recapitulation and elaboration of the earlier development. The movement makes many references to the preceding movements: the beginning of the second group recalls a syncopated motif from the slow movement (mm. 31f.), the development references the slow movement's coda, and the "digressive arabesque" in A♭ major in the recapitulation recalls the scherzo's first trio.[13]
Reception and legacy
The premiere was successful, a critic for the Allgemeine musikalische Zeitung calling the Piano Quartet "a piece full of spirit and vitality which, especially in the two inside movements, was most lovely and appealing, uniting a wealth of beautiful musical ideas with soaring flights of imagination", adding that "it will surely be received with great applause everywhere, as it was here".[8]
Smallman noted that the Piano Quartet was never accorded the same recognition as the Piano Quintet, largely because its principal themes are less immediately attractive. However, he called it "in many ways a more powerful work and, with its wealth of contrapuntal writing, more cogently constructed". He recognized both works as the culmination of virtually all previous exploration of their respective genres, forming the foundations for later composers to build on.[25] For at least a century after Schumann's works for piano and strings, works for similar ensembles increased in significance in chamber music. Schumann established a romantic model that many composers were tempted to emulate, particularly those composers influenced by Austro-German ideals such as Brahms and Dvořák; this continuation can be traced till at least the time of Schoenberg and Hindemith.[26]
See also
References
- ↑ Chernaik 2018, Chapter 1.
- 1 2 Daverio 1997, p. 51.
- ↑ Jensen 2011, p. 24.
- ↑ Krebs 1999, p. 263.
- 1 2 Leisinger 2006, p. IV.
- ↑ Jensen 2011, p. 199.
- 1 2 Keller 2011, pp. 423.
- 1 2 3 Leisinger 2006, p. V.
- ↑ "Robert Schumann: Klavierquartett Es-Dur op. 47". Brahms-Institut (in German). Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ↑ Waldersee, Paul von (1882). Sammlung musikalischer Vorträge. Band 4 (in German). Leipzig: Breitkopf & Härtel. p. 36.
- ↑ Geck 2013, p. 178.
- ↑ Daverio 1997, p. 259.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Daverio 1997, p. 260.
- ↑ Keller 2011, pp. 423–424.
- ↑ Smallman 1994, p. 47.
- 1 2 3 Smallman 1994, p. 48.
- ↑ Murray 2015, p. 361.
- 1 2 3 Keller 2011, p. 424.
- 1 2 Chernaik 2018, Chapter 11.
- 1 2 Donat 2000, p. 2.
- ↑ Böhmer, Karl. "Robert Schumann. Klavierquartett Es-Dur, op. 47". Villa Musica (in German). Retrieved 21 March 2021.
- 1 2 Daverio 1997, p. 261.
- ↑ Daverio 2002, p. 36.
- 1 2 Smallman 1994, p. 50.
- ↑ Smallman 1994, p. 51.
- ↑ Smallman 1994, p. 53.
Sources
- Chernaik, Judith (2018). Schumann: The Faces and the Masks. Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-451-49446-7.
- Daverio, John (1997). Robert Schumann: Herald of a "New Poetic Age". Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-585-33154-6.
- Daverio, John (2002). Crossing Paths: Schubert, Schumann, and Brahms. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-535096-8.
- Donat, Misha (2000). Booklet to Hyperion recording CDA67175 (PDF). Hyperion Records.
- Geck, Martin (2013). Robert Schumann: The Life and Work of a Romantic Composer. Translated by Spencer, Stewart. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-28469-9.
- Keller, James (2011). Chamber Music: A Listener's Guide. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-538253-2.
- Krebs, Harald (1999). Fantasy Pieces: Metrical Dissonance in the Music of Robert Schumann. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-511623-6.
- Leisinger, Ulrich (2006). Schumann. Piano Quartet E flat major op. 47 (Urtext). Munich: G. Henle Verlag. ISMN 979-0-2018-0737-9.
- Murray, Lucy Miller (2015). Chamber Music: An Extensive Guide for Listeners. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-4342-2.
- Jensen, Eric Frederick (2011). Schumann (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-983068-8.
- Smallman, Basil (1994). The Piano Quartet and Quintet: Style, Structure, and Scoring. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-816640-5.
Further reading
- Brown, Julie Hedges (2013). "Study, Copy, and Conquer: Schumann's 1842 Chamber Music and the Recasting of Classical Sonata Form". Journal of Musicology. 30 (3): 369–423. doi:10.1525/jm.2013.30.3.369. ISSN 0277-9269.
External links
- Piano Quartet: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project





