 Steve Jobs showing the first MacBook Air at Apple’s 2008 keynote address | |
| Developer | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Product family | |
| Type | Subnotebook |
| Release date |
|
| Discontinued | November 10, 2020 |
| Operating system | macOS |
| Successor | MacBook Air (Apple silicon) |
| Related | MacBook, MacBook Pro |
| Website | www.apple.com/macbook-air |
The Intel-based MacBook Air is a discontinued line of notebook computers developed and manufactured by Apple Inc. from 2008 to 2020. The Air was originally positioned above the previous MacBook line as a premium ultraportable.[2] Since then, the original MacBook's discontinuation in 2011, and lowered prices on subsequent iterations, made the Air Apple's entry-level notebook.[3]
The MacBook Air was introduced in January 2008 with a 13.3-inch screen, and was promoted as the world's thinnest notebook, opening a laptop category known as the ultrabook family. Apple released a redesigned MacBook Air in October 2010, with a redesigned tapered chassis, standard solid-state storage, and added a smaller 11.6-inch version. Later revisions added Intel Core i5 or i7 processors and Thunderbolt.[4] The Retina MacBook Air was released in October 2018, with reduced dimensions, a Retina display, and combination USB-C/Thunderbolt 3 ports for data and power.
The Intel-based MacBook Air was discontinued in November 2020 following the release of the first MacBook Air with Apple silicon based on the Apple M1 processor.
Original (2008–2009)
Steve Jobs introduced the MacBook Air during Apple's keynote address at the 2008 Macworld conference on January 15, 2008.[5] The original MacBook Air was a 13.3" model, initially promoted as the world's thinnest notebook at 1.9 cm (a previous record holder, 2005's Toshiba Portege R200, was 1.98 cm high).[6][7] It featured a custom[8] Intel Merom CPU and Intel GMA GPU which were 40% as big as the standard chip package.[9] It also featured an anti-glare LED backlit display, a full-size keyboard, and a large trackpad that responded to multi-touch gestures such as pinching, swiping, and rotating.[10] Since the release of Snow Leopard, the trackpad has also supported handwriting recognition of Chinese characters.[11]
The MacBook Air was the first subcompact notebook offered by Apple after the 12" PowerBook G4 discontinued in 2006. It was also Apple's first computer with an optional solid-state drive.[12] It was Apple's first notebook since the PowerBook 2400c without a built-in removable media drive.[13] To read optical disks, users could either purchase an external USB drive such as Apple's SuperDrive or use the bundled Remote Disc software to access the drive of another computer wirelessly[14] that has the program installed.[15][16] Either option can also be used to reinstall the system software from the included installation DVD. Remote Disc supports booting over a network, so the Air can boot from its installation DVD in another computer's drive if Remote Install Mac OS X is running on that computer. The software does not allow playing video DVDs or audio CDs, or installing Windows:[14] for these capabilities, an external USB drive is required.[14] More recent versions of OS X replaced the installation DVD with a USB flash drive containing the software, eliminating the need for remote installation. The MacBook Air also does without a FireWire port, Ethernet port, line-in, and a Kensington Security Slot.[17]
On October 14, 2008, a new model was announced with a low-voltage Penryn processor and Nvidia GeForce graphics.[18] Storage capacity was increased to a 128 GB SSD or a 120 GB HDD,[19] and the micro-DVI video port was replaced by the Mini DisplayPort.[20] A mid-2009 version featured slightly higher battery capacity and a faster Penryn CPU.[21]
Design

Apple incorporated several features in the design of the MacBook Air, such as the reduction of lead to make it more environmentally friendly. The MacBook Air contains no BFRs and PVC wiring, meets Energy Star 5.0 requirements, has a recyclable enclosure, and is rated EPEAT Gold. Its display is made with arsenic-free glass and contains no mercury.[6][22]
Reception
On its introduction, the MacBook Air received mixed reviews which praised its portability, but criticized the compromises it made in terms of features.[23][24][25] The full-sized keyboard, lightness, thinness, and Multi-Touch trackpad were appreciated in reviews, while the limited configuration options and ports, slow speed, non-user-replaceable battery, small hard drive, and price were criticized.[23][24] The flip-down hatch on the side of the original MacBook Air was a tight fit for some headphone plugs and USB devices, requiring users to purchase an extension cable. Apple removed the flip-down hatch on the late 2010 model in favor of open ports like those on the MacBook Pro.[26][27]
Some users have complained of CPU lockup caused by overheating. Apple released a software update in early March 2008 to fix the problem with mixed results: the deactivation of one CPU core was corrected; however, some users reported that the runaway kernel problem continued.[28] The problem is aggravated by system-intensive tasks such as video playback or video chatting.[29]
ArsTechnica found "moderate" performance improvements of the 64-GB[lower-alpha 1] solid-state drive of the original Air over the standard 80 GB hard drive in tests.
"World's thinnest notebook"
At the launch of the MacBook Air in January 2008, Steve Jobs said it was the "world's thinnest notebook". This was literally true, but more important was the fact that the MacBook Air was much thinner than mainstream laptops at the time. Its total component integration and use of an entirely new class of Intel processors with a lower TDP and higher integration than previously available made it the first of a new wave of thin performance laptops. Over the years, Apple has removed the claim of being "the world's thinnest notebook" from their marketing materials as other, similarly thin laptops have come to market.
