Grande Pièce Symphonique, Op.17, FWV 29, is an organ work by French composer and organist César Franck. Written in 1860–62, it is the second and, at an average duration of 25 minutes,[1] the largest piece from Six Pièces pour Grand Orgue. It is dedicated to the composer Charles-Valentin Alkan.
Background
The Six Pièces are an important work of the composer, marking the beginning of the second period of his career[2] and predicting the flowering in his later creative life.[3] His long struggle on the comic opera Le Valet de ferme (1851–1853) ended with a disastrous failure of the production and a disappointment, which paralysed Franck's activity as a composer for several years. The influence of the new Cavaillé-Coll organ at Sainte-Clotilde, Paris, for which he was appointed first organist in 1859, encouraged him to resume composing.[4] Japanese composer Akio Yashiro found out that, in comparison to the C major Fantaisie Op.16 (Six Pièces, No. 1), Franck now makes extensive use of all possibilities of the organ.[1][n 1]
Grande pièce symphonique is written in a single movement, which may be divided into three parts, the second of them being the Andante with a scherzo-like middle section. This feature of the work, sometimes referred to as "organ symphony", has induced comparison with his later chef-d’œuvre, the Symphony in D minor.[3][5] Yashiro regarded this work as prototype of the symphony, based on the following four reasons:[6]
- Unity of the cyclic form, “thème cyclique”
- Similarity of the cyclic themes in both works
- Scherzo is embedded in the slow movement
- Conclusion with "joy of faith" in parallel major.
In addition, Yashiro pointed out that this work shares several features with some of composer's later masterpieces.[6]
The work's dedicatee, the virtuoso pianist and composer Charles Valentin Alkan, had written a symphony for solo piano a few years earlier, as part of the Douze Études dans tous les tons mineurs, Op. 39, published in 1857, which also included the celebrated concerto for solo piano.[5] Franck highly praised Alkan and arranged some of his piano pieces for organ.[1][n 2] The score was published as part of the “Six pièces pour Grand-Orgue” by Mme. Maeyen-Couvreur, Paris. Around 1878, there was a reissue by Durand.[3][7]
Structure
Although the work is written as a single movement,[5] it can be divided into three parts. In this section, the work is going to be analyzed as consisting of three movements.
First movement
Andantino serioso 4/4 F-sharp minor
The work starts with an introduction, presenting the thematic material, which will determine the piece.
Excerpt 1
![\relative c' {
\new PianoStaff <<
\new Staff {
\key fis \minor \time 4/4 \tempo "Andantino serioso" \clef bass
\set crescendoText = \markup { \italic { Rall } }
\set crescendoSpanner = #'text
\override DynamicTextSpanner #'style = #'dotted-line
fis,8 a cis a fis e d cis b d fis d b a gis fis eis d' eis, fis g d' g, gis a d fis\< a gis cis bis gis' gis1\fermata\!
}
\new Staff {
\key fis \minor \time 4/4 \clef bass
<cis, a fis>8 <cis a fis>4 <cis a fis> <cis a fis> <cis a fis>8
<d b fis>8 <d b fis>4 <d b fis> <d b fis> <d b fis>8
<d b gis>8 <d b gis>4 <d b fis> <d b e,> <d b eis,>8
<d a fis>8 <d a fis>4 <d fis,>8 <cis eis,>[ <ais e> <a dis,> <gis fis>]
<cis gis eis cis,>1\fermata _\markup {(pedal)}
}
>>
}](../I/1b57fba6d334da59e00a173dc37e973b.png.webp)
Excerpt 2
![\relative c' {
\new PianoStaff <<
\new Staff \with { \remove "Time_signature_engraver" } {
\key fis \minor \time 4/4
<<
{
\voiceOne
gis''8 ^\markup {\italic {Quasi ad libitum. } }( eis4 cis8 cis4 bis) | a'8( fis4 dis8 \times 2/3 { dis[ eis cis~] } cis4\fermata)
}
\new Voice
{
\voiceTwo
gis2. fis4 | bis8 a4 fis8 fis4 eis
}
>>
}
\new Staff \with { \remove "Time_signature_engraver" } {
\key fis \minor \time 4/4 \clef bass
<eis cis>8( <cis gis>4 <gis eis>8 <gis eis>4 <a! dis,>) |
<fis' dis>8( <dis bis>4 <bis a!>8 <bis a>4 <cis gis>\fermata)
}
>>
}](../I/f45dc1323faeb8df78e8ccc89dbb95cc.png.webp)
Excerpt 3
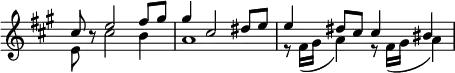
Excerpt 1 is played two times on Grand Orgue, and is answered by excerpt 2 on Récit.[1] Excerpt 1 then appears on pedal and Grand Orgue, accompanied by excerpt 3. After a brief climax in the introduction, the first subject of the sonata form appears (excerpt 4), which ties the whole work as a cyclic theme. Yashiro pointed out the similarity between this theme and that of Franck's symphony in D minor.[6]
Excerpt 4

A chorale-like second subject is introduced in A major after contrapuntal expansion of the first subject, as in traditional sonata form. A recapitulation of excerpt 2 follows and the concluding triplet is extended, forming a streaming accompaniment to excerpt 4, this time played in the Positif. Finally, the recapitulation begins with the first subject in the pedals, followed by the second subject in F-sharp minor.[8] Excerpt 2 then reemerges and ends with a profound, lingering echo (molto lento, fermata).
