| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Boötes |
| Right ascension | 14h 22m 14.00070s[2] |
| Declination | +29° 22′ 11.7179″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.6[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3III[4] |
| U−B color index | +1.46[3] |
| B−V color index | +1.60[3] |
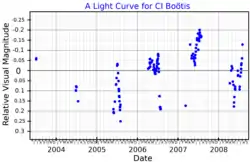
| Variable type | Irregular[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −19.66±0.54[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −39.980[2] mas/yr Dec.: −26.201[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.5229 ± 0.0973 mas[2] |
| Distance | 720 ± 20 ly (221 ± 5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.268[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.8[2] M☉ |
| Radius | 71[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 943[2] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,227[8] K |
| Age | 1.6[2] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HD 126009 or CI Boötis is a variable star[4] in the northern constellation of Boötes.
References
- ↑ Tabur, V.; Bedding, T. R.; Kiss, L. L.; Moon, T. T.; Szeidl, B.; Kjeldsen, H. (December 2009). "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 400 (4): 1945–1961. arXiv:0908.3228. Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986), "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)", Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data. SIMBAD, Bibcode:1986EgUBV........0M
- 1 2 Tabur, V.; Bedding, T. R. (2009), "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 400 (4): 1945–61, arXiv:0908.3228, Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x, S2CID 15358380
- ↑ Mennessier, M. O.; et al. (August 2001), "Long period variable stars: galactic populations and infrared luminosity calibrations", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 374 (3): 968–979, arXiv:astro-ph/0105552, Bibcode:2001A&A...374..968M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010764, S2CID 15721872.
- ↑ Famaey, B.; et al. (2009). "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants,. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 498 (2): 627–640. arXiv:0901.0934. Bibcode:2009A&A...498..627F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698. S2CID 18739721.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2017). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Tycho-2 red giant branch and carbon stars (Gontcharov, 2011)". VizieR On-Line Data Catalog. Bibcode:2017yCat..90370769G.
- ↑ Soubiran, Caroline; Le Campion, Jean-François; Brouillet, Nathalie; Chemin, Laurent (2016). "The PASTEL catalogue: 2016 version". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 591: A118. arXiv:1605.07384. Bibcode:2016A&A...591A.118S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628497. S2CID 119258214.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.