Technical specifications
All of these models are obsolete.[lower-alpha 2][30]
| Original (Early 2008)[31] | Late 2008[20] | Mid 2009[32] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component / Processor | Merom Intel Core 2 Duo | Penryn Intel Core 2 Duo | ||||
| Timeline | Announced | January 15, 2008 | October 14, 2008 | June 8, 2009 | ||
| Released | January 30, 2008[31] | [data missing] | [data missing] | |||
| Discontinued | October 14, 2008[31] | June 8, 2009[20] | October 20, 2010[32] | |||
| Unsupported | October 2014[30] | October 2018[30] | ||||
| Model | Model identifier | MacBookAir1,1 | MacBookAir2,1 | |||
| Model number (on underside) | A1237 | A1304 | ||||
| Part number (order number) | MB003 | MB543 | MB940 | MC233 | MC234 | |
| Display (glossy) | 13.3", native 1280 × 800 pixels (16:10, 113 ppi) TN. 6-bit color panel, Lower resolutions supported | |||||
| Performance | Processor | 1.6 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo Merom (P7500) with 4 MB on-chip L2 cache Optional 1.8 GHz (P7700) Intel Core 2 Duo |
1.6 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo Penryn (SL9300) with 6 MB on-chip L2 cache | 1.86 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo Penryn (SL9400) with 6 MB on-chip L2 cache | 1.86 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo Penryn (SL9400) with 6 MB on-chip L2 cache | 2.13 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo Penryn (SL9600) with 6 MB on-chip L2 cache |
| Front-side bus / DMI | 800 MHz | 1066 MHz | ||||
| Memory | 2 GB[lower-alpha 3] of 667 MHz DDR2 SDRAM | 2 GB of 1066 MHz DDR3 SDRAM | ||||
| Graphics | Intel GMA X3100 using 144 MB of DDR2 SDRAM (shared with system memory) with Micro-DVI output | Nvidia GeForce 9400M using 256 MB of DDR3 SDRAM (shared with system memory) with Mini DisplayPort output | ||||
| Storage | 80 GB 4200-rpm 1.8-inch PATA HDD or 64 GB SSD | 120 GB 4200-rpm 1.8-inch SATA HDD | 128 GB SSD | 120 GB 4200-rpm 1.8-inch SATA HDD | 128 GB SSD | |
| Connectivity | Video camera | iSight (640 × 480) | ||||
| Wireless connectivity | Internal Wi-Fi 4 (802.11a/b/g and draft-n) Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR Built-in infrared (IR) receiver for Apple Remote Optional Apple USB Ethernet Adapter (Year 2008) | |||||
| Peripheral connections | 1× USB 2.0 MagSafe Micro-DVI video port DVI-D/VGA adapter included |
1× USB 2.0 MagSafe 1× Mini DisplayPort video port | ||||
| Audio | 3.5 mm headphone jack Mono speaker | |||||
| Operating system | Minimum | Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard | ||||
| Latest released | Mac OS X 10.7 Lion | OS X 10.11 El Capitan | ||||
| Power | Battery (non-removable lithium-ion polymer) | 37-watt-hour | 40-watt-hour | |||
| Battery cycle count[33] | 300 | 500 | ||||
| Appearance | Unit weight | 3.0 lb (1.36 kg) | ||||
| Dimensions | 12.8 in (33 cm) wide × 8.94 in (23 cm) deep × 0.16 in (0.4 cm) to 0.76 in (1.9 cm) high (13") | |||||
Redesign (2010–2017)

On October 20, 2010, Apple released a redesigned 13.3-inch model with a tapered enclosure, higher screen resolution, improved battery, a second USB port, stereo speakers, and standard solid state storage. An 11.6-inch model was introduced, offering reduced cost, weight, battery life, and performance relative to the 13.3-inch model, but better performance than typical netbooks of the time. Both 11-inch and 13-inch models had an analog audio output/headphone minijack supporting Apple earbuds with a microphone. The 13-inch model received a SDXC-capable SD Card slot.[34][35][36][37][10]
On July 20, 2011, Apple released updated models, which also became Apple's entry-level notebooks due to lowered prices and the discontinuation of the white MacBook around the same time.[3] The Mid 2011 models were upgraded with Sandy Bridge dual-core Intel Core i5 and i7 processors, Intel HD Graphics 3000, backlit keyboards, Thunderbolt, and Bluetooth was upgraded to v4.0.[38][39] Maximum storage options were increased up to 256 GB. These models use a less expensive "Eagle Ridge" Thunderbolt controller that provides two Thunderbolt channels (2 × 10 Gbit/s bidirectional), compared to the MacBook Pro which uses a "Light Ridge" controller that provides four Thunderbolt channels (4 × 10 Gbit/s bidirectional). This revision also replaced the Expose (F3) key with a Mission Control key, and the Dashboard (F4) key with a Launchpad key.
On June 11, 2012, Apple updated the line with Intel Ivy Bridge dual-core Core i5 and i7 processors, HD Graphics 4000, faster memory and flash storage speeds, USB 3.0, an upgraded 720p FaceTime camera, and a thinner MagSafe 2 charging port.[40] It was the first MacBook Air model to support 9 macOS versions, Mac OS X Lion 10.7 through macOS Catalina 10.15.
On June 10, 2013, Apple updated the line with Haswell processors, Intel HD Graphics 5000, and 802.11ac Wi-Fi. The standard memory was upgraded to 4 GB, with a maximum configuration of 8 GB. Storage started at 128 GB SSD, with options for 256 GB and 512 GB. The Haswell considerably improved battery life from the previous models, and the models are capable of 9 hours on the 11-inch model and 12 hours on the 13-inch model; a team of reviewers exceeded expected battery life ratings during their test.[41] The Mid 2013 model is second MacBook Air that supported 9 macOS versions, OS X Mountain Lion 10.8 through macOS Big Sur 11.
In March 2015, the models were refreshed with Broadwell processors, Intel HD Graphics 6000, Thunderbolt 2, and faster storage and memory.[42] In 2017, the 13-inch model received a processor speed increase from 1.6 GHz to 1.8 GHz and the 11-inch model was discontinued. The 2017 model remained available for sale after Apple launched the Retina MacBook Air in 2018. It was discontinued in July 2019. Before its discontinuation it was Apple's last notebook with USB Type-A ports, MagSafe (until it was reintroduced in 2021), a non-Retina display, a backlit rear Apple logo, and the startup chime (until the introduction of macOS Big Sur in 2020).