Second movement
Andante 4/4 B major
The movement starts with a graceful melody (excerpt 5) deduced from excerpt 3,[8] frequently switching between Positif and Récit.
Excerpt 5[n 3]
![\new StaffGroup
\with {
systemStartDelimiter = #'SystemStartBar
}
<<
\new GrandStaff <<
\new Staff \relative c'
{
\key b \major \time 4/4 \tempo "Andante"
dis'4\p( e fis4.) b,8( dis4 e8.[ eis16] fis2) fisis4( gis8.[ dis16] eis4 fis8.[ b,16] dis4 e8.[ cis16] b!2)
}
\new Staff \relative c'
{
\key b \major \time 4/4 \clef bass
<b~ fis>4( <cis b~ gis> <dis b fis>2
<<
{
\voiceOne
b4~ cis8.[ cisis16] s2
s1 s4 cis8.[ e16] <dis b>2
}
\new Voice
{
\voiceTwo
fis,4 <b~ gis> <dis b fis>2
<dis~ cis? ais>4 <dis b~ gis~> <cis b~ gis> <dis~ b fis>
<dis ais~ fisis>4 <ais fis~> fis2
}
>>
}
>>
\new Staff \relative c'
{
\key b \major \time 4/4 \clef bass
b,1~ b1 dis4 gis, cis fis, fisis fis b2
}
>>](../I/1b80ce4b60b82f6d90c2f1c846243580.png.webp)
The conclusion of the melody of excerpt 5 is interrupted by a scherzo (Allegro, 2/4, B minor). It is filled with rapid semiquavers derived from the cyclic theme (excerpt 4).[8] The end of the scherzo part, which in itself comprises a ternary form, leads into a shortened recapitulation of excerpt 5 in B major.
Third movement
"Beaucoup plus largement que précédemment" 4/4 F-sharp major
The third movement begins with a recapitulation of themes from the previous parts, in a similar way as Beethoven did in the finale of his ninth symphony.[9] As with Beethoven, a recitativo from the basses (i.e. the pedals), formed from motifs of excerpt 4, links the reappearances of the theme from the introduction (excerpt 1 in G minor), the scherzo theme in B-flat major and the Andante theme in C major). A long crescendo then prepares the triumphant entrance of the first part main theme in F-sharp major, accompanied by a virtuoso pedal part in quavers:
Excerpt 6

The piece is concluded by a fugue, again based on the beginning of the main theme (excerpt 4), and a lengthy and joyful coda.
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ Although Yashiro wrote the name of church as Church of Saint-Sulpice inconsistently, this is assumed to be Saint-Clotilde from the view of Franck's history as an organist.
- ↑ e.g. "Prelude and Payer", 1889.
- ↑ In the second bar of middle stave, the note b is tied to following note.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Yashiro 1981, p. 31.
- ↑ Yashiro 1981, p. 25.
- 1 2 3 Yashiro 1981, p. 27.
- ↑ Yashiro 1981, pp. 25–26.
- 1 2 3 Corleonis, Adrian. Grande Pièce Symphonique at AllMusic. Retrieved 2013-12-22.
- 1 2 3 Yashiro 1981, p. 29.
- ↑ "IMSLP, Frank: Grande pièce symphonique". Retrieved 2013-12-22.
- 1 2 3 Yashiro 1981, p. 33.
- ↑ Yashiro 1981, pp. 33–35.
Sources
- Yashiro, Akio (1981). 最新名曲解説全集 第16巻 独奏曲III. 音楽之友社.
- Score Franck Grande pièce symphonique, Maeyens-Couvreur, Paris
External links
- Grande Pièce Symphonique: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- Corleonis, Adrian. Grande Pièce Symphonique at AllMusic