Northern Canada
Region of Canada. Northern Canada is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut.
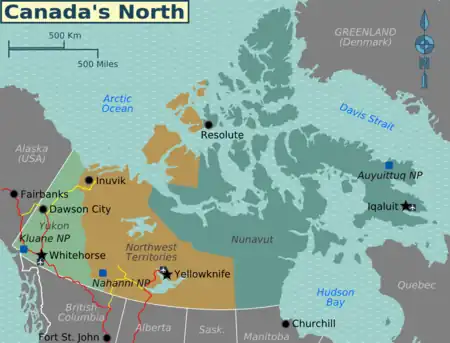
The North of Canada consists of three territories: Yukon, the Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. They extend into the Arctic, and have just over 100,000 inhabitants spread across a land area larger than India.
Territories
| Yukon The most accessible of the three territories with the Alaska Highway providing road links to Alaska and British Columbia. There is gold rush history in Dawson City and the mountainous splendour of Kluane National Park. Whitehorse, the capital, provides a good central hub. |
| Northwest Territories The most populous territory, with a mixed population of European Canadians, First Nation people, Inuit, Métis and visible minorities. |
| Nunavut This territory was created out of the Northwest Territories in 1999, in order to provide self-government for the Inuit people, who make up 85% of its population. |
Cities
In this area the term "city" becomes a relative term, especially when measured by population. However, some rather small places (by Southern standards) can have tremendous importance for huge areas as the only thing even approaching a city for hundreds or even thousands of miles. The most important places are:
- 🌍 Dawson City — historic Klondike gold rush town, now a national historic site
- 🌍 Iqaluit — capital and largest settlement of Nunavut
- 🌍 Inuvik — the most populous town in the Canadian Arctic, almost 200 km north of the Arctic Circle, at the inland end of the Mackenzie Delta and the northern end of the Dempster Highway
- 🌍 Whitehorse — the capital and largest city of the Yukon
- 🌍 Yellowknife — the NWT's capital and largest settlement, with several scenic walking trails, and the territorial museum
Other destinations
Much of this area is untouched wilderness or sparsely populated mining and logging country. As such national parks have a natural draw to them, with North American wildlife. Examples include:
- 🌍 Auyuittuq National Park — its name means "the land that never melts", and it includes many terrains of the Arctic wilderness, such as fjords, glaciers, and ice fields
- 🌍 Kluane National Park — generally accessible only via a flightseeing tour or on a serious mountaineering or ski touring expedition
- 🌍 Nahanni National Park Reserve — a
 UNESCO World Heritage Site home to the South Nahanni River, one of the most spectacular wild rivers in North America, also accessed by chartered plane
UNESCO World Heritage Site home to the South Nahanni River, one of the most spectacular wild rivers in North America, also accessed by chartered plane - 🌍 Tombstone Territorial Park – a hidden gem containing rugged mountains for kilometres on end
- 🌍 Wood Buffalo National Park – a
 UNESCO World Heritage Site and the world's second largest national park protecting some of the last remaining wild populations of wood buffalos
UNESCO World Heritage Site and the world's second largest national park protecting some of the last remaining wild populations of wood buffalos
Understand
The North of Canada is a vast area made up of many different environments; ranging from boreal forest, to mountains, to subarctic all the way to high arctic. This is one of the most remote places on Earth and even the vast majority of Canadians will never visit the region. Travel here is extremely difficult and expensive. Most will want to visit during the summer when the territories aren't shrouded in near constant darkness, snow and freezing temperatures (to put it lightly). However, for those with the funds and motivation, visiting the North of Canada can be an extremely rewarding experience. This is one of the world's most remote and sparsely populated regions. Owing to its huge size and variety of landscapes and climates, not much can be generalized about the region. Larger towns with road access are not so different from the rest of Canada, but most of the region is "trackless" wilderness: there are literally no roads. In these communities, the only access is by sea (seasonally in the autumn only) or air (usually on small "bush planes").