Design and upgradability
Although MacBook Air components are officially non-user-replaceable, third parties do sell upgrade kits for the SSDs. The flash memory and battery are enclosed in the casing, and the RAM is soldered onto the motherboard. The flash memory is difficult to access and has a 128 MB cache[43] and a mSATA connection (updated to a proprietary PCIe interface) to the motherboard.[44]

Issues
Due to a more mature manufacturing process, the CPUs in the 2010–2017 MacBook Air performs better under load, while the original models ran hotter—the processor needed to be throttled to avoid overheating and this further degraded performance.[45]
On October 17, 2013, Apple announced a replacement program for the 64 GB and 128 GB MacBook Air flash storage drives installed in Air systems purchased between June 2012 and June 2013.[46]
Reception
Comparison with iPad and netbooks
Although the 11-inch Air is only 0.6 pounds lighter than the 13-inch Air, the biggest difference is the footprint which gives each model a distinct category; the 13-inch Air is much closer in size to most other conventional laptops, while the 11-inch Air is almost small enough to fit in a space that can hold an iPad.[47][48]
The 11-inch MacBook Air carried the desirable essential attributes of a netbook, but without the drawbacks of a slower processor and less capable operating system,[49] albeit at a higher price.[50][51][52][53][54] At the low end, Apple introduced the iPad—a different form factor than the netbook, but with improved computing capabilities and lower production cost. Both of these led to a decline in netbook sales, and most PC manufacturers have consequently discontinued their netbook lines in response.[55] Capitalizing on the success of the MacBook Air,[56] Intel promoted ultrabooks as a new high-mobility standard, which has been hailed by some analysts as succeeding where netbooks failed.[57][58][59]
Intel's ultrabook competition
Intel developed a set of specifications for the ultrabook, a higher-end type of subnotebook produced by various PC manufacturers and usually running Windows. Competing directly with the Air, ultrabooks are intended to reduce size and weight, and extend battery life without compromising performance.[60][61][62]
Through July 1, 2013, the MacBook Air took in 56 percent of all ultrabook sales in the United States, despite being one of the higher-priced competitors.[63] Apple had previously dominated the premium PC market, in 2009 having a 91 percent market share for PCs priced at more than $1,000, according to NPD, and ultrabooks were an attempt by other PC manufacturers to move in on Apple's turf.[64] While Apple's MacBook lines were not immune to this consumer trend towards mobile devices,[65] they still managed to ship 2.8 million MacBooks in Q2 2012 (the majority of which were the MacBook Air) compared to 500,000 total ultrabooks,[66][67] despite there being dozens of ultrabooks from various manufacturers on the market while Apple only offered 11-inch and 13-inch models of the Macbook Air.[68] Forrester Research analyst Frank Gillett attributes Apple's increased success in the enterprise market to the 2010 MacBook Air and the iPad.[69]
While several ultrabooks were able to claim individual distinctions such as being the lightest or thinnest, the MacBook Air was regarded by reviewers as the best all-around ultrabook in regard to "OS X experience, full keyboard, superior trackpad, Thunderbolt connector and the higher-quality, all-aluminum unibody construction".[63]
Microsoft's Surface Pro 2 has a similar size and price to the 11-inch MacBook Air;[70][71] Apple CEO Tim Cook has criticized the Surface Pro and other ultrabook hybrids running the touch-based Windows 8, that attempt to combine PC and tablet functionality in one device, saying that such devices were confusing like trying to "combine a fridge and a toaster".[72][73]
When released in October 2010, the 13-inch model's screen resolution was higher than the average 1366×768 screens of similar sized laptops. However, by 2013, with many premium ultrabooks having high resolution screens (1080p or greater) as standard or upgrades, the MacBook Air was increasingly criticized for sticking with a low-resolution screen. Many in the tech community had expected Apple to release a MacBook Air with Retina Display by the summer of 2013, similar to the MacBook Pro Retina which came out in 2012.[74] The October 2013 refresh of the 13-inch MacBook Pro Retina, with a slimmer chassis and a lower price point, was mentioned as a potential MacBook Air alternative as the battery life is not much shorter while not being considerably bulkier.[2][75] Apple released an entry-level version of the 13-inch MacBook Pro on October 27, 2016, which was specifically targeted towards MacBook Air users.[76] A Retina MacBook Air was released in late 2018.
The 11.6-inch MacBook Air, introduced in October 2010, is only slightly larger and heavier (when closed) than the iPad 2. The 11.6-inch Air has been regarded as thin and light compared to other ultraportables, such as the Sony VAIO Z and the 11-inch Samsung Series 9.[77]
As of 2013, several ultrabooks such as the Sony VAIO Pro have managed smaller dimensions than the MacBook Air by using carbon fiber construction.[78][79][80]
Technical specifications
| Obsolete[81] | Vintage | Discontinued |
| Model | Late 2010[82][83] | Mid 2011[84][85] | Mid 2011 (Education only) | Mid 2012[86][87] | Mid 2012 (Education only)[88] | Mid 2013[89][90] | Early 2014[91][92] | Early 2015[93][94] | 2017[95] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component / Processor | Penryn Intel Core | Sandy Bridge Intel Core | Ivy Bridge Intel Core | Haswell Intel Core | Broadwell Intel Core | ||||||||||||
| Released Date | 11" | October 20, 2010 | July 20, 2011 | — | June 11, 2012 | — | June 10, 2013 | April 29, 2014 | March 9, 2015 | — | |||||||
| 13" | February 12, 2012 | September 12, 2012 | June 5, 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| Discontinued Date | 11" | July 20, 2011 | June 11, 2012 | — | June 10, 2013 | — | April 29, 2014 | March 9, 2015 | October 27, 2016 | — | |||||||
| 13" | June 11, 2012 | February 13, 2013 | June 5, 2017 | July 9, 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Unsupported Date | 11" | November 12, 2020[30] | — | November 30, 2022[30] | — | September 26, 2023[30] | Security updates only[30] | — | |||||||||
| 13" | November 12, 2020[30] | November 30, 2022[30] | Security updates only[30] | ||||||||||||||
| Model identifier | 11" | MacBookAir3,1 | MacBookAir4,1 | — | MacBookAir5,1 | — | MacBookAir6,1 | MacBookAir7,1 | — | ||||||||
| 13" | MacBookAir3,2 | MacBookAir4,2 | MacBookAir5,2 | MacBookAir6,2 | MacBookAir7,2 | ||||||||||||
| Model number (on underside) | 11" | A1370 | — | A1465 | — | A1465 | — | ||||||||||
| 13" | A1369 | A1466 | |||||||||||||||
| Part/order number ($USD Price) | 11" | MC505 ($999) | MC506 ($1199) | MC968 ($999) | MC969 ($1199) | — | MD223 ($999) | MD224 ($1099) | — | MD711/A ($999) | MD712/A ($1199) | MD711/B ($899) | MD712/B ($1099) | MJVM2 ($899) | MJVP2 ($1099) | — | |
| 13" | MC503 ($1299) | MC504 ($1599) | MC965 ($1299) | MC966 ($1599) | MD508 (pack of five for $4995)[96] | MD231 ($1199) | MD232 ($1499) | MD628 (pack of five for $4995) | MD760/A ($1099) | MD761/A ($1299) | MD760/B ($999) | MD761/B ($1199) | MJVE2 Starting April 19, 2016: MMGF2 ($999) |
MJVG2 Starting April 19, 2016: MMGG2 ($1199) |
MQD32 ($999) | MQD42 ($1199) | |
| Processor | 11" | 1.4 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo (SU9400) Penryn with 3 MB on-chip L2 cache | 1.6 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo (SU9600) Penryn with 3 MB on-chip L2 cache | 1.6 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (2467M) Sandy Bridge with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 1.8 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (2677M) Sandy Bridge with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$150) |
