In archaeology a fill is the material that has accumulated or has been deposited into a cut feature such as ditch or pit of some kind of a later date than the feature itself.[1] Fills are an important part of the archaeological record as their formation and composition can throw light on many aspects of archaeological study.
Primary fills
A primary fill is the context that first appears in the sequence after the context representing the cut it "fills". In many cases this will be a silt or naturally accumulating material that forms in the base of some hole or trench before its function is realized. For example, a medieval rubbish pit may be open for some time before rubbish is placed in it allowing natural processes to silt up the base, but the interpretation may mark the end of a cut feature's use. Similarly, a ditch that silts up by neglect could represent the start of the end of the features function in the record. Secondary and subsequent fills all form above the primary fill.
Primary fills, in the plural sense, are all the fills within a feature that are sealed by layer(s) possibly representing a change in phase or function.
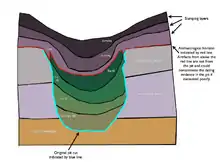
Slumping
Slumping is a process that can occur to any context in the archaeological record and not just fills. Slumping represents how a context's deposition morphology may deform from its original position by natural settling action. This is readily apparent with fills which have a tendency to settle radically over time. This settling is termed slumping and has a bearing on the excavation of cut features. As fills slump the overlying layers which seal the feature will slump in sympathy creating false impressions of fills below the lip of the cut and introduce the possibility of contaminated dating evidence into the features excavation. (See archaeological section in fig 1). also the degree of slumping of the primary fills compared to the slumping of overlying sealing layers is a possible measure of time differences between the formation of the fills the overlying sequence. This is because sealing layers laid down over a slumping feature with the intent of leveling the area for a specific purpose such as construction will either conform to the slumped fills as though the slump has occurred at the time of the sealing layers formation. Or the sealing layers will not take into account the slumping because the slumping is yet to occur. This can lead to sympathetic slumping up the sequence of other features including later structures.
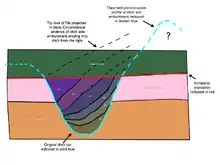
Tip lines
Tip lines are an intrinsic characteristic of fills, but they can apply to many other types of context such as dumps. Tip lines are the angles which the contexts form as an indicator of action in the past. As fills of a feature form stratigraphically, the direction off the horizontal by which they form may give us information. For example, a ditch that has fills all angled, so one side of each fill is higher on a specific side of the ditch, would suggest that the ditch was backfilled from the side where the fills were highest. (See archaeological section in fig 2). This can be circumstantial evidence for features or detail not preserved in the archaeological record. This reading of a fills deposition morphology is an example of why deposits and contexts are important discoveries in themselves independent of whether they represent structures or contain artifacts.
See also
References
- ↑ "fill". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)