Lauderdale, Mississippi | |
|---|---|
 Lauderdale welcome sign | |
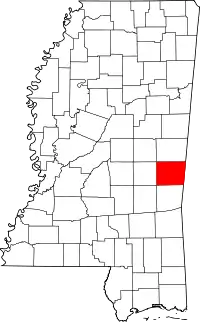
 Lauderdale  Lauderdale | |
| Coordinates: 32°31′15″N 88°30′41″W / 32.52083°N 88.51139°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Mississippi |
| County | Lauderdale |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2.86 sq mi (7.41 km2) |
| • Land | 2.86 sq mi (7.41 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) |
| Elevation | 215 ft (66 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 395 |
| • Density | 138.11/sq mi (53.32/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 39335 |
| Area code | 601 |
| FIPS code | 28-39600 |
| GNIS feature ID | 2586601 |
Lauderdale is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Lauderdale County, Mississippi, United States. The population of Lauderdale was 395 at the 2020 census.[2] It is located along U.S. Highway 45, 16 miles (26 km) northeast of Meridian.[3]
History
Early history
Lauderdale was first inhabited by Native Americans. The first recorded Native Americans in the area were the Choctaw, who had a village named Panti on Ponta Creek near the present site of Lauderdale.[4] In 1800, Samuel Dale guided some of the first European settlers to the area, including James Lauderdale. Lauderdale was originally from Tennessee but settled at the mineral springs in the area and named them Lauderdale Springs.[4] During the War of 1812, Lauderdale served under Andrew Jackson at the Battle of Talladega and was killed at the Battle of New Orleans.[4]
In 1837, a post office opened under the name Mingo Houma, then under the name Springs Depot from 1856 to 1859.[4] The community was incorporated on March 12, 1856 when the Mobile and Ohio Railroad was completed near Lauderdale Springs.[5] A resort was then built at the mineral springs and included a two-story, 300 foot long hotel with surrounding cottages.[4] Jefferson Davis, Octavia Walton Le Vert, and other notable people attended the springs for gatherings and political events.[4] The post office began operating under the name Lauderdale Springs in 1859 and used that name until 1894.[5]
Civil War
During the Civil War, the resort was converted to a Confederate hospital that operated until the end of the war.[4] Soldiers who were treated at the Confederate hospital fought at multiple battles, including Battle of Shiloh, Battle of Corinth, Battle of Iuka, Battle of Jackson, Battle of Vicksburg, and General Nathan Bedford Forrest's North Mississippi battles.[4] Mortally wounded soldiers were buried in a nearby cemetery, now known as the Lauderdale Springs Confederate-Union Cemetery.[6]
During William Tecumseh Sherman's Meridian campaign, the 32nd Wisconsin Infantry Regiment burned Lauderdale Springs.[7] Joseph Emory Davis, Jefferson Davis' older brother, stayed for a time in Lauderdale Springs after moving from Hurricane Plantation after the Siege of Vicksburg.[4]
Company C of the 5th Mississippi Infantry Regiment was mustered into service at Lauderdale Springs on August 6, 1861.[8] The 1st and 4th Missouri Infantry Regiment (Consolidated) and 2nd and 6th Missouri Infantry Regiment (Consolidated) were both stationed at Lauderdale Springs for a time.[9]
Post-Civil War
After the Civil war, the resort grounds were used by the Mississippi Baptist Convention as the Home for Confederate Orphans.[4] Company H of the 16th Infantry Regiment were assigned to the Post of Lauderdale during Reconstruction from 1868 to 1870 and occupied the former hospital buildings.[4] The post office name was changed to Lauderdale in 1894.[5] The East Tennessee, Virginia and Georgia Railway ceased service in Lauderdale in 1898.[4]
20th century
In 1900, Lauderdale had several stores, two churches, a grist mill, and a population of 288.[10]
By 1936, it had a population of 1,000, two cotton gins, a saw mill, planing mill, three churches, a school, and a hotel. The community was also home to a lumber company and pottery factory.[11]
Geography
Lauderdale is located in northeastern Lauderdale County at 32°31′15″N 88°30′41″W / 32.52083°N 88.51139°W. According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has an area of 2.9 square miles (7.4 km2), all of it recorded as land.[12] The community is in the valley of Possum Creek, just south of where it joins Ponta Creek, an east-flowing tributary of the Sucarnoochee River, part of the Tombigbee River watershed.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 395 | — | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[13] | |||
| Race | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 146 | 36.96% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 231 | 58.48% |
| Native American or Alaska Native (NH) | 1 | 0.25% |
| Asian (NH) | 1 | 0.25% |
| Some Other Race (NH) | 2 | 0.51% |
| Mixed/Multi-Racial (NH) | 10 | 2.53% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 4 | 1.01% |
| Total | 395 |
As of the 2020 United States census, there were 395 people, 165 households, and 71 families residing in the CDP.
