Bustards are birds in the family Otididae in the monotypic order Otidiformes. There are currently 26 extant species of bustards recognised by the International Ornithologists' Union.[1] Many species of fossil bustards are known from the Miocene onwards; however, their exact number and taxonomy are unsettled due to ongoing discoveries.[2]
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (3 species) |
| EN | Endangered (1 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (4 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (7 species) |
| LC | Least concern (11 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the bustard's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IOC World Bird List for that species unless otherwise noted. Population estimates are of the number of mature individuals and are taken from the IUCN Red List.
This list follows the taxonomic treatment (designation and order of species) and nomenclature (scientific and common names) of version 13.2 of the IOC World Bird List.[1] Where the taxonomy proposed by the IOC World Bird List conflicts with the taxonomy followed by the IUCN[lower-alpha 1] or the 2023 edition of The Clements Checklist of Birds of the World,[4] the disagreement is noted next to the species's common name (for nomenclatural disagreements) or scientific name (for taxonomic disagreements).
Classification
The International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) recognises 26 species of bustards in twelve genera. This list does not include hybrid species, extinct prehistoric species, or putative species not yet accepted by the IOU.
Family Otididae
- Genus Otis: one species
- Genus Ardeotis: four species
- Genus Chlamydotis: two species
- Genus Neotis: four species
- Genus Eupodotis: two species
- Genus Heterotetrax: three species
- Genus Lophotis: three species
- Genus Afrotis: two species
- Genus Lissotis: two species
- Genus Houbaropsis: one species
- Genus Sypheotides: one species
- Genus Tetrax: one species
Bustards
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Great bustard
|
O. tarda Linnaeus, 1758 Two subspecies
|
Palearctic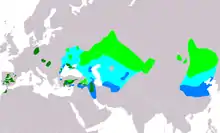 |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arabian bustard
|
A. arabs (Linnaeus, 1758) Four subspecies
|
Africa and Middle East | NT
|
| Kori bustard
|
A. kori (Burchell, 1822) Two subspecies
|
Africa | NT
|
| Great Indian bustard
|
A. nigriceps (Vigors, 1831) |
India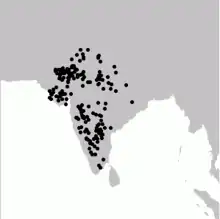 |
CR
|
| Australian bustard
|
A. australis (Gray, J. E., 1829) |
Australia and New Guinea | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Houbara bustard
|
C. undulata (Jacquin, 1784) Two subspecies
|
North Africa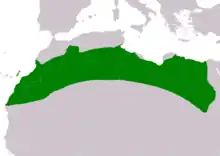 |
VU
|
| Macqueen's bustard
|
C. macqueenii (Gray, J. E., 1832) |
Asia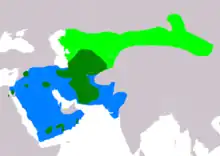 |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ludwig's bustard
|
N. ludwigii (Rüppell, 1837) |
Southern Africa | EN
|
| Denham's bustard
|
N. denhami (Children and Vigors, 1826) Three subspecies
|
Africa |
NT
|
| Heuglin's bustard
|
N. heuglinii (Hartlaub, 1859) |
East Africa | LC
|
| Nubian bustard
|
N. nuba (Cretzschmar, 1826) |
Africa | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| White-bellied bustard
|
E. senegalensis (Vieillot, 1821) Five subspecies
|
Africa | LC
|
| Blue korhaan
|
E. caerulescens (Vieillot, 1821) |
South Africa and Lesotho | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Karoo korhaan
|
H. vigorsii (Smith, A., 1831) Two subspecies
|
Africa | LC
|
| Rüppell's korhaan
|
H. rueppelii (Wahlberg, 1856) Two subspecies
|
Namibia and Angola | LC
|
| Little brown bustard | H. humilis (Blyth, 1855) |
Ethiopia and Somalia | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Savile's bustard
|
L. savilei Lynes, 1920 |
Africa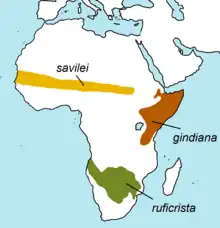 |
LC
|
| Buff-crested bustard
|
L. gindiana (Oustalet, 1881) |
East Africa |
LC
|
| Red-crested korhaan
|
L. ruficrista (Smith, A., 1836) |
Southern Africa |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southern black korhaan
|
A. afra (Linnaeus, 1758) |
South Africa | VU
|
| Northern black korhaan
|
A. afraoides (Smith, A., 1831) Three subspecies
|
Southern Africa | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black-bellied bustard
|
L. melanogaster (Rüppell, 1835) Two subspecies
|
Africa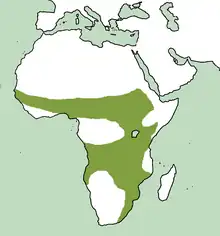 |
LC
|
| Hartlaub's bustard
|
L. hartlaubii (Heuglin, 1863) |
East Africa | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bengal florican
|
H. bengalensis (Müller, P. L. S., 1776) Two subspecies
|
Southeast Asia and northeastern South Asia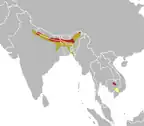 |
CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lesser florican
|
S. indicus (Miller, J. F., 1782) |
India |
CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Little bustard
|
T. tetrax (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Palearctic of Asia, Europe, and North Africa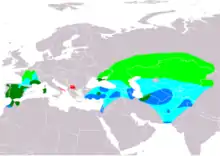 |
NT
|
Notes
- ↑ The IUCN follows the taxonomy proposed by the HBW and BirdLife Taxonomic Checklist.[3]
References
- 1 2 Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (July 2023). "Turacos, bustards, cuckoos, mesites, sandgrouse". IOC World Bird List. v 13.2. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ "Fossilworks: Otididae". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ "Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 7". HBW and BirdLife International. 2022. Archived from the original on 25 September 2019. Retrieved 11 September 2023.
