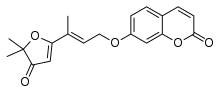
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
7-{[(2E)-3-(5,5-Dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)but-2-en-1-yl]oxy}-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Geiparvarin |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H18O5 | |
| Molar mass | 326.343 g/mol |
| Density | 1.242 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 533 °C (991 °F; 806 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Geiparvarin is a coumarin derivative found in the leaves of the Australian Willow (Geijera parviflora).[1] It is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.[2]
Several analogues of geiparvarin have been studied for antitumor properties.[3][4][5]
References
- ↑ Lahey FN, Macleod JK (September 1967). "The coumarins of Geijera parviflora Lindl". Aust J Chem. 20 (9): 1943–55. doi:10.1071/CH9671943.
- ↑ Carotti A, Carrieri A, Chimichi S, et al. (December 2002). "Natural and synthetic geiparvarins are strong and selective MAO-B inhibitors. Synthesis and SAR studies". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 12 (24): 3551–3555. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(02)00798-9. PMID 12443774.
- ↑ Baraldi PG, Guarneri M, Manfredini S, Simoni D, Balzarini J, De Clercq E (February 1989). "Synthesis and cytostatic activity of geiparvarin analogues". J Med Chem. 32 (2): 284–288. doi:10.1021/jm00122a002. PMID 2913291.
- ↑ Valenti P, Rampa A, Recanatini M, et al. (September 1997). "Synthesis, cytotoxicity and SAR of simple geiparvarin analogues". Anticancer Drug Des. 12 (6): 443–51. PMID 9311554.
- ↑ Viola G, Vedaldi D, dall'Acqua F, et al. (September 2004). "Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis induction in human tumor cells by geiparvarin analogues". Chemistry & Biodiversity. 1 (9): 1265–1280. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200490089. PMID 17191904. S2CID 22355393.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.