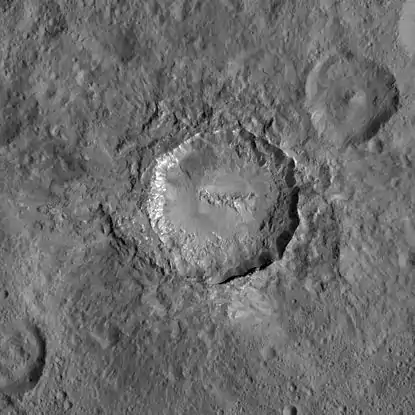
 Haulani imaged by Dawn from LAMO | |
| Location | Ceres |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 5°20′N 10°35′E / 5.34°N 10.58°E[1][2] |
| Diameter | 34 kilometres (21 mi)[3] |
| Naming | Haulani, Hawaiian goddess of plants |
Haulani /haʊˈlɑːni/ is an impact crater located on Ceres that contains "Spot 1", one of the bright spots observed by the Dawn spacecraft. The crater was named after Haulani, the Hawaiian goddess of plants.[1][2] In July 2018, NASA released a comparison of physical features, including Haulani crater, found on Ceres with similar ones present on Earth.[4]
Haulani is one of the youngest craters on Ceres, estimated to have been formed between 1.7 and 5.9 Myr (million years) ago,[5] and as such has numerous unique geological features, with much evidence of tectonic activity.[3] The crater is internally divided between its east, which lies on a raised plateau, and its west, which is of a low altitude.[5]
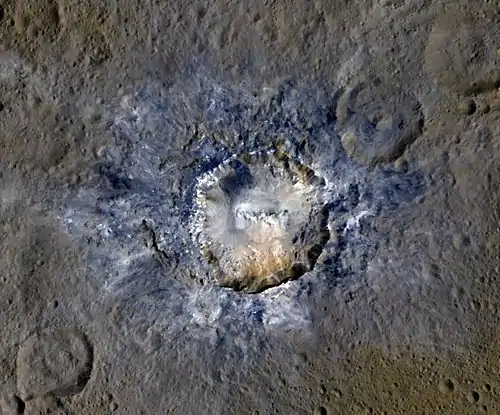
Haulani in enhanced color
See also
References
- 1 2 Staff (6 July 2015). "Planetary Names: Crater, craters: Haulani on Ceres". USGS. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- 1 2 Staff (13 July 2015). "USGS: Ceres nomenclature" (PDF). USGS. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- 1 2 Krohn, Katrin; et al. (December 2018). "The unique geomorphology and structural geology of the Haulani crater of dwarf planet Ceres as revealed by geological mapping of equatorial quadrangle Ac-6 Haulani" (PDF). Icarus. Elsevier. 316: 84–98. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2017.09.014. S2CID 125918420.
- ↑ Landau, Elizabeth; McCartney, Gretchen (24 July 2018). "What Looks Like Ceres on Earth?". NASA. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- 1 2 Tosi, Federico; et al. (10 April 2018). "Mineralogy and temperature of crater Haulani on Ceres". Meteoritics & Planetary Science. Wiley-Blackwell. 53 (9): 1902–1924. doi:10.1111/maps.13078. S2CID 134355068.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

