| Jamnith | |
|---|---|
| Jabnith; Jamnia; Kh. Banit | |
 Photo of Safed taken in 1948 from atop Mount Canaan (near Kh. Banit) | |
| Nearest city | Safed |
| Coordinates | 32°59′29″N 35°31′01″E / 32.99139°N 35.51694°E |
| Established | Hellenistic period (?) |
Jamnith (Greek: Ἰαμνειθ), also Jabnith, Yavnit (Hebrew: יבנית), Iamnia, or in medieval parlance, Ibnit / Abnit / Ovnit, is a ruin in the Upper Galilee that came to renown during the First Jewish Revolt in the 1st-century CE. The ruin, known locally by the name Khurbet esh-Sheikh Banit, or simply Kh. Banît, lies about 3.4 kilometres (2.1 mi) to the northeast of Safed, in the Biriya Forest, and was once a fortified town towards the northeast of Mount Canaan (Hebrew: Har Kena'an), upon a hill called Har Yavnit.[1] The hill on which the village ruins lie rises 836 metres (2,743 ft) above sea level and overlooks the Hula valley. Access to the ruin is now restricted because of an enclosed military installation built over the site.
The village is mentioned twice in the writings of Josephus as being in the Upper Galilee; once in The Jewish War (2.20.6) under the appellation Ἰαμνειθ, and again in Vita §37 under the name Ίαμνια, and is distinguished from the Jamnia of Judaea. Josephus testifies of himself that he assisted in building the wall of the village,[2] the reference perhaps being to funding its building project. The hilltop fortress has no natural spring, suggesting that its inhabitants relied upon rock-cut cisterns for water, of which several can be found on the site.
The fate of the town's defenders is not known, but they are presumed to have surrendered after the fall of Tarichaea.[3]
Victor Guérin visited the site in the late 19th-century and found on the plateau of the elevated hill, which he called Kharbet Benit, what he described as "a village, now overthrown from top to bottom, and of which there are only many piles of stones from demolished houses."[4] Earlier, in 1838, the site was visited by Edward Robinson, who wrote, "here (Benit) are the slight remains of a former village, situated directly on the brow of the mountains enclosing the Huleh, and commanding a splendid view over the whole basin and the surrounding region."[5]
Michael Avi-Yonah thought that the priestly course known as Bilgah had its place of residence in Yavnit.[6]
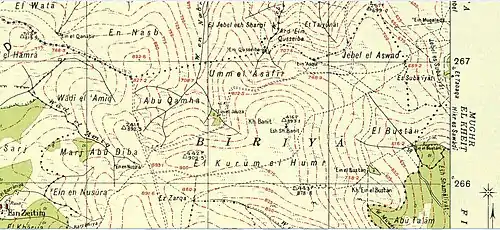
Identification
While most modern historical geographers are unanimous as to Jamnith's identification with the ruin Kh. Banit,[7][8][9][10][11][12][13] Edward Robinson and Eli Smith who surveyed the ancient sites of Palestine were uncertain of its location.[14] Neubauer thought that the site of Jamnia in Galilee may have been identical with Yabneel of the Hebrew Bible (Joshua 19:33), a place later known as Kefar Yammah.[15] However, this last site is not in the Upper Galilee.
Jamnia, known as Ibnit, had been resettled by local Arabs as late as 1948.[16]

Rabbinic burial ground
Jewish tradition holds that Talmudic scholars Abaye and Rava are buried in a cave shown on Har Yavnit (Ovnit).[16][17] R. Yudan Nesi'ah,[18] upon whom was conferred the title of nasi, is also said to have been buried on the mountain,[19] along with his two sons.[16] Visitors may access the burial sites as they lie outside the restricted area. The mountain affords a good prospect of the Hula valley on its east and southeastern side, including the town of Rosh Pina and the northern part of the Sea of Galilee.
Gallery
 View of Har Yavnit from east
View of Har Yavnit from east Old footpath leading up to Jamnith (Kh. Banit)
Old footpath leading up to Jamnith (Kh. Banit) Alleged burial cave of Abaye and Rava
Alleged burial cave of Abaye and Rava Stone inscription at alleged burial site of Abaye and Rava
Stone inscription at alleged burial site of Abaye and Rava Visitors' observation point on Har Yavnit
Visitors' observation point on Har Yavnit Shrine built as memorial to R. Yudan Nesiah, Har Yavnit
Shrine built as memorial to R. Yudan Nesiah, Har Yavnit Modern stone structure at Har Yavnit, made from reused stones found at Kh. Banit
Modern stone structure at Har Yavnit, made from reused stones found at Kh. Banit View from Har Yavnit, looking north
View from Har Yavnit, looking north
References
- ↑ Vilnai, Ze'ev (1978). Ariel: Encyclopedia le-Yedi'at Ha-Aretz (in Hebrew). Vol. 8–10. Tel-Aviv: 'Am 'Oved. p. 2690. OCLC 14912218.
