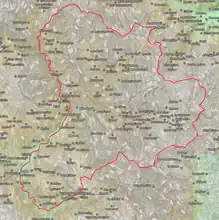
Argithea
Αργιθέα | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Argithea Location within the region 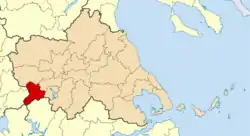 | |
| Coordinates: 39°21′N 21°32′E / 39.350°N 21.533°E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | Thessaly |
| Regional unit | Karditsa |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 372.9 km2 (144.0 sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 150.4 km2 (58.1 sq mi) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Municipality | 3,450 |
| • Municipality density | 9.3/km2 (24/sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 1,374 |
| • Municipal unit density | 9.1/km2 (24/sq mi) |
| Community | |
| • Population | 209 (2011) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Vehicle registration | ΚΑ |
Argithea (Greek: Αργιθέα) is a village and a historic municipality in the Karditsa regional unit of Greece. The seat of the municipality is in Anthiro.[2] The name derives from ἀργός + θέα (argós + théa, “white view”).
Municipality
The municipality Argithea was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 3 former municipalities, that became municipal units:[2]
- Acheloos
- Anatoliki Argithea
- Argithea
The municipality has an area of 372.877 km2, the municipal unit 150.377 km2.[3]
History
Anciently, Argithea or Argethia (Ancient Greek: Ἀργεθία) was the capital of Athamania straddling the border between Ancient Epirus and Ancient Thessaly, to the left of the main stream of the Achelous River.[4] The first evidence we have of the place is epigraphic. In the fourth century BCE, the appointment of a proxenos of Argithea is documented. Circa 230-220 BCE, a theorodokoi for the city is appointed to receive theoroi from Delphi.[5] It was also a polis (city-state).[5]
In the time of Livy it was the capital of Athamania. In the year 189 BCE. there was a rebellion by the Athamanians to try to reestablish Amynander of Athamania in power, which the help of the Aetolian League and this rebellion succeeded in expelling the garrison left by Philip V of Macedon. Later Philip sent more troops against Argithea in an attempt to recover the city, but the effort failed.[6]
The editors of the Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World and Mogens Herman Hansen locate the ancient city at the modern village of Hellenika (or Ellinika) in the community of Hellenika, municipal unit and municipality of Argithea.[7][5] Hellenika is located at 39°22′54″N 21°23′30″E / 39.38167°N 21.39167°E.
References
- 1 2 "Απογραφή Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2011. ΜΟΝΙΜΟΣ Πληθυσμός" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority.
- 1 2 "ΦΕΚ A 87/2010, Kallikratis reform law text" (in Greek). Government Gazette.
- ↑ "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-21.
- ↑ Livy. Ab urbe condita Libri [History of Rome]. Vol. Liv. 38.1.
- 1 2 3 Mogens Herman Hansen & Thomas Heine Nielsen (2004). "Thessaly and Adjacent Regions". An inventory of archaic and classical poleis. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 727. ISBN 0-19-814099-1.
- ↑ Livy. Ab urbe condita Libri [History of Rome]. Vol. 38, 1-2.
- ↑ Richard Talbert, Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World, (ISBN 0-691-03169-X), Map 55.