- ↑ Clements, James F.; Schulenberg, T. S.; Iliff, M. J.; Fredericks, T. A.; Gerbracht, J. A.; Lepage, Denis; Billerman, S. M.; Sullivan, B. L.; Wood, C. L. (2022). "The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2022". Clements Checklist. Retrieved 2023-09-07.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2017). "Otis tarda". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22691900A119044104. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T22691900A119044104.en. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2018). "Ardeotis arabs". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22691924A129917069. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22691924A129917069.en. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Ardeotis kori". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691928A93329549. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691928A93329549.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2018). "Ardeotis nigriceps". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22691932A134188105. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22691932A134188105.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Ardeotis australis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691940A93330335. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691940A93330335.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Chlamydotis undulata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22728245A90341807. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22728245A90341807.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2019). "Chlamydotis macqueenii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T22733562A205364424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T22733562A205364424.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2018). "Neotis ludwigii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22691910A129456278. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691910A129456278.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Neotis denhami". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691905A93327715. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691905A93327715.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Neotis heuglinii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691920A93328934. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691920A93328934.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Neotis nuba". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691914A93328585. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691914A93328585.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Eupodotis senegalensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691996A93332403. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691996A93332403.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2017). "Eupodotis caerulescens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22692000A118449147. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T22692000A118449147.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Heterotetrax vigorsii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691986A93331917. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691986A93331917.en. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Heterotetrax rueppelii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691980A93331758. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691980A93331758.en. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Heterotetrax humilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691991A93332115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691991A93332115.en. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2017). "Lophotis savilei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22691955A118859689. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T22691955A118859689.en. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Lophotis gindiana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691960A93330878. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691960A93330878.en. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Lophotis ruficrista". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691965A93331085. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691965A93331085.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Afrotis afra". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691975A93331501. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691975A93331501.en. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Afrotis afraoides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22691970A93331294. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691970A93331294.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Lissotis melanogaster". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22692007A93332996. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22692007A93332996.en. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Lissotis hartlaubii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22692011A93333424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22692011A93333424.en. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2021). "Houbaropsis bengalensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T22692015A130184896. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22692015A130184896.en.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2021). "Sypheotides indicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T22692024A199959007. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2018). "Tetrax tetrax". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22691896A129913710. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22691896A129913710.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.












_male.jpg.webp)




_male_(13799426305)%252C_crop.jpg.webp)

_male.jpg.webp)


_(cropped).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
%252C_Castuera%252C_Extremadura%252C_Spain.jpg.webp)