— | 1.7 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (3317U) Ivy Bridge with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 2.0 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (3667U) Ivy Bridge with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$150 for MD224, +$100 for MD232) |
— | 1.3 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (4250U) Haswell with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 1.7 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (4650U) Haswell with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$150) |
1.4 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (4260U) Haswell with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 1.7 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (4650U) Haswell with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$150) |
1.6 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (5250U) Broadwell with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 2.2 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (5650U) Broadwell with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$150) |
— | ||||||
| 13" | 1.86 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo (SL9400) Penryn with 6 MB on-chip L2 cache | 2.13 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo (SL9600) Penryn with 6 MB on-chip L2 cache | 1.7 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (2557M) Sandy Bridge with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 1.8 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (2677M) Sandy Bridge with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$100) |
1.6 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (2467M) Sandy Bridge with 3 MB shared L3 cache | 1.8 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (3427U) Ivy Bridge with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 2.0 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (3667U) Ivy Bridge with 4 MB shared L3 cache (+$150 for MD224, +$100 for MD232) |
1.7 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (3317U) Ivy Bridge with 3 MB shared L3 cache | 1.8 GHz 2-core Intel Core i5 (5350U) Broadwell with 3 MB shared L3 cache Optional 2.2 GHz 2-core Intel Core i7 (5650U) Broadwell with 4 MB shared L3 cache | ||||||||||
| Front-side bus / DMI | 11" | 800 MHz | — | Intel Direct Media Interface, 5.0 GT/s | — | Intel Direct Media Interface, 5.0 GT/s | — | ||||||||||
| 13" | 1066 MHz | Intel Direct Media Interface, 5.0 GT/s | |||||||||||||||
| Graphics (shared with system memory) |
11" | Nvidia GeForce 320M using 256 MB DDR3 SDRAM with Mini DisplayPort output | Intel HD Graphics 3000 processor using 256 MB DDR3 SDRAM | — | Intel HD Graphics 4000 processor with up to 512 MB DDR3L SDRAM shared from main memory | — | Intel HD Graphics 5000 processor with up to 1.5 GB LPDDR3 SDRAM shared from main memory | Intel HD Graphics 6000 processor with up to 1.5 GB LPDDR3 SDRAM shared from main memory | — | ||||||||
| 13" | Intel HD Graphics 3000 processor using 384 MB DDR3 SDRAM | Intel HD Graphics 3000 processor using 256 MB DDR3 SDRAM | Intel HD Graphics 4000 processor with up to 512 MB DDR3L SDRAM shared from main memory | Intel HD Graphics 6000 processor with up to 1.5 GB LPDDR3 SDRAM shared from main memory | |||||||||||||
| Memory | 2 GB (IEC defined GiB) 1066 MHz DDR3 SDRAM Optional 4 GB (+$100) |
2 GB (11") 1333 MHz DDR3 SDRAM Optional 4 GB (+$100) 4 GB (13") 1333 MHz DDR3 SDRAM |
4 GB 1333 MHz DDR3 SDRAM | 2 GB 1333 MHz DDR3 SDRAM | 4 GB 1600 MHz DDR3L SDRAM Optional 8 GB (+$100) |
4 GB 1600 MHz DDR3L SDRAM | 4 GB 1600 MHz LPDDR3 SDRAM Optional 8 GB (+$100) |
4 GB 1600 MHz LPDDR3 SDRAM Optional 8 GB Starting April 19, 2016: 8 GB standard for the 13" version |
8 GB 1600 MHz LPDDR3 SDRAM | ||||||||
| Solid-state drive (on all models) | 11" | 64 GB | 128 GB | 64 GB | 128 GB Optional 256 GB (+$300) |
— | 64 GB | 128 GB Optional 256 (+$300 or 512 GB (+$800 both for MD224 model only) |
— | 128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$300) |
128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$300) |
128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$300) |
— | |
| 13" | 128 GB | 256 GB | 128 GB | 256 GB | 64 GB | 128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$500) |
64 GB | 128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$300) |
128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$300) |
128 GB | 256 GB Optional 512 GB (+$300) |
128 GB (MQD32) | 256 GB (MQD42) Optional 512 GB | |
| Type | Solid-state drive (SSD) | PCIe-based SSD | |||||||||||||||
| Display (glossy) |
11" | 11.6", native 1366 × 768 pixels (16:9, 135 ppi) TN. 6-bit color panel, Lower resolutions supported | — | 11.6", native 1366 × 768 pixels (16:9, 135 ppi) TN. 6-bit color panel, Lower resolutions supported | — | 11.6", native 1366 × 768 pixels (16:9, 135 ppi) TN. 6-bit color panel, Lower resolutions supported | — | ||||||||||
| 13" | 13.3", native 1440 × 900 pixels (16:10, 128 ppi) TN. 6-bit color panel, Lower resolutions supported | ||||||||||||||||
| Video camera | iSight (480p) | FaceTime HD (720p) | |||||||||||||||
| Audio | 3.5 mm headphone jack Stereo speakers | ||||||||||||||||
| Connectivity | Internal Wi-Fi 4 (802.11 a/b/g/n) (Broadcom BCM43224, dual-band 300 Mbit/s) | Internal Wi-Fi 5 (802.11 a/b/g/n/ac) (Broadcom BCM4360-based, dual-band 867 Mbit/s) | |||||||||||||||
| Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR | Bluetooth 4.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| Optional Apple USB Ethernet 100 Mbit Adapter | Optional Apple USB Ethernet 100 Mbit Adapter Optional Apple Thunderbolt to Gigabit Ethernet Adapter Optional Apple Thunderbolt to FireWire 800 Adapter | ||||||||||||||||
| Peripheral connections | 2× USB 2.0 | 2× USB 3.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 1× Mini DisplayPort video port | 1× Thunderbolt port | 1× Thunderbolt 2 port Up to 3840 × 2160 @ 60 Hz | |||||||||||||||
| MagSafe | MagSafe 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1× SDXC card slot (13" only) | |||||||||||||||||
| Operating system | Minimum | Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard | Mac OS X 10.7 Lion | OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion | OS X 10.9 Mavericks | OS X 10.10 Yosemite | macOS 10.12 Sierra[lower-alpha 4] | ||||||||||
| Latest release | macOS 10.13 High Sierra | macOS 10.15 Catalina | macOS 11 Big Sur | macOS 12 Monterey | |||||||||||||
| Battery | 11" | 35-watt-hour | — | 35-watt-hour | — | 38-watt-hour | — | ||||||||||
| 13" | 50-watt-hour | 54-watt-hour | |||||||||||||||
| Type | Non-removable lithium-ion polymer | ||||||||||||||||
| Cycles[33] | 1000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Unit weight | 11" | 2.38 lb (1.08 kg) | — | 2.38 lb (1.08 kg) | — | 2.38 lb (1.08 kg) | — | ||||||||||
| 13" | 2.96 lb (1.34 kg) | ||||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | 11" | 11.8 in (30 cm) wide × 7.56 in (19.2 cm) deep × 0.11 in (0.3 cm) × 0.68 in (1.7 cm) high | — | 11.8 in (30 cm) wide × 7.56 in (19.2 cm) deep × 0.11 in (0.3 cm) × 0.68 in (1.7 cm) high | — | 11.8 in (30 cm) wide × 7.56 in (19.2 cm) deep × 0.11 in (0.3 cm) × 0.68 in (1.7 cm) high | — | ||||||||||
| 13" | 12.8 in (33 cm) wide × 8.94 in (22.7 cm) deep × 0.11 in (0.3 cm) × 0.68 in (1.7 cm) high | ||||||||||||||||
Retina (2018–2020)
.png.webp)
On October 30, 2018, Apple released the Retina MacBook Air, with Amber Lake processors, a 13.3-inch Retina display with a resolution of 2560×1600 pixels, Touch ID, a Force Touch trackpad, and two combination USB-C 3.1 gen 2/Thunderbolt 3 ports plus one audio jack. The screen displays 48% more color and the bezels are 50% narrower than the previous non-Retina models, and occupies 17% less volume. Thickness is reduced to 15.6mm and weight to 1.25 kg (2.75 pounds). It is available in three finishes, silver, space gray, and gold. Unlike the 2011–2017 models, this model cannot be configured with an Intel Core i7 processor, possibly because Intel never released the i7-8510Y CPU that would have been used.
