| Henschel Hs 121 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Advanced trainer |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Henscel Flugzeug-Werke A.G. |
| Designer | Erich Koch |
| First flight | 4 January 1934 |
| Number built | 1 |
The Henschel Hs 121 was the first aircraft built by the German Henschel company. It was a high-wing monoplane with an inline engine, fixed undercarriage and single, open cockpit, designed as an advanced trainer. Only one aircraft was produced, in 1933–4, as a testpiece for the Air Ministry.
Development
Henschel & Son of Kassel were originally known as manufacturers of locomotives, though they later produced lorries and buses. In 1933 they set up an aviation subsidiary based at Schönefeld with a branch at Johannisthal.[1] New aircraft manufacturers who intended to produce aircraft for the Luftwaffe had first to make a testpiece or masterpiece (Befahigungsnachweis) to prove their competence and the Hs 121 was Henschel's offering.
It was a high-wing braced monoplane, with gull wing roots to enhance the pilot's forward view from the open cockpit set well back behind the trailing edge. The wing was built around two metal spars with metal-covered leading edges and fabric elsewhere. There was solid bracing from near mid-wing to the lower fuselage and from this bracing inwards to the shoulder of the gull wing. The oval fuselage had a metal structure with metal covering. The tail was also a metal structure, with metal covering on the fin and tailplane but with fabric-covered control surfaces. There was wire bracing between fin and tailplane. The spatted main-wheels were carried on streamlined legs which angled outwards from the lower fuselage to increase the track.[1]
Power was from a 180 kW (240 hp) Argus As 10C inverted in-line engine.[1]
It flew for the first time at Johannisthal on 4 January 1934. A test flight programme produced some modifications: the fin was braced, the tailplane extended and more bracing was added between the landing gear and the fuselage. Only one Hs 121 was built.
Specifications
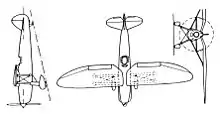
Data from Grey 1972, p. 157c
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 7.3 m (23 ft 11.5 in)
- Wingspan: 10.0 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Height: 2.8 m (9 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 14.0 m2 (150 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 760 kg (1,672 lb)
- Gross weight: 960 kg (2,112 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Argus As 10C eight-cylinder inverted air-cooled in-line , 180 kW (240 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 278 km/h (173 mph, 150 kn)
- Cruise speed: 250 km/h (155 mph, 135 kn)
- Endurance: 2 hours
- Service ceiling: 6,500 m (21,320 ft)
- Rate of climb: 8.3 m/s (1,640 ft/min) to 2,000 m (6,560 ft)
References
- Citation
- Cited sources
- Grey, C.G. (1972). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1938. London: David & Charles. ISBN 0-7153-5734-4.