 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]butane-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
HEPBS | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.294 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H22N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 266.356 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 (predicted) |
| Melting point | 211–216 °C (412–421 °F; 484–489 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.3 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
HEPBS (N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N'-(4-butanesulfonic acid)) is a zwitterionic organic chemical buffering agent; one of Good's buffers. HEPBS and HEPES have very similar structures and properties, HEPBS also having an acidity (pKa) in the physiological range (7.6-9.0 useful range). This makes it possible to use it for cell culture work.
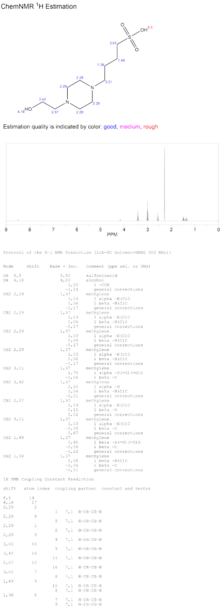
HEPBS 1H NMR spectrum.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.