The base 2018 model comes with 8 GB of 2133 MHz LPDDR3 RAM, 128 GB SSD, Intel Core i5 processor (1.6 GHz base clock, with Turbo up to 3.6 GHz) and Intel UHD Graphics 617.[97]
Apple released updated models in July 2019 with True Tone display technology using the same components as the Mid 2019 MacBook Pro.[98][99] A test found that the 256 GB SSD in the 2019 model has a 35% lower read speed than the 256 GB SSD in the 2018 model, though the write speed is slightly faster.[100]
Updated models were released in March 2020 with Ice Lake processors, updated graphics, support for 6K output to run the Pro Display XDR, and replaced the butterfly keyboard with a Magic Keyboard design similar to that found in the 2019 16-inch MacBook Pro.[101][102]
Design
The Retina MacBook Air follows the design of the 2010–2017 models with a tapered aluminum enclosure, but takes some design elements from the Retina MacBook and MacBook Pro, such as a flush display with black bezels and a glossy opaque Apple logo on the rear, and an edge-to-edge trackpad.[103]
Apple repair expert Louis Rossmann has criticised the Retina MacBook Air's hardware layout, noting that the fan's position makes it sub-optimal for cooling and can lead to overheating-related issues.[104][105]
Technical specifications
| Discontinued |
| 2018[106] | 2019[107] | 2020[108] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component / Processor | Amber Lake Intel Core | Ice Lake Intel Core | ||||
| Timetable | Released | October 30, 2018 | July 9, 2019 | March 18, 2020 | ||
| Discontinued | July 9, 2019 | March 18, 2020 | November 10, 2020 | |||
| Unsupported | Supported | |||||
| Model | Model identifier | MacBookAir8,1[109] | MacBookAir8,2 | MacBookAir9,1 | ||
| Model number | A1932 | A2179 | ||||
| Apple order number (Space Gray) | MRE82 | MRE92 MUQT2 (512 GB 16 MB)[109] |
MVFH2 | MVFJ2 MVH62 (512 GB 16 MB)[109] |
MWTJ2 MVH22 (Core i5) | |
| Apple order number (Silver) | MREA2 | MREC2 MUQU2 (512 GB 16 MB)[109] |
MVFK2 | MVFL2 | MWTK2 MVH42 (Core i5) | |
| Apple order number (Gold) | MREE2 | MREF2 MUQV2 (512 GB 16 MB)[109] |
MVFM2 | MVFN2 MVH82 (512 GB 16 MB)[109] |
MWTL2 MVH52 (Core i5) | |
| Display (glossy) |
13.3", native 2560 × 1600 pixels (16:10, 227 ppi) IPS. Lower resolutions supported | 13.3", native 2560 × 1600 pixels (16:10, 227 ppi) IPS. True Tone display. Lower resolutions supported | ||||
| Performance | Graphics | Intel UHD Graphics 617 with up to 1.5 GB LPDDR3 SDRAM shared from main memory | Intel Iris Plus Graphics (shared with system memory) | |||
| DMI | 4 GT/s On Package DMI interconnect Interface 3.0 (OPI) (Max. Theoretical Bandwidth 4 GB/s) | |||||
| Processor | 1.6 GHz 2‑core Intel Core i5 (i5-8210Y) Amber Lake (8th Gen), Turbo Boost 3.6 GHz, with 4 MB L3‑cache | 1.1 GHz 2-core Intel Core i3 (i3-1000NG4) Ice Lake (10th Gen), Turbo Boost 3.2 GHz, with 4 MB L3-cache Optional 1.1 GHz 4-core Intel Core i5 (i5-1030NG7) Ice Lake (10th Gen), Turbo Boost 3.5 GHz, with 6 MB L3-cache Optional 1.2 GHz (i7-1060NG7) 4-core Intel Core i7 Ice Lake (10th Gen), Turbo Boost 3.8 GHz, with 8 MB L3-cache | ||||
| Memory Standard | 8 GB of 2133 MHz LPDDR3 SDRAM[110] | 8 GB of 3733 MHz LPDDR4X SDRAM | ||||
| Memory optional | 16 GB at the time of purchase | |||||
| Storage (PCIe-based SSD) Upgrades only at the time of purchase | 128 GB Optional 256 GB, 512 GB, or 1.5 TB[111] |
256 GB Optional 512 GB or 1.5 TB |
128 GB Optional 256 GB, 512 GB, or 1.5 TB |
256 GB Optional 512 GB or 1.5 TB |
128 GB (education institutions only),[112] 256, 512 GB Optional 512 GB, 1.0 TB, or 2.0 TB | |
| Security chip | Apple T2 | |||||
| Keyboard | Third-generation butterfly mechanism | Magic Keyboard (scissor-switch) | ||||
| Video camera | FaceTime HD (720p) | |||||
| Wireless Connectivity | Internal Wi-Fi 5 (802.11 a/b/g/n/ac) Bluetooth 4.2 |
Internal Wi-Fi 5 (802.11 a/b/g/n/ac) Bluetooth 5.0 | ||||
| Peripheral connections | 2× Thunderbolt 3 (USB-C 3.1 Gen 2) ports supporting charging and DisplayPort Supports two 4096×2304 displays or one 5120×2880 (MST) display 1× 3.5 mm headphone jack |
2× Thunderbolt 3 (USB-C 3.1 Gen 2) ports supporting charging Supports two 4096×2304 displays or one 6016×3384 (MST) display 1× 3.5 mm headphone jack | ||||
| Battery | Power | 11.4 V 49.9 W·h (4,379 mA·h) (non-removable lithium-ion polymer)[113] | ||||
| Battery cycle count | 1000[33] | |||||
| Greenhouse gas emissions | 176 kg CO2e[114] | 174 kg CO2e[115] | ||||
| Appearance | Unit weight | 2.75 lb (1.25 kg) | 2.8 lb (1.29 kg) | |||
| Dimensions | 11.97 in (30 cm) wide × 8.36 in (21.2 cm) deep × 0.16 in (0.4 cm) to 0.61 in (1.5 cm) high | 11.97 in (30 cm) wide × 8.36 in (21.2 cm) deep × 0.16 in (0.4 cm) to 0.63 in (1.6 cm) high | ||||
| Operating system | Minimum | macOS 10.14 Mojave | macOS 10.15 Catalina | |||
| Latest release | macOS 14 Sonoma | |||||
Supported operating systems
Supported macOS releases
macOS Ventura, the current release of macOS, will work with Wi-Fi and graphics acceleration on unsupported MacBook Air computers with a compatible patch utility.[116] As of 2022, the Mid 2012 and Mid 2013 MacBook Air are the only models officially supported by Apple with 9 versions of the Mac operating system.
