Loreto | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Loreto | |
 Flag | |
| Nickname: Last Frontier of Dinagat | |
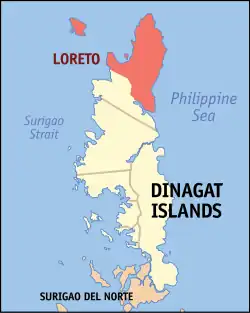 Map of Dinagat Islands with Loreto highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap | |
.svg.png.webp) Loreto Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 10°21′31″N 125°34′54″E / 10.358567°N 125.581567°E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Caraga |
| Province | Dinagat Islands |
| District | Lone district |
| Founded | January 1, 1919 |
| Barangays | 10 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Doandre Bill A. Ladaga |
| • Vice Mayor | Richard C. Tan |
| • Representative | Alan 1 B. Ecleo |
| • Municipal Council | Members |
| • Electorate | 7,951 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 255.87 km2 (98.79 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 3 m (10 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 764 m (2,507 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 9,690 |
| • Density | 38/km2 (98/sq mi) |
| • Households | 2,427 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 4th municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 31.45 |
| • Revenue | ₱ 120.3 million (2020) |
| • Assets | ₱ 409.5 million (2020) |
| • Expenditure | ₱ 108.9 million (2020) |
| • Liabilities | ₱ 62.82 million (2020) |
| Service provider | |
| • Electricity | Dinagat Island Electric Cooperative (DIELCO) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 8415 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)86 |
| Native languages | Surigaonon Cebuano Tagalog Waray |
Loreto, officially the Municipality of Loreto (Cebuano: Lungsod sa Loreto; Surigaonon: Lungsod nan Loreto; Tagalog: Bayan ng Loreto; Waray: Bungto han Loreto), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Dinagat Islands, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 9,690 people.[3]
History
The town became a part of the province of Dinagat Islands on October 2, 2006, when the province was created from Surigao del Norte by Republic Act No. 9355. However, in February 2010, the Supreme Court ruled that the law was unconstitutional, as the necessary requirements for provincial land area and population were not met. The town reverted to Surigao del Norte.[5] On October 24, 2012, however, the Supreme Court reversed its ruling from the previous year, and upheld the constitutionality of RA 9355 and the creation of Dinagat Islands as a province.[6]
Geography
Barangays
Loreto is politically subdivided into 10 barangays. Each barangay consists of puroks while some have sitios.
Climate
| Climate data for Loreto, Dinagat Islands | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 27 (81) |
27 (81) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (83) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23 (73) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
24 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 210 (8.3) |
161 (6.3) |
123 (4.8) |
85 (3.3) |
148 (5.8) |
186 (7.3) |
164 (6.5) |
157 (6.2) |
141 (5.6) |
190 (7.5) |
223 (8.8) |
200 (7.9) |
1,988 (78.3) |
| Average rainy days | 21.0 | 16.8 | 18.5 | 18.2 | 24.9 | 27.7 | 28.4 | 27.0 | 26.1 | 27.6 | 24.6 | 22.0 | 282.8 |
| Source: Meteoblue[8] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 2,193 | — |
| 1939 | 6,623 | +3.12% |
| 1948 | 6,212 | −0.71% |
| 1960 | 8,324 | +2.47% |
| 1970 | 5,020 | −4.93% |
| 1975 | 5,270 | +0.98% |
| 1980 | 5,530 | +0.97% |
| 1990 | 7,340 | +2.87% |
| 1995 | 8,048 | +1.74% |
| 2000 | 8,751 | +1.81% |
| 2007 | 9,030 | +0.43% |
| 2010 | 8,920 | −0.45% |
| 2015 | 9,309 | +0.82% |
| 2020 | 9,690 | +0.79% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[9][10][11][12] | ||
Economy
The town is endowed with rich mineral resources like aluminous laterite ore, chromite, gold, niceliferous laterite, sand and gravel, guano, rock phosphate, limestone, and siliceous sand. It is also considered as an excellent fishing ground.
References
- ↑ Municipality of Loreto | (DILG)
- ↑ "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- 1 2 Census of Population (2020). "Caraga". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ↑ "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- ↑ Tetch Torres (2010-02-11). "Dinagat Islands province back to being a town". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on 12 February 2010. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- ↑ "IRA Shares for LGUs Jump by 37.5% in 2013". Office of the President of the Philippines. January 9, 2013. Archived from the original on September 3, 2014.
- ↑ "An Act Converting into Barrios Certain Sitios in the Province of Surigao, and Dividing the Barrio of Macalaya into two barangays, Municipality of Placer, in the Same Province". LawPH.com. Archived from the original on 2012-07-11. Retrieved 2011-04-12.
- ↑ "Loreto: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ↑ Census of Population (2015). "Caraga". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Caraga" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Caraga". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Province of". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ↑ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- ↑ "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 29 November 2005.
- ↑ "2003 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 23 March 2009.
- ↑ "City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates; 2006 and 2009" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 3 August 2012.
- ↑ "2012 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "Municipal and City Level Small Area Poverty Estimates; 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2022.