Notable people
- Lovell Harden, former Negro league pitcher[17]
- Peggy Wilson, professional golfer who played on the LPGA Tour[18]
Gallery
 Kansas City Southern Railway crossing in Lauderdale
Kansas City Southern Railway crossing in Lauderdale Lauderdale Post Office
Lauderdale Post Office Former Lauderdale Methodist Church, now closed. The current Lauderdale Methodist Church is located in a newer building south of this location.
Former Lauderdale Methodist Church, now closed. The current Lauderdale Methodist Church is located in a newer building south of this location. Lauderdale Presbyterian Church, PCA
Lauderdale Presbyterian Church, PCA Lauderdale Springs Cemetery, founded in 1835
Lauderdale Springs Cemetery, founded in 1835 Lauderdale Springs Confederate-Union Cemetery
Lauderdale Springs Confederate-Union Cemetery Informational sign for the Lauderdale Springs Confederate-Union Cemetery
Informational sign for the Lauderdale Springs Confederate-Union Cemetery
References
- ↑ "2020 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 24, 2022.
- ↑ "Total Population: 2010 Census DEC Summary File 1 (P1), Lauderdale CDP, Mississippi". data.census.gov. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 31, 2020.
- ↑ "Lauderdale, Mississippi". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Lawrence, Betty (2002). A History of Lauderdale Springs, Mississippi (PDF) (3rd ed.). Meridian, Mississippi: Lauderdale County Department of Archives & History, Inc.
- 1 2 3 Howe, Tony. "Lauderdale, Mississippi". Mississippi Rails. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Lauderdale Springs". Visit Meridian, Mississippi. Retrieved March 27, 2023.
- ↑ The Medical and Surgical History of the War of the Rebellion. (1861-65). Washington, D. C.: United States Government Printing Office. 1875. p. XCIX.
- ↑ Rowland, Dunbar, ed. (1908). The Official and Statistical Register of the State of Mississippi. Vol. 2. Jackson, Mississippi: Mississippi Department of Archives and History. p. 551.
- ↑ Bevier, Robert S. (1879). History of the First and Second Missouri Confederate Brigades: 1861-1865. St. Louis, Missouri: Bryan, Brand & Company. p. 231.
- ↑ Rowland, Dunbar (1907). Mississippi: Comprising Sketches of Counties, Towns, Events, Institutions, and Persons, Arranged in Cyclopedic Form (PDF). Vol. 2. Southern Historical Publishing Association. p. 57.
- ↑ Lawrence, Betty (2002). A History of Lauderdale Springs, Mississippi (PDF) (3rd ed.). Meridian, Mississippi: Lauderdale County Department of Archives & History, Inc.
- ↑ "U.S. Gazetteer Files: 2019: Places: Mississippi". U.S. Census Bureau Geography Division. Retrieved March 31, 2020.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- ↑ "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved June 1, 2022.
- ↑ https://www.census.gov/
- ↑ "About the Hispanic Population and its Origin". www.census.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2022.
- ↑ "Lovell Harden Career Stats". Baseball Reference. Retrieved December 9, 2022.
- ↑ Elliott, Len; Barbara Kelly (1976). Who's Who in Golf. New Rochelle, New York: Arlington House. p. 202. ISBN 0-87000-225-2.