| Supported macOS releases | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS release | Original design | Redesign | Retina | ||||||||||
| Early 2008 | Late 2008 | Mid 2009 | Late 2010 | Mid 2011 | Mid 2012 | Mid 2013 | Early 2014 | Early 2015 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| 10.4 Tiger | unofficial | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 10.5 Leopard | 10.5.1 | 10.5.5 | 10.5.7 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 10.6 Snow Leopard | 10.6.4 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| 10.7 Lion | 10.7.4 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||
| 10.8 Mountain Lion | Patch | 10.8.4 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||
| 10.9 Mavericks | Patch | 10.9.2 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 10.10 Yosemite | Patch | 10.10.2 | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 10.11 El Capitan | Patch | — | — | — | — | ||||||||
| 10.12 Sierra | Patch | 10.12.5 | — | — | — | ||||||||
| 10.13 High Sierra | Patch | — | — | — | |||||||||
| 10.14 Mojave | Patch | 10.14.1 | 10.14.5 | — | |||||||||
| 10.15 Catalina | Patch | 10.15.4 | |||||||||||
| 11 Big Sur | Patch | ||||||||||||
| 12 Monterey | Patch | ||||||||||||
| 13 Ventura | Patch | ||||||||||||
| 14 Sonoma | Patch | ||||||||||||
Windows through Boot Camp
Boot Camp Assistant allows Intel Macs to dual-boot Windows.
| Supported Windows versions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS release | Original design | Redesign | Retina | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Early 2008-Mid 2009 | Late 2010 | Mid 2011 | Mid 2012 | Mid 2013-Early 2014 | Early 2015 and later | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows XP[Note 1][117][118] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows Vista 32-bit[Note 2][117][118] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows Vista 64-bit[Note 2][117] |
Not Compatible With MacBook Air | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows 7 32-bit[Note 3][117][119] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows 7 64-bit[Note 4][117][120] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows 8 [Note 5][Note 6][117] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows 8.1 [Note 7][121][120] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Windows 10 [Note 8][122][120] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Timeline
| Timeline of portable Macintoshes |
|---|
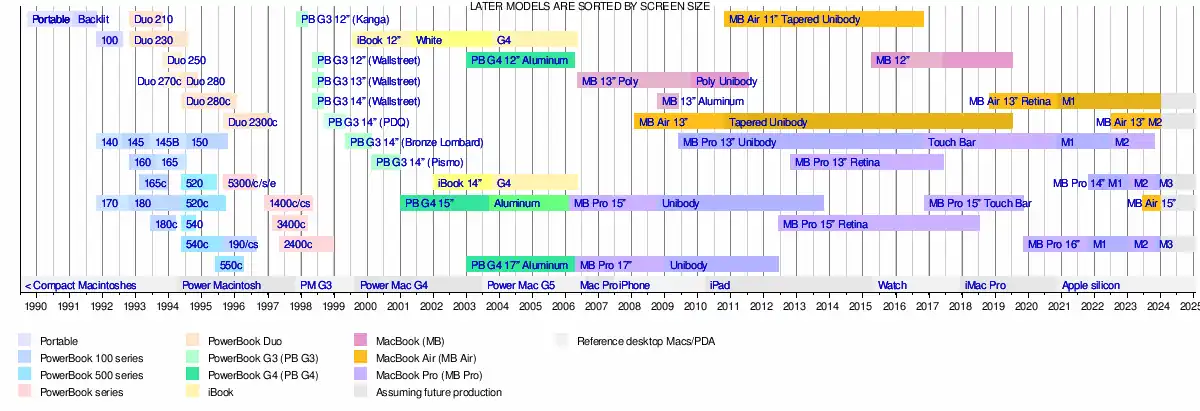 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ In this article, the conventional prefixes for computer storage denote base-10 values whereby kilobyte (KB) = 103 bytes, megabyte (MB) = 106 bytes and gigabyte (GB) = 109 bytes.
- ↑ Apple products that were discontinued 7 years ago and no longer receive hardware support nor spare parts
- ↑ In this article, the conventional prefixes for computer RAM denote base-2 values whereby kilobyte (KB) = 210 bytes, megabyte (MB) = 220 bytes and gigabyte (GB) = 230 bytes.
- ↑ Although these shipped with Sierra, OS X 10.11 El Capitan can also be installed since the 2017 and 2015 use the same firmware
References
- ↑ "Press Info – MacBook Air Now Shipping". Apple. January 30, 2008. Archived from the original on December 21, 2016. Retrieved April 29, 2014.
- 1 2 "13-inch MacBook Pro with Retina display review (2013)". The Verge. Vox Media. October 30, 2013. Archived from the original on December 4, 2020. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- 1 2 Dan Ackerman (January 25, 2008). "Apple MacBook Air review – CNET". CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 28, 2013. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "MacBook Air". Archived from the original on March 19, 2013. Retrieved March 16, 2013.
- ↑ "Macworld 2008 Steve Jobs Apple Keynote Highlights". Inside MacTV. January 15, 2008. Archived from the original on April 3, 2012. Retrieved April 15, 2012.
- 1 2 "Apple Introduces MacBook Air—The World's Thinnest Notebook" (Press release). Apple Inc. January 15, 2008. Archived from the original on October 6, 2011. Retrieved January 16, 2008.
- ↑ "Toshiba discontinued products – Portege R200". Toshiba official specifications. Archived from the original on October 14, 2018. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "The MacBook Air CPU Mystery: More Details Revealed". AnandTech. Archived from the original on March 25, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Cohen, Peter (January 15, 2008). "Apple introduces MacBook Air". Macworld. Archived from the original on January 19, 2008. Retrieved January 21, 2008.
- 1 2 "MacBook Air features". Apple Inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2022. Retrieved November 26, 2010.
- ↑ Ogg, Erica (June 16, 2009). "Snow Leopard features hint at Apple tablet". CNET. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011. Retrieved July 28, 2011.
- ↑ Choney, Suzanne (January 24, 2008). "Lighter laptops move to flash-based drives". NBCNews.com. NBCUniversal. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved January 24, 2008.
- ↑ "Apple Macintosh 2400c/180 specs". EveryMac. Archived from the original on August 18, 2009. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- 1 2 3 Mossberg, Walter S (January 24, 2008). "Apple's MacBook Air Is Beautiful and Thin, But Omits Features". The Wall Street Journal. Dow Jones & Company. Archived from the original on January 21, 2015. Retrieved January 24, 2008.