- ↑ Josephus, The Jewish War 2.20.6 (2.572, 576); idem, Vita 188 (s. 37)
- ↑ Josephus, The Jewish War, iv.1. "After the fall of Jotapata some of the Galilaeans had remained in revolt against Rome; but when Tarichaea was overthrown they surrendered, and the Romans took over all the fortresses and towns except Gischala and the garrison of Mt Tabor."
- ↑ Guérin 1880, p. 439.
- ↑ Robinson, E.; Smith, E. (1856), p. 434; cf. pp. 439, 449-450, 575
- ↑ Avi-Yonah, Michael (1964). "The Caesarea Inscription of the Twenty-Four Priestly Courses". Eretz-Israel: Archaeological, Historical and Geographical Studies (in Hebrew). L.A. Mayer Memorial Volume (1895–1959): 25. JSTOR 23614642.; on this priestly ward, see Mishnah Sukkah 5:8, Tosefta Sukkah 4:28, and 1 Chronicles 24:14
- ↑ Avi-Yonah 1976, p. 67.
- ↑ Aviam 2004, p. 93 (chapter 9).
- ↑ Har-el 1972, pp. 123–130.
- ↑ Bar-Kochva 1974, p. 109 (map).
- ↑ Conder & Kitchener 1881, p. 206.
- ↑ Thomsen 1966.
- ↑ Klein 1939, p. 163.
- ↑ Robinson & Smith 2015, p. 74.
- ↑ Neubauer 1868, p. 225.
- 1 2 3 Yitzhaki, Arieh [in Hebrew] (1978). "Ḥurvat Yavnit". Israel Guide - Upper Galilee, Huleh Basin and Jordan Source Region (A useful encyclopedia for the knowledge of the country) (in Hebrew). Vol. 2. Jerusalem: Keter Publishing House, in affiliation with the Israel Ministry of Defence. pp. 138–139. OCLC 745203905.
- ↑ Zissil: Encyclopedia of Kivrei Tzadikim. This view, however, is disputed, as another source puts the burial site of Abaye and Rava in Banias, about which, see: Levi-Naḥum, Yehuda (1986), p. 248, s.v. בעאם (sic); should be corrected to read בניאס.
- ↑ Identity uncertain, although thought to be referring to Judah III. Cf. Vatican Ms. of the Jerusalem Talmud, Seder Zera'im (Vat. ebr. 133, folio 31v), where Judah II, the grandson of Rabbi Judah HaNasi, is also called R. Yudan Nesi'ah.
- ↑ Levi-Naḥum, Yehuda (1986), p. 252, chapter: Tombs of the forefathers and righteous [3], s.v. באבנית
Bibliography
- Aviam, Mordechai (2004). Jews, Pagans and Christians in the Galilee (Land of Galilee 1). Rochester: University of Rochester Press. ISBN 1-58046-171-9.
- Avi-Yonah, M. (1976). "Gazetteer of Roman Palestine". Qedem. Institute of Archaeology, Hebrew University of Jerusalem. 5: 3–112. JSTOR 43587090.
- Bar-Kochva, Bezalel (1974). "Notes on the Fortresses of Josephus in Galilee". Israel Exploration Journal. Jerusalem: Israel Exploration Society. 24 (2): 108–116. JSTOR 27925451.
- Conder, C.R.; Kitchener, H.H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology. Vol. 1. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Guérin, V. (1880). Description Géographique Historique et Archéologique de la Palestine (in French). Vol. 2: Galilée, pt. 3. Paris: L'Imprimerie Nationale.
- Har-el, M. (1972). "The Zealots' Fortresses in Galilee". Israel Exploration Journal. 22 (2/3): 123–130. JSTOR 27925338.
- Klein, S. (1939). Sefer Ha-Yishuv (in Hebrew). Vol. 1. Jerusalem: Bialik Institute / Devir Publishers. OCLC 18115508.
- Levi-Naḥum, Yehuda (1986). Sefer ṣohar le-ḥasifat ginzei teiman (in Hebrew). Ḥolon, Israel: Mifʻal ḥaśifat ginze Teman. OCLC 15417732.
- Neubauer, A. (1868). Géographie du Talmud (in French). Paris: Michel Lévy Frères.
- Robinson, E.; Smith, E. (1856). Biblical Researches in Palestine, and in the Adjacent Regions (A Journal of the Travels in the Year 1838). Vol. 2. Boston and London: Crocker & Brewster. OCLC 640235350.
- Robinson, E.; Smith, Eli (2015). Biblical Researches in Palestine and the Adjacent Regions - A Journal of Travels in the Years 1838 and 1852. Vol. 3. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-07990-7.
- Thomsen, Peter (1966). Loca Sancta. Hildesheim: Olms. (first printed in Leipzig 1907)
External links
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 4: IAA, Wikimedia commons