Much of the population are Indigenous peoples, namely the Inuit and Inuvialuit (formerly, but never now, called "Eskimos"), the Dene and Cree peoples (still legally called "Indians", but more frequently now called "First Nations"), and the Métis (formerly, but never now, called "half-breeds"). The lifestyles of these people have been dramatically changed in the last century or so by the arrival of Southern government authorities, businesses, and religious missionaries. Many have wage-paying jobs in the towns, shop in grocery stores stocked with imported produce, watch TV, and attend Christian churches. Nevertheless, they still to varying degrees rely on hunting, trapping, fishing, and gathering to supplement their diets and incomes, many speak their local language in preference to English, and often follow cultural practices and ceremonies that the Christian missionaries couldn't suppress.
The wildlife here are truly wild and free ranging. This is perhaps the largest piece of the earth outside of Antarctica that is basically not enclosed or fenced in any meaningful way. Moose and deer roam the forests. Bears forage for berries along the valleys. Caribou (reindeer) herds in the tens of thousands migrate across the region. Muskox and wolves confront each other on the tundra. Polar bears walk across the sea ice to hunt seals. Likewise the seas are mostly safe from commercial fishing and shipping, and can therefore support elephant seals, belugas and other large mammals.
Travel to this region presents challenges, but provides the opportunity to see something truly distinct.
Get in
- See also: Next to impossible destinations
By car

There are highways through the Yukon which reach Whitehorse, Dawson and even Inuvik. Another road goes to Yellowknife. All these roads are open year round but may be closed temporarily by storms; see winter driving.
Many other locations (including all of Nunavut) can only be accessed by sea or air. Flights to these areas can often be extremely expensive; see general aviation. A few cruise ships go to the Canadian arctic; this is likely the most comfortable way to visit.
By train
- See also: Rail travel in Canada
- White Pass and Yukon Route, ☏ +1-800-343-7373, info@wpyr.com. Operates out of Skagway, Alaska, and stops in Northern British Columbia on its way to Carcross, Yukon. Provides access to a trailhead of the Chilkoot Trail. Service operates from May to early October. (updated Aug 2022)
By plane
The largest airports in the region are in Whitehorse and Yellowknife. Whitehorse has limited seasonal international flights, and otherwise there are no international flights directly to the region.
Churchill, Manitoba (YYQ) is reachable by rail and by air from Thompson and Winnipeg; from there, flights depart for Arviat, Baker Lake, Chesterfield Inlet, Coral Harbour, Rankin Inlet, Repulse Bay and Whale Cove.
All communities in Nunavut are fly-in/fly-out.
Get around
Distances tend to be large and there are few roads and no passenger railways north of the 60th parallel. There are no roads connecting between any communities in Nunavut. Weather may impede movement during parts of the year and often access is only by boat or plane. Winter roads are available in some places but the road conditions are poor.
See
Itineraries
The major route across the southern part of the Yukon is the famous Alaska Highway, which originates in British Columbia.
The main route into the NWT from the south (Alberta) is the Mackenzie Highway which has an extension to Yellowknife.
The only highway in Canada that crosses the Arctic Circle is the Dempster Highway, from Dawson City to Inuvik, and since 2017 an extension has allowed vehicle travel to the shores of the Arctic Ocean for the first time.
Do
- Going for dog sled rides is a popular activity in the winter.
- Hunting and fishing are popular in the summer, ice fishing in the winter.
- Hike or paddle sections of the Trans Canada Trail.
- Camping is very popular in summer, and locals even do it in winter.
- Cross country skiing, ice skating, and snowmobiling
- Guided excursions and Arctic expeditions organized by outfitters are an excellent way of seeing the great white north
Eat
Look out for traditional foods, including fish, caribou, and other "country food", which is distinguished from food brought in from southern Canada.
In many communities, food must be shipped in on planes, so be prepared to pay extraordinarily high prices for perishables, such as milk, fruit, and vegetables.
Drink
Pay attention to your destination and research in advance whether alcohol is allowed. Some villages are dry communities (no alcohol permitted). Carrying alcohol into dry communities is considered to be bootlegging and you may be fined or imprisoned for violating this policy.
Stay safe
- See also: Winter in North America
There is no 9-1-1 emergency number in most communities in the Canadian high Arctic. As of 2016, the Yukon is making efforts to expand a very basic 9-1-1 (which is already available in Whitehorse) territory-wide. Elsewhere, 1-1-2 or 9-1-1 may merely reach a recording with no useful information.
Use the seven-digit local numbers for the individual services in each community to summon help in an emergency.
The articles cold weather, winter driving and dangerous animals all have advice which will be relevant to many travellers in the Arctic.