- ↑ Yager, Tom. "MacBook Air, a detailed preview". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on June 17, 2008. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- ↑ "MacBook Air". Apple. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved January 15, 2008.
- ↑ "MacBook Air's tradeoffs". Macworld. Archived from the original on June 9, 2010. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- ↑ "Intel comments on chips in new MacBook". CNET. Archived from the original on June 7, 2019. Retrieved April 5, 2019.
- ↑ 1 GB = one billion bytes
- 1 2 3 Technical specifications of MB543 and MB940 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ↑ "Apple Updates MacBook Pro Family with New Models & Innovative Built-in Battery for Up to 40% Longer Battery Life" (Press release). Apple. June 8, 2009. Archived from the original on January 4, 2010. Retrieved May 22, 2010.
- ↑ Jobs, Steve. "A Greener Apple". Apple Inc. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
- 1 2 Snell, Jason. "Apple MacBook Air/1.6 GHz". Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- 1 2 Block, Ryan. "MacBook Air review". Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on May 25, 2010. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- ↑ Ackerman, Dan. "MacBook Air review". CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 21, 2010. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- ↑ Block, Ryan (January 24, 2008). "Adding insult to injury: USB 3G modems won't fit in the MacBook Air". Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on October 29, 2010. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- ↑ Cheng, Jacqui (February 3, 2008). "Thin is in: Ars Technica reviews MacBook Air". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 5, 2008. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- ↑ Elmer-DeWitt, Philip (March 13, 2008). "Apple's MacBook (hot) Air problem". Fortune. CNN. Archived from the original on July 8, 2009. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- ↑ Asher, Moses (March 13, 2008). "Apple fans burned by hot Airs". Melbourne: The Age. Archived from the original on July 30, 2010. Retrieved June 7, 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Obtaining service for your Apple product after an expired warranty". support.apple.com. March 20, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- 1 2 3 Technical specifications of MB003 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- 1 2 Technical specifications of MC233 and MC234 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- 1 2 3 "Apple support: Mac notebooks: Determining battery cycle count". Archived from the original on January 10, 2014. Retrieved January 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Apple's new 11.6-in. MacBook Air: Don't call it a netbook". Computer World. October 28, 2010. Archived from the original on April 21, 2014. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Special Event October 2010". Apple Inc. October 2010. Archived from the original on May 5, 2012.
- ↑ "Apple Reinvents Notebooks With New MacBook Air" (Press release). Apple Inc. October 20, 2010. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ↑ "Apple Unveils New MacBook Air, Lion Operating System". Bloomberg. October 20, 2010. Archived from the original on November 5, 2013. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Apple Updates MacBook Air With Next Generation Processors, Thunderbolt I/O & Backlit Keyboard" (Press release). Apple Inc. July 20, 2011. Archived from the original on June 2, 2016. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Dana Wollman (July 20, 2011). "Apple refreshes MacBook Air with Sandy Bridge, Thunderbolt, and backlit keyboards". Engadget. Archived from the original on April 17, 2019. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "MacBook Air – Technical Specifications". Apple. Archived from the original on October 1, 2009. Retrieved June 10, 2013.
- ↑ Tim Stevens (June 2013). "MacBook Air review (13-inch, mid-2013)". Engadget. AOL Inc. Archived from the original on December 27, 2013. Retrieved December 27, 2013.
- ↑ "MacBook Air (13-inch, Early 2015) – Technical Specifications". support.apple.com. Archived from the original on November 25, 2021. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ↑ "Kingston SSD Now vPlus 180". Tech Spot. January 11, 2011. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Morgenstern, David (October 22, 2010). "MacBook Air storage: Not a DIMM". ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 16, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ↑ "Apple's 2010 MacBook Air (11 & 13 inch) Thoroughly Reviewed". AnandTech. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Apple issues recall for MacBook Air flash storage drives". GigaOM. Archived from the original on October 18, 2013. Retrieved October 18, 2013.
- ↑ Vivek Gowri. "AnandTech – The 2013 MacBook Air Review (11-inch)". Anandtech. Archived from the original on May 29, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Apple MacBook Air 11-inch (Mid 2013)". PC Magazine. Archived from the original on October 31, 2018. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Haslam, Karen. "How the Mac changed, and continues to change, the world". Macworld. Archived from the original on October 6, 2017. Retrieved March 28, 2018.
- ↑ Nuttall, Chris (October 22, 2010). "MacBook Air — my new favourite netbook". Financial Times. Pearson PLC. Archived from the original on December 29, 2010. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Ngo, Dong (November 1, 2012). "MacBook Air a great Windows Netbook, for a price". CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 23, 2011. Retrieved May 10, 2012.
- ↑ Krasnoff, Barbara (October 29, 2010). "Apple's new MacBook Air: A netbook by any other name". Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on January 29, 2011. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ↑ Hodge, Karl (October 21, 2010). "Apple's Netbook? The 11.6" MacBook Air debuts". Computer Weekly. Reed Business Information. Archived from the original on January 26, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ↑ Lanxon, Nate (October 20, 2010). "Apple unveils a netbook: An 11" MacBook Air". Wired. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on May 6, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ↑ Caulfield, Brian (November 28, 2011). "The NetBook Is Dead, The iPad Killed It, Don't Buy One". Forbes. Archived from the original on April 14, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2012.
- ↑ MacBook Air vs. Ultrabooks Archived July 4, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, PC Magazine
- ↑ Enterprise Mobility: Ultrabooks Will Succeed Where Netbooks Failed: 10 Reasons Why, eWeek
- ↑ The Ultrabook Revolution Archived March 18, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, PC World, August 21, 2012
- ↑ Dvorak, John C. "Where Did All the Netbooks Go?". PC Magazine. Archived from the original on October 31, 2018. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Ultrabooks threaten MacBook Air". Gulf News. Archived from the original on August 26, 2014. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Stern, Joanna (February 10, 2012). "MacBook Air with Windows 7 review: the ultrabook to rule them all?". The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on August 6, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ↑ Westover, Brian (December 20, 2011). "MacBook Air Review". PC Magazine. Archived from the original on July 4, 2017. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- 1 2 "NPD: MacBook Air owns 56 percent of the US ultrabook market". Electronista. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013. Retrieved December 23, 2013.
