Bambuí | |
|---|---|
_consorciado_com_Guandu_(Cajanus_cajan_L._Millsp.)_no_sistema_de_al%C3%A9ias._-_panoramio.jpg.webp) | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Location in São Paulo state | |
 Bambuí Location in Brazil | |
| Coordinates: 20°00′21″S 45°58′37″W / 20.00583°S 45.97694°W | |
| Country | Brazil |
| Region | Southeast |
| State | São Paulo |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,455,380 km2 (561,930 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 725.9 m (2,381.6 ft) |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (BRT) |
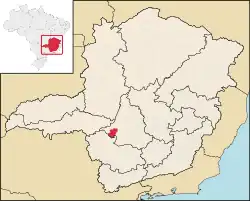
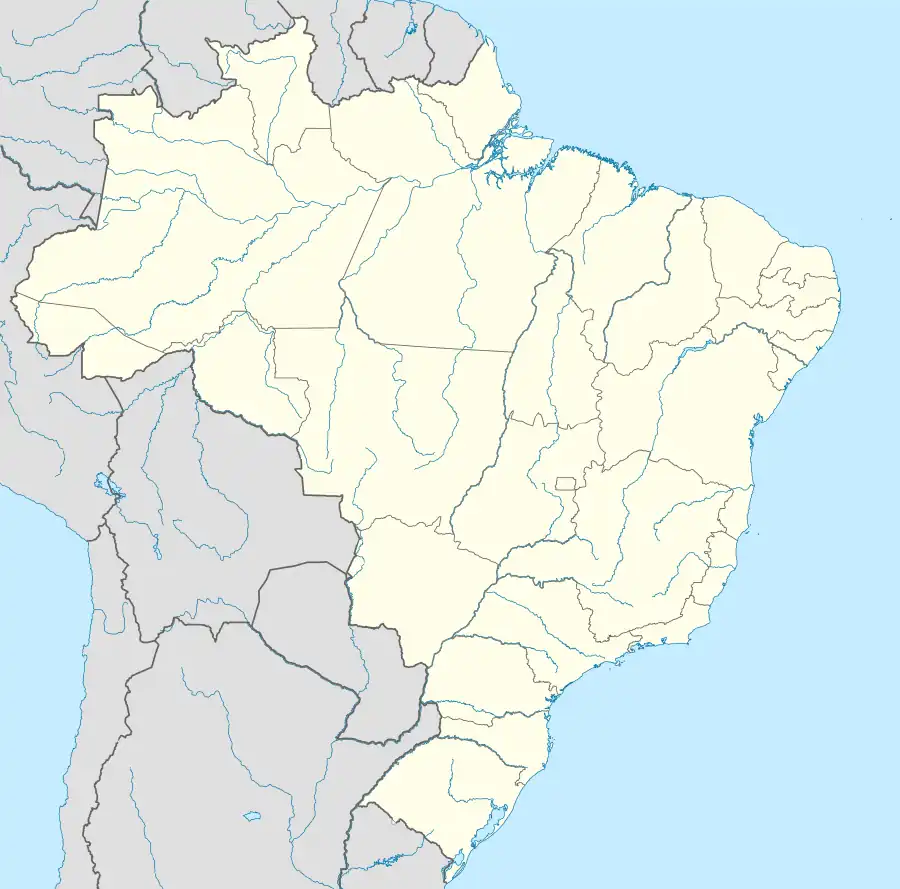
Bambuí is a Brazilian municipality located in the west of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 23,898 people living in a total area of 1,455 square kilometres (562 sq mi), for a density of 15/km2 (39/sq mi).[1] The city belongs to the meso-region of Oeste de Minas and to the micro-region of Piumhi. It became a municipality in 1881.[2]
Location
The city center of Bambuí is located at an elevation of 706 meters on a plateau and straddles the 20th parallel. Neighboring municipalities are: Tapiraí and Córrego Danta (N), Luz (NE), Iguatama (E), Doresópolis (SE), Piumhi (S), São Roque de Minas and Medeiros (W).[3]
Communications and distances
Bambuí is connected to major population centers by highways MG-050, BR-354 and BR-262. The distance to Belo Horizonte is 270 km.
Origin of the name
Some historians believe that the name of the city was given by the Negros who lived in the region and belonged to a runaway slave colony called Campo Grande. This hypothesis is reinforced by the existence of a city with the same name in Cameroon, in Africa. Another interpretation for the name of the city is that it is of indigenous origin and means "river of dirty waters".[4]
Economic activities
Services, mining of kaolin, and agriculture are the most important economic activities. The GDP in 2005 was approximately R$168 million, with 10 million reais from taxes, 86 million reais from services, 11 million reais from industry, and 61 million reais from agriculture. There were 1,361 rural producers on 90,000 hectares of land. 196 farms had tractors (2006). Approximately 4,000 persons were dependent on agriculture. The main crops are coffee (4,300 hectares in 2006), rice, beans, and corn. There were 76,000 head of cattle (2006), one quarter of which were raised for milk and cheese production.[2]
There were 3 banks (2007) and 3,950 automobiles (2007), giving a ratio of 5 inhabitants per automobile.[2]
Working population in 2005
- Workers in 74 transformation industries: 264
- Workers in 395 units of commerce: 1,160
- Workers in public administration: 552 [2]
Health and education
In the health sector there were 9 public health clinics (2005) and 2 hospitals with 195 beds. Patients with more serious health conditions are transported to Araxá or to Divinópolis, which are connected by good roads. Educational needs of 4,400 students were met by 12 primary schools, 4 middle schools, and 6 pre-primary schools.[2]
- Municipal Human Development Index: 0.787 (2000)
- State ranking: 84 out of 853 municipalities as of 2000
- National ranking: 872 out of 5,138 municipalities as of 2000
- Literacy rate: 88%
- Life expectancy: 73 (average of males and females)[5]
In 2000 the per capita monthly income of R$246.00 was below the state and national average of R$276.00 and R$297.00 respectively.
The highest ranking municipality in Minas Gerais in 2000 was Poços de Caldas with 0.841, while the lowest was Setubinha with 0.568. Nationally the highest was São Caetano do Sul in São Paulo with 0.919, while the lowest was Setubinha. In more recent statistics (considering 5,507 municipalities) Manari in the state of Pernambuco has the lowest rating in the country—0,467—putting it in last place.[5]
References
- ↑ IBGE 2020
- 1 2 3 4 5 IBGE Archived January 9, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Citybrazil". Archived from the original on 2008-09-28. Retrieved 2008-08-17.
- ↑ Portuguese Wikipedia
- 1 2 Frigoletto Archived 2011-07-06 at the Wayback Machine
See also