 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | VX-809 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.241.800 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
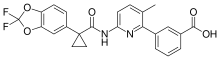
| Formula | C24H18F2N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 452.414 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lumacaftor (VX-809) is a pharmaceutical drug that acts as a chaperone during protein folding and increases the number of CFTR proteins that are trafficked to the cell surface.[1] It is available in a single pill with ivacaftor; the combination, lumacaftor/ivacaftor (brand name Orkambi), is used to treat people with cystic fibrosis who are homozygous for the F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, the defective protein that causes the disease.[2] It was developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and the combination was approved by the FDA in 2015.[3] As of 2015, lumacaftor had no medical use on its own.[1]
See also
- Ataluren, targeting premature stop codons
References
- 1 2 Kuk K, Taylor-Cousar JL (December 2015). "Lumacaftor and ivacaftor in the management of patients with cystic fibrosis: current evidence and future prospects". Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease. 9 (6): 313–26. doi:10.1177/1753465815601934. PMID 26416827.
- ↑ Lumacaftor label. Last updated July 2015. Check index page here for label updates
- ↑ "Orkambi (lumacaftor and ivacaftor)". CenterWatch. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.