 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
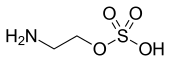
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Aminoethyl hydrogen sulfate | |
| Other names
Aminoethyl sulfate; 2-Aminoethyl hydrogen sulphate; Sulfuric acid mono 2-aminoethyl ester; WAS-34 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | EOS |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.942 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H7NO4S | |
| Molar mass | 141.14 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 277 °C (531 °F; 550 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Ethanolamine-O-sulfate (EOS) is an ester of sulfuric acid and ethanolamine. EOS is a GABA transaminase inhibitor which prevents the metabolism of GABA.[2] It is used as a biochemical tool in studies involving GABA.
EOS is also a diuretic[3] and an anticonvulsant.[4]
References
- ↑ 2-Aminoethyl hydrogen sulfate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Gudelsky GA, Apud JA, Masotto C, Locatelli V, Cocchi D, Racagni G, Muller EE (1983). "Ethanolamine-O-sulfate enhances gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion into hypophysial portal blood and lowers serum prolactin concentrations". Neuroendocrinology. 37 (5): 397–9. doi:10.1159/000123580. PMID 6646351.
- ↑ German Patent DE2345291: Diuretic aminoalkyl sulfates; Somani, Pitambar; Martin, Donald Lyons (1974)
- ↑ Anlezark, Gill; Horton, Roger W.; Meldrum, Brian S.; Sawaya, M. Christina B. (1976). "Anticonvulsant action of ethanolamine-O-sulfate and di-n-propylacetate and the metabolism of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in mice with audiogenic seizures". Biochemical Pharmacology. 25 (4): 413–417. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(76)90343-9. PMID 779794.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.