- ↑ "Why Ultrabook Sales Have Flopped So Far". PCWorld. July 12, 2012. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Apple's Holiday MacBook Sales Down 6% in 2012, PCs down 11%". The Mac Observer. Archived from the original on April 11, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "MacBook Air Continues to Trounce Ultrabooks". Trusted Reviews. February 9, 2022. Archived from the original on June 30, 2017. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "MacBook Air continues to dominate Ultrabook market, while competition awaits Windows 8". Macworld. UK. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "The MacBook Air Is Killing Ultrabook Sales". Cult of Mac. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Keizer, Gregg (January 26, 2012). "Apple breaks Microsoft's 'lock' on enterprise workers, argues analyst". Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 25, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Apple MacBook Air (11-inch) vs. Microsoft Surface Pro 2". laptopmag.com. December 9, 2013. Archived from the original on May 8, 2015. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "2013 MacBook Air (11-inch) vs. Microsoft Surface Pro". gizmag.com. June 18, 2013. Archived from the original on May 10, 2016. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Tim Cook On Windows 8 And Surface – Business Insider". Business Insider. October 22, 2013. Archived from the original on March 1, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Price, David. "iPad Pro (or iPad Plus) release date rumours and leaked images – News – Macworld UK". Macworld UK. Archived from the original on February 18, 2014. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Samsung ATIV Book 9 Plus vs Sony Vaio Pro 13, MacBook Air and Acer Aspire S7". ultrabookreview.com. August 14, 2013. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Wollman, Dana. "MacBook Pro with Retina display review (13-inch, 2013)". Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on February 3, 2020. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Welch, Chris (October 27, 2016). "Apple's $1,499 13-inch MacBook Pro has an escape key, but no Touch Bar". The Verge. Archived from the original on October 28, 2016. Retrieved October 27, 2016.
- ↑ "Apple MacBook Air review (11-inch, Summer 2011)". Cnet. CBS Interactive. July 22, 2011. Archived from the original on December 28, 2013. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ↑ Goldman, Joshua (August 23, 2013). "Sony Vaio Pro 13 Touch review – CNET". CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on March 22, 2014. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Goldman, Joshua (June 5, 2013). "Sony Vaio Pro 11 review – CNET". CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Sony VAIO Pro review: 'we're going to war with the MacBook Air'". The Verge. Vox Media. June 4, 2013. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Vintage and obsolete products". Apple. Archived from the original on November 16, 2018. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MC505, MC506 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved July 31, 2011.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MC503, MC504 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved July 31, 2011.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MC968, MC969 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved July 31, 2011.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MC965, MC966 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved July 31, 2011.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MD223, MD224 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved September 21, 2013.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MD231, MD232 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved September 21, 2013.
- ↑ "Apple MacBook Air "Core i5" 1.7 13" (Edu only) Specs". EveryMac. Archived from the original on February 14, 2021. Retrieved February 14, 2021.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MD711/A, MD712/A from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved September 21, 2013.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MD760/A, MD761/A from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved September 21, 2013.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MD710B, MD711B from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MD760/B, MD761/B from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MJVM2, MJVP2 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MJVE2, MJVG2 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MQD32, MQD42 from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ↑ "Apple MacBook Air "Core i5" 1.6 13" (Edu only) Specs". EveryMac. Archived from the original on January 3, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2020.
- ↑ Wiliam, Martin. "Apple MacBook Air 2018 Review: Everything You Need To Know". Best Buy Ninja. Archived from the original on December 1, 2018. Retrieved December 1, 2018.
- ↑ Apple adds True Tone display to the MacBook Air and Touch Bar to the entry-level MacBook Pro Archived November 25, 2021, at the Wayback Machine. The Verge. 9 July 2019.
- ↑ New MacBook Air and Base 13-Inch MacBook Pro Have Same Keyboard as Higher-End 2019 MacBook Pros Archived November 25, 2021, at the Wayback Machine. Mac Rumors. 9 July 2019.
- ↑ The new 2019 MacBook Air features a slower SSD than 2018 model Archived November 25, 2021, at the Wayback Machine. iMore. 15 July 2019.
- ↑ Welch, Chris (March 18, 2020). "Apple announces new MacBook Air with improved keyboard, faster performance, and more storage". The Verge. Archived from the original on November 25, 2021. Retrieved March 18, 2020.
- ↑ "Pro Display XDR – Technical Specifications". Apple. Archived from the original on March 9, 2022. Retrieved March 18, 2020.
- ↑ Herzig, Benjamin (October 31, 2018). "Apple: New Design & Retina display for the MacBook Air 2018 (Update)". Notebookcheck. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved October 21, 2019.
- ↑ "2020 MacBook Air issues: overheating, noisy fan & ineffective cooling". Mac World. May 19, 2020. Archived from the original on May 27, 2020. Retrieved May 26, 2020.
- ↑ "Does the 2020 MacBook Air have an overheating problem? Debate rages on". Forbes. April 18, 2010. Archived from the original on May 27, 2020. Retrieved June 2, 2020.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MacBook Air (Retina, 13-inch, 2018) from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved March 3, 2023.
- ↑ Technical specifications of MacBook Air (Retina, 13-inch, 2019) from Apple's knowledge base and from EveryMac.com. Retrieved March 3, 2023.
- ↑ "MacBook Air (Retina, 13-inch, 2020) - Technical Specifications". support.apple.com. March 18, 2021. Retrieved February 27, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Identify your MacBook Air model". Apple Support. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved January 2, 2019.
- ↑ "MacBook Air 13" Retina 2018 Teardown". iFixit. November 8, 2018. Archived from the original on November 27, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple significantly lowers Mac SSD upgrade pricing, 1 TB MacBook Air now available". July 9, 2019. Archived from the original on June 19, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "US Education Institution – Hardware and Software Price List" (PDF). March 18, 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved December 9, 2020.
- ↑ "MacBook Air 13" Retina 2018 Teardown". iFixit. November 8, 2018. Archived from the original on November 27, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ↑ "Product Environmental Report 13-inch MacBook Air with Retina display" (PDF). Apple and the Environment. October 30, 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 11, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ↑ "13-inch MacBook Air with Retina Display Product Environmental Report" (PDF). Apple. March 18, 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 19, 2020. Retrieved March 19, 2020.
- ↑ "Supported Models | OpenCore Legacy Patcher". dortania.github.io. Archived from the original on February 1, 2022. Retrieved June 14, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "System requirements to install Windows on your Mac via Boot Camp". March 10, 2015. Archived from the original on March 12, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
- 1 2 Keizer, Gregg (August 2, 2011). "OS X Lion requires Windows 7 for Boot Camp". Computerworld. Archived from the original on November 3, 2011. Retrieved August 2, 2011.
- ↑ Hu, Jonathan (August 12, 2015). "Apple Released Boot Camp 6.1 with Windows 10 Support". nextofwindows. Archived from the original on August 9, 2020. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
- 1 2 3 "System requirements to install Windows using Boot Camp for macOS". Apple Support. December 6, 2018. Archived from the original on March 12, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
- ↑ "Use Windows 8.1 on your Mac with Boot Camp". Apple Support. September 24, 2018. Archived from the original on September 6, 2017. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
- ↑ "Install Windows 10 on your Mac with Boot Camp Assistant". Apple Support. June 16, 2020. Archived from the original on August 21, 2020. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
External links
- MacBook Air – official site
